Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
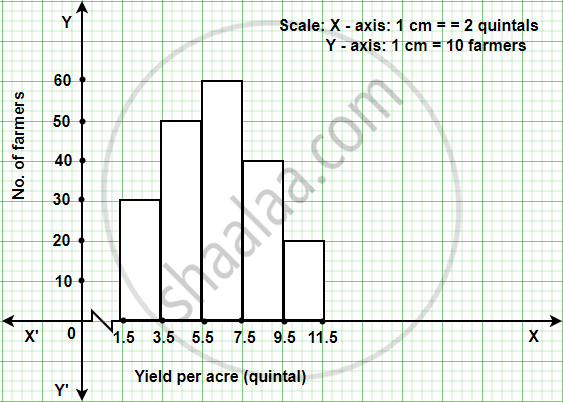
The table below shows the yield of jowar per acre. Show the data by histogram.
| Yield per acre (quintal) | 2 - 3 | 4 - 5 | 6 - 7 | 8 - 9 | 10 - 11 |
| No. of farmers | 30 | 50 | 55 | 40 | 20 |
Solution
The given classes are not continuous. Converting into the continuous classes, we get
| Yield per acre (quintal) | Class (continuous) | No. of farmers |
| 2 - 3 | 1.5 - 3.5 | 30 |
| 4 - 5 | 3.5 - 5.5 | 50 |
| 6 - 7 | 5.5 - 7.5 | 55 |
| 8 - 9 | 7.5 - 9.5 | 40 |
| 10 - 11 | 9.5 - 11.5 | 20 |
RELATED QUESTIONS
The marks scored by students in Mathematics in a certain Examination are given below:
| Marks Scored | Number of Students |
| 0 — 20 | 3 |
| 20 — 40 | 8 |
| 40 — 60 | 19 |
| 60 — 80 | 18 |
| 80 — 100 | 6 |
Draw histogram for the above data.
Represent the following data by Histogram:
|
Price of Sugar per kg (in Rs.) |
Number of Weeks |
| 18-20 | 4 |
| 20-22 | 8 |
| 22-24 | 22 |
| 24-26 | 12 |
| 26-28 | 8 |
| 28-30 | 6 |
Draw a histogram for the frequency table made for the data in Question 3 and answer the following questions.
(1) Which group has the maximum number of workers?
(2) How many workers earn Rs 850 and more?
(3) How many workers earn less than Rs 850?
Draw histogram for the following frequency distributions:
| Class Interval | 30 – 39 | 40 – 49 | 50 – 59 | 60 – 69 | 70 – 79 |
| Frequency | 24 | 16 | 09 | 15 | 20 |
Draw a histogram of the following data:
| Class interval: | 10−15 | 15−20 | 20−25 | 25−30 | 30−35 | 34−40 |
| Frequency: | 30 | 98 | 80 | 58 | 29 | 50 |
Construct histograms for following frequency distribution:
| Class Interval | 0-10 | 10-20 | 20-30 | 30-40 | 40-50 | 50-60 |
| Frequency | 8 | 20 | 34 | 22 | 10 | 6 |
Distribution of height in cm of 100 people is given below:
| Class interval (cm) | Frequency |
| 145 - 155 | 3 |
| 155 - 165 | 35 |
| 165 - 175 | 25 |
| 175 - 185 | 15 |
| 185 - 195 | 20 |
| 195 - 205 | 2 |
Draw a histogram to represent the above data.
Draw a histogram and frequency polygon to represent the following data (on the same scale) which shows the monthly cost of living index of a city in a period of 2 years:
| Cost of living Index | Number of months |
| 440 - 460 | 2 |
| 460 - 480 | 4 |
| 480 - 500 | 3 |
| 500 - 520 | 5 |
| 520 - 540 | 3 |
| 540 - 560 | 2 |
| 560 - 580 | 1 |
| 580 - 600 | 4 |
| Total | 24 |
(Use a graph paper for this question.) The daily pocket expenses of 200 students in a school are given below:
| Pocket expenses (in ₹) |
Number of students (frequency) |
| 0 - 5 | 10 |
| 5 - 10 | 14 |
| 10 - 15 | 28 |
| 15 - 20 | 42 |
| 20 - 25 | 50 |
| 25 - 30 | 30 |
| 30 - 35 | 14 |
| 35 - 40 | 12 |
Draw a histogram representing the above distribution and estimate the mode from the graph.
In a village, there are 570 people who have cell phones. An NGO survey their cell phone usage. Based on this survey a histogram is drawn
Are people using cell phone for less than 1 hour?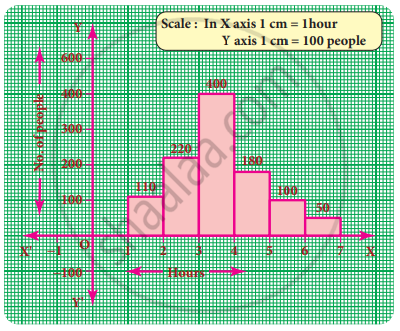
The graphical representation of grouped data is _________
The height of a rectangle in a histogram shows the ______.
The number of people having books more than 20 and less than 40 is ______.
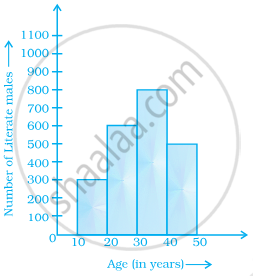
From the histogram given on the right, we can say that 1500 males above the age of 20 are literate.
Draw a histogram for the following data.
| Class interval | 10 – 15 | 15 – 20 | 20 – 25 | 25 – 30 | 30 – 35 | 35 – 40 |
| Frequency | 30 | 98 | 80 | 58 | 29 | 50 |
Show the following data by a frequency polygon:
| Electricity bill (₹) | Families |
| 200 – 400 | 240 |
| 400 – 600 | 300 |
| 600 – 800 | 450 |
| 800 – 1000 | 350 |
| 1000 – 1200 | 160 |
The following table shows the classification of percentage of marks of students and the number of students. Draw frequency polygon from the table without drawing histogram:
| Result (Percentage) | Number of Students |
| 20 - 40 | 25 |
| 40 - 60 | 65 |
| 60 - 80 | 80 |
| 80 - 100 | 15 |
The given graph with a histogram represents the number of plants of different heights grown in a school campus. Study the graph carefully and answer the following questions:
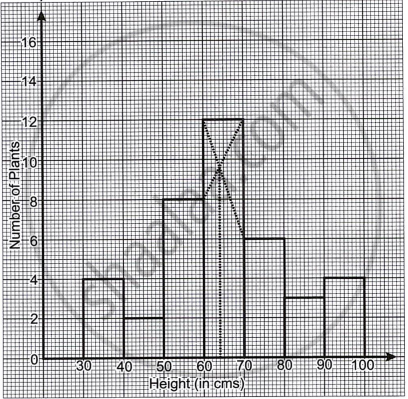
- Make a frequency table with respect to the class boundaries and their corresponding frequencies.
- State the modal class.
- Identify and note down the mode of the distribution.
- Find the number of plants whose height range is between 80 cm to 90 cm.
