Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Three cards are drawn at random (without replacement) from a well shuffled pack of 52 cards. Find the probability distribution of number of red cards. Hence, find the mean of the distribution .
Solution
Let X denotes the number of red cards drawn.
Then, X can take the values 0, 1, 2 or 3.
Now,
\[P\left( X = 0 \right) = P\left( BBB \right) = \frac{26}{52} \times \frac{25}{51} \times \frac{24}{50} = \frac{2}{17}, \]
\[P\left( X = 1 \right) = P\left( RBB \text{ or }BRB \text{ or } BBR \right) = 3 \times \frac{26}{52} \times \frac{26}{51} \times \frac{25}{50} = \frac{13}{34}, \]
\[P\left( X = 2 \right) = P\left( RRB \text{ or } RBR \text{ or } BRR \right) = 3 \times \frac{26}{52} \times \frac{25}{51} \times \frac{26}{50} = \frac{13}{34}, \]
\[P\left( X = 3 \right) = P\left( RRR \right) = \frac{26}{52} \times \frac{25}{51} \times \frac{24}{50} = \frac{2}{17}\]
Thus, the probability distribution of X is given by
| X | P(X) |
| 0 |
\[\frac{2}{17}\]
|
| 1 |
\[\frac{13}{34}\]
|
| 2 |
\[\frac{13}{34}\]
|
| 3 |
\[\frac{2}{17}\]
|
\[\text{ Mean } = \sum p_i x_i = 0 \times \frac{2}{17} + 1 \times \frac{13}{34} + 2 \times \frac{13}{34} + 3 \times \frac{2}{17}\]
\[ = 0 + \frac{13}{34} + \frac{26}{34} + \frac{6}{17}\]
\[ = \frac{51}{34}\]
\[ = \frac{3}{2}\]
\[ = 1 . 5\]
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Find the probability distribution of number of heads in four tosses of a coin.
There are 4 cards numbered 1 to 4, one number on one card. Two cards are drawn at random without replacement. Let X denote the sum of the numbers on the two drawn cards. Find the mean and variance of X.
Which of the following distributions of probabilities of a random variable X are the probability distributions?
(i)
| X : | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | −1 |
| P (X) : | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.1 | 0.05 |
| X : | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| P (X) : | 0.6 | 0.4 | 0.2 |
(iii)
| X : | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| P (X) : | 0.1 | 0.5 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
(iv)
| X : | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| P (X) : | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.1 |
Let X be a random variable which assumes values x1, x2, x3, x4 such that 2P (X = x1) = 3P(X = x2) = P (X = x3) = 5 P (X = x4). Find the probability distribution of X.
Two cards are drawn successively with replacement from a well shuffled pack of 52 cards. Find the probability distribution of the number of kings.
Three cards are drawn successively with replacement from a well-shuffled deck of 52 cards. A random variable X denotes the number of hearts in the three cards drawn. Determine the probability distribution of X.
From a lot of 10 bulbs, which includes 3 defectives, a sample of 2 bulbs is drawn at random. Find the probability distribution of the number of defective bulbs.
The probability distribution of a random variable X is given below:
| x | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| P(X) | k |
\[\frac{k}{2}\]
|
\[\frac{k}{4}\]
|
\[\frac{k}{8}\]
|
Determine the value of k .
The probability distribution of a random variable X is given below:
| x | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| P(X) | k |
\[\frac{k}{2}\]
|
\[\frac{k}{4}\]
|
\[\frac{k}{8}\]
|
Find P(X ≤ 2) + P(X > 2) .
Find the mean and standard deviation of each of the following probability distribution:
| xi : | 1 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| pi: | 0.4 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.3 |
Find the mean and standard deviation of each of the following probability distribution :
| xi : | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| pi : | 0.4 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.1 |
Find the mean and standard deviation of each of the following probability distribution :
| xi : | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| pi : |
\[\frac{1}{6}\]
|
\[\frac{5}{18}\]
|
\[\frac{2}{9}\]
|
\[\frac{1}{6}\]
|
\[\frac{1}{9}\]
|
\[\frac{1}{18}\]
|
A pair of fair dice is thrown. Let X be the random variable which denotes the minimum of the two numbers which appear. Find the probability distribution, mean and variance of X.
In a game, a man wins Rs 5 for getting a number greater than 4 and loses Rs 1 otherwise, when a fair die is thrown. The man decided to thrown a die thrice but to quit as and when he gets a number greater than 4. Find the expected value of the amount he wins/loses.
If X denotes the number on the upper face of a cubical die when it is thrown, find the mean of X.
