Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
What is Transformer?
Solution
The transformer is an electrical device that converts low alternating voltage at high current to high alternating voltage at low current and vice-versa.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
State the principle on which transformer works.
Explain the construction and working of the transformer.
Derive an expression for ratio of e.m.f.s and currents in terms of number of turns in primary and secondary coil.
State the principle of the step-down transformer and its working.
Find the ratio of primary and secondary currents in terms of turn ratio in an ideal transformer.
The primary coil of an ideal step-up transformer has 100 turns and the transformation ratio is also 100. The input voltage and power are 220 V and 1100 W, respectively. Calculate the
(a) number of turns in secondary
(b) current in the primary
(c) a voltage across secondary
(d) current in secondary
(e) power in secondary
Name two factors on which the magnitude of an induced e.m.f. in the secondary coil depends.
How is the e.m.f. across primary and secondary coils of a transformer related with the number of turns of the coil in them?
You are required to make an electromagnet from a soft iron bar by using a cell, an insulated coil of copper wire and a switch. (a) Draw a circuit diagram to represent the process. (b) label the poles of the electromagnet.
The following diagram in Fig.10.42 shows a coil of several turns of copper wire connected to a sensitive centre zero galvanometer G near a magnet NS. The coil is free to move in the direction shown in the diagram.
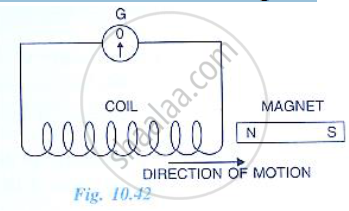
(i) Describe the observation if the coil is rapidly moved.
(ii) How would the observation be altered if (a) the coil has twice as many turns (b the coil was made to move three times as fast?
The following diagram in Fig. 10.44 shows a coil X connected to a sensitive centre –zero galvanometer G and a coil P connected to a battery through a switch S.
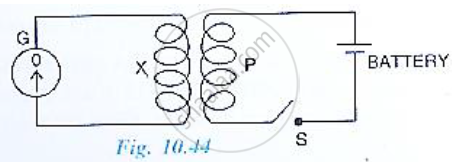
(a) Describe the observation when the switch S is (i) closed suddenly, (ii) then kept closed, (iii) finally opened.
(b) Name and state the law which explains the above observations.
For what purpose are the transformers used? Can they be used with a direct current source?
The transformer is used in ______ current circuits.
In a transformer, the frequency of A.C. voltage ______.
The primary coil of a transformed has 800 urns and the secondary coil has 8 turns. It is connected to a 220 V a.c. supply. What will be the output voltage?
The input and output voltage of a transformer are 220 V and 44 V respectively. Find: the turns ratio.
State the underlying principle of a transformer. How is the large scale transmission of electric energy over long distances done with the use of transformers?
Describe briefly and two energy losses, giving the reasons for their occurrence in actual transformers ?
State the principle of working of a transformer. Can a transformer be used to step up or step down a d.c. voltage? Justify your answer.
Draw a labeled diagram of a full wave rectifier circuit. State its working principle. Show the input-output waveforms ?
Describe briefly, with the help of labelled diagram, working of a step-up transformer.
A step-up transformer converts a low voltage into high voltage. Does it not violate the principle of conservation of energy? Explain.
In an ideal transformer, an output of 66 kV is required when an input voltage of 220 V is available. If the primary has 300 turns, how many turns should the secondary have?
What is a transformer? On what principle does it work?
Can a transformer be used with direct current source? Give reason.
Name three losses of energy in a transformer. How are they minimized?
(i) Draw a clear labelled diagram of an electric bell.
(ii) Explain in brief, its working.
(iii) What material is used for the core of an electric bell? State the reason.
Copy the given diagram of a transformer and complete it. Name the parts A and B. Name the part you have drawn to complete the diagram. What is the material of this part? Is this transformer a step-up or step-down? Give reason.
Applying e.m. f to primary coil is 210 V. If the number of turns in primary coil is 200 turns and that of in secondary coil is 20 turns, then find out the output voltage. Name the type of transformer.
A transformer lowers e.m.f. from 220 V to 15 V. If 400 W power is given in primary, calculate (i) the current in primary coil and (ii) the current in secondary coil.
