Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Without using set squares or protractor.
(i) Construct a ΔABC, given BC = 4 cm, angle B = 75° and CA = 6 cm.
(ii) Find the point P such that PB = PC and P is equidistant from the side BC and BA. Measure AP.
Solution
(i) Draw BC = 4 cm. Draw BA at B such that ∠ABC = 75°. Cut CA = 6 cm. Then ΔABC is the required Δ.
(ii) Draw single bisector of ∠B. Draw ⊥ bisector of BC. Their point of intersection (P) is the requisite point.
AP = 3·9 cm.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Use ruler and compasses only for this question:
I. Construct ABC, where AB = 3.5 cm, BC = 6 cm and ABC = 60o.
II. Construct the locus of points inside the triangle which are equidistant from BA and BC.
III. Construct the locus of points inside the triangle which are equidistant from B and C.
IV. Mark the point P which is equidistant from AB, BC and also equidistant from B and C. Measure and records the length of PB.
Angle ABC = 60° and BA = BC = 8 cm. The mid-points of BA and BC are M and N respectively. Draw and describe the locus of a point which is:
- equidistant from BA and BC.
- 4 cm from M.
- 4 cm from N.
Mark the point P, which is 4 cm from both M and N, and equidistant from BA and BC. Join MP and NP, and describe the figure BMPN.
Ruler and compasses may be used in this question. All construction lines and arcs must be clearly shown and be of sufficient length and clarity to permit assessment.
- Construct a ΔABC, in which BC = 6 cm, AB = 9 cm and angle ABC = 60°.
- Construct the locus of all points inside triangle ABC, which are equidistant from B and C.
- Construct the locus of the vertices of the triangles with BC as base and which are equal in area to triangle ABC.
- Mark the point Q, in your construction, which would make ΔQBC equal in area to ΔABC, and isosceles.
- Measure and record the length of CQ.
Use ruler and compasses only for this question. Draw a circle of radius 4 cm and mark two chords AB and AC of the circle of lengths 6 cm and 5 cm respectively.
(i) Construct the locus of points, inside the circle, that are equidistant from A and C. prove your construction.
(ii) Construct the locus of points, inside the circle that are equidistant from AB and AC.
In Δ PQR, s is a point on PR such that ∠ PQS = ∠ RQS . Prove thats is equidistant from PQ and QR.
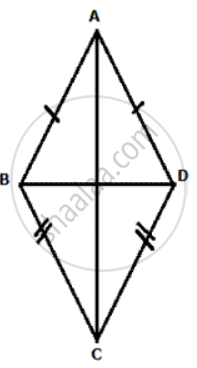
In given figure, ABCD is a kite. AB = AD and BC =CD. Prove that the diagona AC is the perpendirular bisector of the diagonal BD.
Construct a triangle ABC, such that AB= 6 cm, BC= 7.3 cm and CA= 5.2 cm. Locate a point which is equidistant from A, B and C.
Use ruler and compass only for the following question. All construction lines and arcs must be clearly shown.
- Construct a ΔABC in which BC = 6.5 cm, ∠ABC = 60°, AB = 5 cm.
- Construct the locus of points at a distance of 3.5 cm from A.
- Construct the locus of points equidistant from AC and BC.
- Mark 2 points X and Y which are at a distance of 3.5 cm from A and also equidistant from AC and BC. Measure XY.
Using a ruler and compass only:
(i) Construct a triangle ABC with BC = 6 cm, ∠ABC = 120° and AB = 3.5 cm.
(ii) In the above figure, draw a circle with BC as diameter. Find a point 'P' on the circumference of the circle which is equidistant from Ab and BC.
Measure ∠BCP.
Using ruler and compasses construct:
(i) a triangle ABC in which AB = 5.5 cm, BC = 3.4 cm and CA = 4.9 cm.
(ii) the locus of point equidistant from A and C.
(iii) a circle touching AB at A and passing through C.
