Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Answer the following question.
What is methane? Draw its electron dot structure. Name the type of bonds formed in this compound. Why are such compounds:
(i) poor conductors of electricity? and
(ii) have low melting and boiling points? What happens when this compound burns in oxygen?
Solution
Methane is a colorless, odorless, and highly flammable gas which is the main component of natural gas. It is also called as marsh gas as it is produced when vegetation decomposes naturally in any swampy or marshlands.

Electron Dot structure of methane is:
The type of bonds present in methane is all covalent bonds between four hydrogen atoms and the single carbon atom at the center of the molecule.
- Methane is a poor conductor of electricity because in methane all bonds are covalent bonds and therefore no free electrons are present in the molecule that can help in the conduction of electricity.
- Covalent compounds have low intermolecular forces of attraction between the molecules and thus show low melting and boiling points. Since methane is also a covalent compound thus methane has very low melting and low boiling point. When methane is burned in the presence of Oxygen it forms Carbon dioxide gas and water as a product of the reaction.
\[\ce{\underset{\text{Methane}}{CH4} +\underset{\text{Water}}{O2} -> \underset{\text{Carbon dioxide}}{CO2}+\underset{\text{Water}}{H2O}}\]
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Give reason why carbon compounds are generally poor conductors of electricity.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Which of the following is a common characteristic of a covalent compound?
1) high melting point
2) consists of molecules
3) always soluble in water
4) Conducts electricity when it is in the molten state
Name the hardest natural substance known.
What type of chemical bond is formed between carbon and bromine?
Explain why covalent compounds have generally high melting points?
Why is graphite used for making dry cell electrodes but diamond is not?
Name one covalent compound containing chlorine.
Draw the electron-dot structure of H2O compound and state the type of bonding.
The atomic numbers of four elements P, Q, R and S are 6, 10, 12 and 17 respectively. Which two elements can combine to form a covalent compound?
(a) P and R
(b) Q and S
(c) P and S
(d) R and S
Which element exhibits the property of catenation to maximum extent and why?
The covalent bond in which the electrons are shared equally between the combining atoms.
Explain the following briefly:
Sodium chloride dissolves in water but carbon tetra chloride is insoluble in water.
Explain the following:
Polar covalent compounds are good conductors of electricity.
The electronic configuration of N2 is 2, 5. How many electrons in the outer shell of a N atom are not involved in the formation of a nitrogen molecule?
Potassium chloride is an electrovalent compound, while hydrogen chloride is a covalent compound, But, both conduct electricity in their aqueous solutions. Explain.
Define a covalent bond.
Write an Explanation.
Alkene
Complete the following activity.
Write the names of the hydrocarbons for the following structural formula.
(isobutylene, cyclohexane, propene, cyclohexene, cyclopentane, benzene, propyne, isobutane, propane)
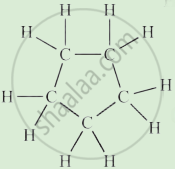 |
Which of the following are correct structural isomers of butane?
- \[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\\
|\phantom{....}|\phantom{....}|\phantom{....}|\\
\ce{H - C - C - C - C - H}\\
|\phantom{....}|\phantom{....}|\phantom{....}|\\
\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\\
\end{array}\] - \[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\\
|\phantom{....}|\phantom{....}|\\
\ce{H - C - C - C - H}\\
|\phantom{.....}|\phantom{.....}|\\
\ce{H}\ce{H-C-H}\ce{H}\\
|\\
\ce{H}\\
\end{array}\] - \[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\\
|\phantom{....}|\phantom{....}|\\
\ce{H - C - C - C - H}\\
|\phantom{.....}\backslash\phantom{..}|\\
\phantom{....}\ce{H}\phantom{......}\ce{C - H}\phantom{}\\
\phantom{.......}|\\
\phantom{.......}\ce{H}\\
\end{array}\] - \[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\\
|\phantom{....}|\\
\ce{H - C - C - H}\\
|\phantom{....}|\\
\ce{H - C - C - H}\\
|\phantom{....}|\\
\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\\
\end{array}\]
The bond which is formed by the mutual sharing of electrons is called ______ bond.