The primary and secondary coils of a transformer each have an inductance of 200 x 10-6 H. The mutual inductance between the windings is 4 x 10-6 H. What percentage of the flux from one coil reaches the other?
State the mathematical relation between a number of turns in the primary coil to a secondary coil in the step-up transformer.
The primary of a transformer has 40 turns and works on 100 V and 100 W. Find a number of turns in the secondary to step up the voltage to 400 V. Also calculate the current in the secondary and primary.
Transformer works on ______.
In a series resonant RLC circuit, the voltage across 100 Ω resistor is 40 V. The resonant frequency ω is 250 rad/s. If the value of C is 4 µF, then the voltage across L is
What are step-up and step-down transformers?
A 200V/120V step-down transformer of 90% efficiency is connected to an induction stove of resistance 40 Ω. Find the current drawn by the primary of the transformer.
The output power in step-up transformer used in practice is ______.
A 220 V input is supplied to a transformer. The output circuit draws a current of 2.0 A at 440 V. If the ratio of output to input power is 0.8, then the current drawn by primary winding is ______.
Assertion: A transfonner cannot work on D.C. supply.
Reason: D.C. changes neither in magnitude nor in direction.
For an ideal step-down transformer, the quantity which is constant for both the coils is ______.
Read the following paragraph and answer the question:

Long distance power transmissions
The large-scale transmission and distribution of electrical energy over long distances is done with the use of transformers. The voltage output of the generator is stepped up. It is then transmitted over long distances to an area sub-station near the consumers. There the voltage is stepped down. It is further stepped down at distributing sub-stations and utility poles before a power supply of 240 V reaches our homes.
If the secondary coil has a greater number of turns than the primary, ______.
A transformer is essentially an a.c. device. It cannot work on d.c. It changes alternating voltages or currents. It does not affect the frequency of a.c. It is based on the phenomenon of mutual induction. A transformer essentially consists of two coils of insulated copper wire having different numbers of turns and wound on the same soft iron core.
The number of turns in the primary and secondary coils of an ideal transformer is 2000 and 50 respectively. The primary coil is connected to a main supply of 120 V and secondary coil is connected to a bulb of resistance 0.6 Ω.
The value of voltage across the secondary coil is ______.
The primary coil of a transformer has 800 turns and the secondary coil has 8 turns. It is connected to a 220 V ac supply. What will be the output voltage?
A transformer is used ______
A step down transformer connected to an ac mains supply of 220 V is made to operate at 11 V, 44 W lamp. Ignoring power losses in the transformer, what is the current in the primary circuit?
For an LCR circuit, the power transferred from the driving source to the driven oscillator is P = I2Z cos φ.
- Here, the power factor cos φ ≥ 0, P ≥ 0.
- The driving force can give no energy to the oscillator (P = 0) in some cases.
- The driving force cannot syphon out (P < 0) the energy out of oscillator.
- The driving force can take away energy out of the oscillator.
The line that draws power supply to your house from street has ______.
- zero average current.
- 220 V average voltage.
- voltage and current out of phase by 90°.
- voltage and current possibly differing in phase `phi` such that `|phi| < pi/2`.
A 60 W load is connected to the secondary of a transformer whose primary draws line voltage. If a current of 0.54 A flows in the load, what is the current in the primary coil? Comment on the type of transformer being used.
The magnetic flux through a coil perpendicular to its plane is varying according to the relation Φ = (5t3 + 4t2 + 2t - 5) Weber. If the resistant of the coil is 5 ohm, then the induced current through the coil at t = 2 sec will be ______.
Magnetic flux Φ in weber in a closed circuit of resistance 10Ω varies with time Φ (sec) as Φ = 6t2 - 5t + 1. The magnitude of induced current at t = 0.25s is ______.
An ideal transformer converts 220 V a.c. to 3.3 kV a.c. to transmit a power of 4.4 kW. If primary coil has 600 turns, then alternating current in secondary coil is ______.
The large scale transmission of electrical energy over long distances is done with the use of transformers. The voltage output of the generator is stepped-up because of ______.
Efficiency of transformer is the ratio of ______.
