Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Which of the following phenomena occur when a small amount of acid is added to water?
- Ionisation
- Neutralisation
- Dilution
- Salt formation
Options
(i) and (ii)
(i) and (iii)
(ii) and (iii)
(ii) and (iv)
Solution
(ii) and (iv)
Explanation -
Water helps in the ionisation of acid and also in its dilution.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Why do acids not show acidic behaviour in the absence of water?
What happens when dilute hydrochloric acid is added to sodium carbonate? Write a balanced chemical equation of the reaction involved.
10 mL of a solution of NaOH is found to be completely neutralised by 8 mL of a given solution of HCl. If we take 20 mL of the same solution of NaOH, the amount of HCl solution (the same solution as before) required to neutralise it will be:
(a) 4 mL
(b) 8 mL
(c) 12 mL
(d) 16 mL
What is meant by strong bases and weak bases? Classify the following into strong bases and weak bases:
NH4OH, Ca(OH)2, NaOH, KOH, Mg(OH)2
What happens when carbon dioxide gas is passed through lime water for a considerable time ?
Write equations of the reactions involved.
Write the main difference between an acid and a base.
Answer the following question.
Blue litmus solution is added to two test tubes A and B containing dilute HCl and NaOH solution respectively. In which test tube a colour change will be observed? State the colour change and give its reason.
In the experimental set-up to show that "the germinating seeds give out carbon dioxide", answer the following questions:
(i) Why do we keep the conical flask airtight?
(ii) Name the substance kept in the small test tube inside the conical flask. Write its role.
(iii) Why does water rise in the delivery tube?
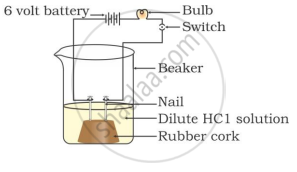
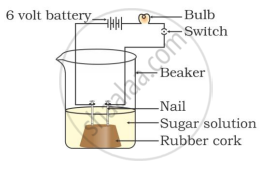
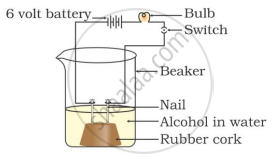
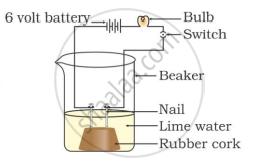
In which of the following setups would the bulb glow?
Identify the correct representation of reaction occurring during chloralkali process