If a random variable X has the following probability distribution:
| X : | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| P (X) : | a | 3a | 5a | 7a | 9a | 11a | 13a | 15a | 17a |
then the value of a is
A random variable X has the following probability distribution:
| X : | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| P (X) : | 0.15 | 0.23 | 0.12 | 0.10 | 0.20 | 0.08 | 0.07 | 0.05 |
For the events E = {X : X is a prime number}, F = {X : X < 4}, the probability P (E ∪ F) is
A random variable X takes the values 0, 1, 2, 3 and its mean is 1.3. If P (X = 3) = 2 P (X = 1) and P (X = 2) = 0.3, then P (X = 0) is
From a lot of 15 bulbs which include 5 defective, a sample of 4 bulbs is drawn one by one with replacement. Find the probability distribution of number of defective bulbs. Hence, find the mean of the distribution.
Three cards are drawn successively with replacement from a well shuffled pack of 52 cards. Find the probability distribution of the number of spades. Hence, find the mean of the distribtution.
Three different aeroplanes are to be assigned to carry three cargo consignments with a view to maximize profit. The profit matrix (in lakhs of ₹) is as follows :
| Aeroplanes | Cargo consignments | ||
| C1 | C2 | C3 | |
| A1 | 1 | 4 | 5 |
| A2 | 2 | 3 | 3 |
| A3 | 3 | 1 | 2 |
How should the cargo consignments be assigned to the aeroplanes to maximize the profit?
The defects on a plywood sheet occur at random with an average of the defect per 50 sq. ft. What Is the probability that such sheet will have-
(a) No defects
(b) At least one defect
[Use e-1 = 0.3678]
Determine whether each of the following is a probability distribution. Give reasons for your answer.
| x | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| P(x) | 0.1 | 0.5 | 0.2 | –0.1 | 0.3 |
A die is thrown 4 times. If ‘getting an odd number’ is a success, find the probability of 2 successes
The probability that a bulb produced by a factory will fuse after 200 days of use is 0.2. Let X denote the number of bulbs (out of 5) that fuse after 200 days of use. Find the probability of X = 0
Find the probability of throwing at most 2 sixes in 6 throws of a single die.
Solve the following problem :
Following is the probability distribution of a r.v.X.
| x | – 3 | – 2 | –1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| P(X = x) | 0.05 | 0.1 | 0.15 | 0.20 | 0.25 | 0.15 | 0.1 |
Find the probability that X is non-negative
Solve the following problem :
Find the probability of the number of successes in two tosses of a die, where success is defined as six appears in at least one toss.
Solve the following problem :
If a fair coin is tossed 4 times, find the probability that it shows head in the first 2 tosses and tail in last 2 tosses.
Solve the following problem :
It is observed that it rains on 10 days out of 30 days. Find the probability that it rains on at most 2 days of a week.
The probability distribution of a random variable X is given below:
| X | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| P(X) | k | `"k"/2` | `"k"/4` | `"k"/8` |
Determine P(X ≤ 2) and P(X > 2)
Find the probability distribution of the maximum of the two scores obtained when a die is thrown twice. Determine also the mean of the distribution.
The probability distribution of a random variable x is given as under:
P(X = x) = `{{:("k"x^2, "for" x = 1"," 2"," 3),(2"k"x, "for" x = 4"," 5"," 6),(0, "otherwise"):}`
where k is a constant. Calculate E(3X2)
The probability distribution of a discrete random variable X is given below:
| X | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| P(X) | `5/"k"` | `7/"k"` | `9/"k"` | `11/"k"` |
The value of k is ______.
Find the mean of number randomly selected from 1 to 15.
The probability that a bomb will hit the target is 0.8. Complete the following activity to find, the probability that, out of 5 bombs exactly 2 will miss the target.
Solution: Here, n = 5, X =number of bombs that hit the target
p = probability that bomb will hit the target = `square`
∴ q = 1 - p = `square`
Here, `X∼B(5,4/5)`
∴ P(X = x) = `""^"n""C"_x"P"^x"q"^("n" - x) = square`
P[Exactly 2 bombs will miss the target] = P[Exactly 3 bombs will hit the target]
= P(X = 3)
=`""^5"C"_3(4/5)^3(1/5)^2=10(4/5)^3(1/5)^2`
∴ P(X = 3) = `square`
Kiran plays a game of throwing a fair die 3 times but to quit as and when she gets a six. Kiran gets +1 point for a six and –1 for any other number.
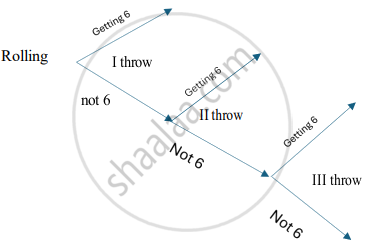
- If X denotes the random variable “points earned” then what are the possible values X can take?
- Find the probability distribution of this random variable X.
- Find the expected value of the points she gets.
