Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
What are reducing and non-reducing sugars?
Solution
1. Reducing sugars: Those carbohydrates which contain free aldehyde or ketonic group and reduces Fehling’s solution and Tollen’s reagent are called reducing sugars. All monosaccharides whether aldose or ketone are reducing sugars.
2. Non-reducing sugars: Carbohydrates that do not reduce Tollen’s reagent and Fehling’s solution are called non – reducing sugars. Example Sucrose. They do not have a free aldehyde group.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
The glycosidic linkage in maltose is formed between _______________
What is the action of the following reagents on glucose?
hydroxylamine
Explain D and L configuration in sugars.
Write a commercial method for preparation of glucose.
Which enzymes would work sequentially on potatoes consumed by an individual?
Which of the following monosaccharides is a tetrose sugar?
Formation of lactose by conden ation results in the release of how many molecules of water?
Identify the sugar having the molecular formula C6H1206.
Which among the following compounds is obtained when glucose reacts with hydrogen cyanide?
By which of the following feature we can identify the relatively small DNA molecules of plasmids?
Which reagent among the following is used to confirm presence of aldehydic carbonyl group in glucose?
All these carbohydrates contain \[\ce{1 -> 4β}\] glycosidic linkage, EXCEPT ____________.
Which element among the following is not present in saccharine?
Stachyose is ____________.
Which one of the following carbohydrates is insoluble in water?
Which following reagent is used to detect presence of five hydroxyl groups in a glucose molecule?
Which among the following sugars does not reduce Tollen's reagent?
What is the quantity of glucose obtained when 68.4 g of sucrose is hydrolyzed in laboratory under ideal condition?
(Molar mass of sucrose = 342 g mol−1)
Identify the number of oxygen atoms present in saccharic acid?
What is the molecular formula of glyceraldehyde?
Which among the following reagents is used to obtain gluconic acid from glucose?
Which among the following is a product of hydrolysis of one mole raffinose?
When one mole of lactose is hydrolysed, the hydrolysate contains ____________.
Which one given below is a non-reducing sugar?
\[\ce{Glucose ->[(HCN)] Product ->[(hydrolysis)] Product ->[(HI + Heat)] A}\], the compound A is:
The number of sp2 and sp3 hybridised carbon in fructose are respectively ____________.
Glucose is an aldose. Which one of the following reactions is not expected with glucose?
Why carbohydrates are generally optically active?
Is the following sugar, D-sugar or L-sugar?
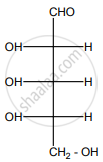
If 'n' represents total number of asymmetric carbon atoms in a compound, then the possible· number of optical isomers of the compound is ______.
Lactose is made of ______.
\[\ce{CH2OH - CO - (CHOH)4 - CH2OH}\] is an example of ______.
CH2 OH - CO - (CHOH)4 - CH2 OH is an example of ______.
Why carbohydrates are generally optically active?
\[\ce{CH2OH - CO - (CHOH)4 - CH2OH}\] is an example of ______.
\[\ce{CH2OH - CO - (CHOH)4 - CH2OH}\] is an example of ______.
Why carbohydrates are generally optically active.
