Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Would you expect the first ionization enthalpies for two isotopes of the same element to be the same or different? Justify your answer.
Solution 1
The ionization enthalpy of an atom depends on the number of electrons and protons (nuclear charge) of that atom. Now, the isotopes of an element have the same number of protons and electrons. Therefore, the first ionization enthalpy for two isotopes of the same element should be the same.
Solution 2
Ionization enthalpy, among other things, depends upon the electronic configuration (number of electrons) and nuclear charge (number of protons). Since isotopes of an element have the same electronic configuration and same nuclear charge, they have same ionization enthalpy.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Energy of an electron in the ground state of the hydrogen atom is –2.18 × 10–18 J. Calculate the ionization enthalpy of atomic hydrogen in terms of J mol–1.
Hint: Apply the idea of mole concept to derive the answer.
Among the second period elements the actual ionization enthalpies are in the
order Li < B < Be < C < O < N < F < Ne.
Explain why Be has higher ΔiH than B?
Among the second period elements the actual ionization enthalpies are in the
order Li < B < Be < C < O < N < F < Ne.
Explain why O has lower ΔiH than N and F?
How would you explain the fact that the first ionization enthalpy of sodium is lower than that of magnesium but its second ionization enthalpy is higher than that of magnesium?
What are the various factors due to which the ionization enthalpy of the main group elements tends to decrease down a group?
The first ionization enthalpy values (in kJmol–1) of group 13 elements are:-
| B | Al | Ga | In | Tl |
| 801 | 577 | 579 | 558 | 589 |
How would you explain this deviation from the general trend?
Which one of the following statements is incorrect in relation to ionization enthalpy?
Among the elements \[\ce{B, Al, C}\] and \[\ce{Si}\], which element has the highest first ionisation enthalpy?
Nitrogen has positive electron gain enthalpy whereas oxygen has negative. However, oxygen has lower ionisation enthalpy than nitrogen. Explain.
Arrange the elements \[\ce{N, P, O}\] and \[\ce{S}\] in the order of increasing first ionisation enthalpy. Give reason for the arrangement assigned.
Explain the deviation in ionisation enthalpy of some elements from the general trend by using the given figure.
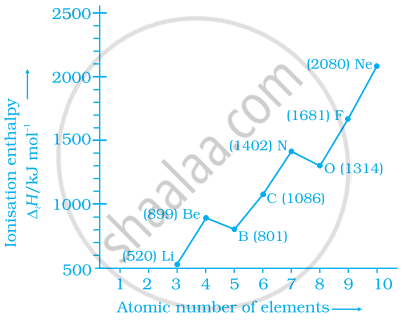
Explain the following:
Ionisation enthalpy decrease in a group from top to bottom?
Assertion (A): Generally, ionisation enthalpy increases from left to right in a period.
Reason (R): When successive electrons are added to the orbitals in the same principal quantum level, the shielding effect of inner core of electrons does not increase very much to compensate for the increased attraction of the electron to the nucleus.
Define ionisation enthalpy. Discuss the factors affecting ionisation enthalpy of the elements and its trends in the periodic table.
In general, the property (magnitudes only) that shows an opposite trend in comparison to other properties across a period is ______.
Consider the elements Mg, Al, S, P and Si, the correct increasing order of their first ionization enthalpy is ______.
`"A"_0/2` atoms of X(g) are converted into X+(g) by absorbing energy E1. `"A"_0/2` ions of X+(g) are converted into X−(g) with release of energy E2. Hence ionization energy and electron affinity of X(g) are ______.
Which of the following atoms has the highest first ionization energy?
