Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Write chemical reaction for following conversions
glucose into glucoxime
Solution
Glucose forms glucoxime by reaction with hydroxylamine:
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{}\ce{CHO}\phantom{.............}\ce{CH = N - OH}\phantom{.}\\
\phantom{.}|\phantom{..................}|\phantom{...............}\\
\ce{(CHOH)4 ->[NH2 - OH](CHOH)4 + H2O}\\
\phantom{}|\phantom{..................}|\phantom{..............}\\
\phantom{}\ce{\underset{\text{Glucose}}{CH2OH} \phantom{..........}\underset{\text{Oxime}}{CH2OH}}\phantom{........}
\end{array}\]
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
\[\ce{CH2OH-CO-(CHOH)4-CH2OH}\] is an example of ______.
Write the name of the polysaccharide used for the commercial preparation of glucose.
Explain the classification of carbohydrates with examples.
Explain D and L configuration in sugars.
What is monosaccharide?
Identify the WRONG statement.
Identify the CORRECT combination.
Which carbon atoms of α- D glucopyranose and β-D-fructofuranose respectively are linked together to form glycosidic linkage in sucrose?
4-O-(α-D-Glucopyranosyl)-D-glucopyranose is ____________.
Which of the following monosaccharide is a ketohexose?
Which one of the following is an oligosaccharide?
Which one of the following is Tetrose sugar?
Which one of the following sugar does NOT have same empirical fonnula as that of carbohydrate?
Which among the following sugars does not reduce Tollen's reagent?
Which among the following reagents is used for conversion of glucose to glucoxime?
Which among the following reagents is used to obtain gluconic acid from glucose?
What is the product obtained when Br2 water reacts with glucose?
Glucose is an aldose. Which one of the following reactions is not expected with glucose?
Classify the following into monosaccharides, oligosaccharides and polysaccharides.
Maltose
Is the following sugar, D-sugar or L-sugar?
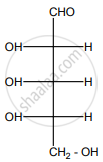
Why carbohydrates are generally optically active?
Describe the action of the following reagent on glucose:
Bromine water
Write the ring structure of glucose.
Why carbohydrates are generally optically active.
Why carbohydrates are generally optically active.
Why are carbohydrates generally optically active?
Write the Zwitter ion structure of alanine.
Why carbohydrates are generally optically active.
