Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Why is exposure to X-rays injurious to health but not exposure to visible light, when both are electromagnetic waves?
Solution
X-rays have more penetrating power compared to visible light. As a result, they can penetrate the human body and can also damage the cells of the body. Prolonged exposure to X-rays can lead to cancer or genetic defects.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
How are infrared waves produced?
Identify the part of the electromagnetic spectrum which is suitable for radar system used in aircraft navigation.
To which part of electromagnetic spectrum does a wave of frequency 3 × 1013 Hz belong?
What physical quantity is the same for X-rays of wavelength 10−10 m, red light of wavelength 6800 Å and radiowaves of wavelength 500 m?
What do you understand by the statement, "Electromagnetic waves transport momentum"?
The wavelengths for the light of red and blue colours are roughly 7.8 × `10^7` m and 4.8 × `10^7` m respectively.
(a) Which colour has the greater speed in vacuum?
(b) Which colour has the greater speed in glass?
State the approximate range of wavelength associated with the ultraviolet rays.
An electromagnetic wave has a frequency of 500 MHz and a wavelength of 60 cm.name the medium through which it is travelling
Can X-rays be used for photoelectric effect?
An X-ray beam can be deflected
The X-ray beam emerging from an X-ray tube
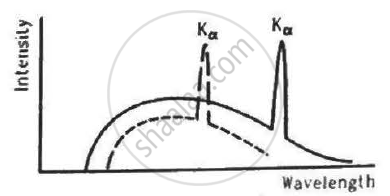
The figure shows the intensity-wavelength relations of X-rays coming from two different Coolidge tubes. The solid curve represents the relation for the tube A in which the potential difference between the target and the filament is VA and the atomic number of the target material is ZA. These quantities are VB and ZB for the other tube. Then,
What potential difference should be applied across an X-ray tube to get X-ray of wavelength not less than 0.10 nm? What is the maximum energy of a photon of this X-ray in joule?
(Use Planck constant h = 6.63 × 10-34 Js= 4.14 × 10-15 eVs, speed of light c = 3 × 108 m/s.)
When 40 kV is applied across an X-ray tube, X-ray is obtained with a maximum frequency of 9.7 × 1018 Hz. Calculate the value of Planck constant from these data.
(Use Planck constant h = 6.63 × 10-34 Js= 4.14 × 10-15 eVs, speed of light c = 3 × 108 m/s.)
Suppose a monochromatic X-ray beam of wavelength 100 pm is sent through a Young's double slit and the interference pattern is observed on a photographic plate placed 40 cm away from the slit. What should be the separation between the slits so that the successive maxima on the screen are separated by a distance of 0.1 mm?
The fundamental frequency of an open organ pipe is 300 Hz. The first overtone of this pipe has same frequency as first overtone of a closed organ pipe. If speed of sound is 330 m/s, then the length of closed organ pipe is:
What happens to the intensity of light from a bulb if the distance from the bulb is doubled? As a laser beam travels across the length of a room, its intensity essentially remains constant. What geometrical characteristic of LASER beam is responsible for the constant intensity which is missing in the case of light from the bulb?
Name one radiation having the wavelength longer than the wavelength of these radiations.
