Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
What are the limitations of Rutherford’s model of the atom?
Solution
(i) An electron orbiting around the nucleus is accelerated towards it. An accelerating charged particle must produce radiation and lose energy. Thus, electrons in an atom must constantly emit radiation and lose energy. Because of this energy loss, the electron will slow down and cannot withstand the nucleus' attraction. As a result, the electron should spiral and eventually fall into the nucleus (see image).
If this occurs, the atom should collapse in approximately 10-8 seconds. However, this does not occur; atoms are stable. This suggests that something is amiss with Rutherford's nuclear model of atoms.
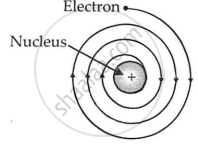
(ii) Rutherford's atomic model says nothing about how electrons are arranged in an atom.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
On the basis of Rutherford’s model of an atom, which subatomic particle is present in the nucleus of an atom?
In Rutherford’s experiment, generally the thin foil of heavy atoms, like gold, platinum etc. have been used to be bombarded by the α-particles. If the thin foil of light atoms like aluminium etc. is used, what difference would be observed from the above results?
State whether the following statement is true or false :
Thomson proposed that the nucleus of an atom contains protons and neutrons.
Which part of an atom was discovered by Rutherford's alpha particle scattering experiment?
Give the evidence for the existence of nucleus in an atom.
What important information is furnished about the nucleus of an atom by the alpha particle scattering experiment of Rutherford?
Describe the Rutherford's model of an atom. State one drawback of Rutherford's model of the atom.
Draw a neat labelled diagram
Rutherford's scattering experiment
State true or false. If false, correct the statement.
In an atom, electrons revolve around the nucleus in fixed orbits.
How was it shown that atom has empty space?
