Advertisements
Advertisements
What is meant by the drift speed of free electrons?
Concept: Ohm's Law (V = IR)
On which conservation principle is Kirchoff's Second Law of electrical networks based?
Concept: Kirchhoff’s Rules
Two resistors R1= 60 Ω and R2 = 90Ω are connected in parallel. If electric power consumed by the resistor R1 is15 W, calculate the power consumed by the resistor R2.
Concept: Combination of Resistors - Series and Parallel
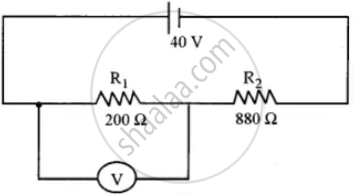
Figure below shows two resistors R1 and R2 connected to a battery having an emf of 40V and negligible internal resistance. A voltmeter having a resistance of. 300 Ω is used to measure the potential difference across R1 Find the reading of the voltmeter.
Concept: Potentiometer
If R1 and R2 are filament resistances of a 200 W and a 100 W bulb respectively, designed to operate on the same voltage, then:
Concept: Resistivity of Various Materials
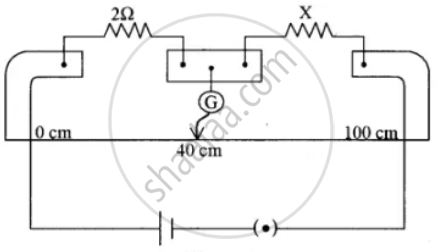
In a meter bridge circuit, resistance in the left-hand gap is 2 Ω and an unknown resistance X is in the right-hand gap as shown in the figure below. The null point is found to be 40 cm from the left end of the Wire. What resistance should be connected to X so that the new null point is 50 cm from the left end of the wire?
Concept: Combination of Resistors - Series and Parallel
A solenoid L and a resistor R are connected in series to a battery, through a switch. When the switch is put on, current I flowing through it varies with time t as shown in which of the graphs given below:
Concept: Combination of Resistors - Series and Parallel
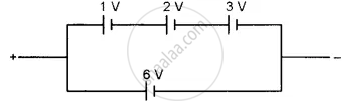
Find the emf of the battery shown in the figure:
Concept: Cells, Emf, Internal Resistance
In Figure 3 given below, find the value of resistance x for which points A and B are at the same potential:
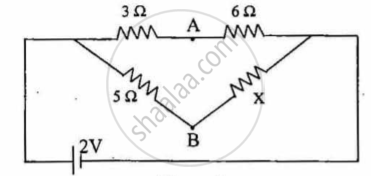
figure 3
Concept: Electrical Resistivity and Conductivity
Define temperature coefficient of resistance of the material of a conductor.
Concept: Temperature Dependence of Resistance
Draw a labelled circuit diagram of a potentiometer to compare emfs of two cells. Write the working formula (Derivation not required).
Concept: Potentiometer
How much resistance should be connected to 15 Ω resistor shown in the circuit in figure below so that the points M and N are at the same potential:
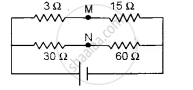
Concept: Combination of Resistors - Series and Parallel
With reference to free-electron theory of conductivity, explain the terms:
(a) Drift speed
(b) Relaxation time
Concept: Conductivity and Conductance;
What is the colour code of a carbon resistor having a resistance of 470 Ω and a tolerance of 5%?
Concept: Electrical Resistivity and Conductivity
A metallic wire has a resistance of 3.0 Ω at 0°C and 4.8 Ω at 150°C. Find the temperature coefficient of resistance of its material.
Concept: Temperature Dependence of Resistance
In the circuit shown in the figure below, E1 and E2 are two cells having emfs 2 V and 3 V respectively, and negligible internal resistance. Applying Kirchhoff’s laws of electrical networks, find the values of currents l1 and I2.
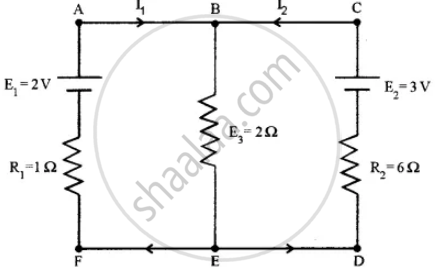
Concept: Kirchhoff’s Rules
An electric current (I) flowing through a metallic wire is gradually increased. The graph of heating power (P) developed in it versus the current (I) is ______.
Concept: Flow of Electric Charges in a Metallic Conductor
Write balancing condition of a Wheatstone bridge.
Concept: Wheatstone Bridge
Eight identical cells, each of emf 2V and internal resistance 3 Ω, are connected in series to form a row. Six such rows are connected in parallel to form a battery. This battery is now connected to an external resistor R of resistance 6 Ω. Calculate:
- emf of the battery.
- internal resistance of the battery.
- current flowing through R.
Concept: Combination of Resistors - Series and Parallel
In the circuit shown in Figure below, E1 and E2 are batteries having emfs of 25V and 26V. They have an internal resistance of 1 Ω and 5 Ω respectively. Applying Kirchhoff’s laws of electrical networks, calculate the currents I1 and I2.
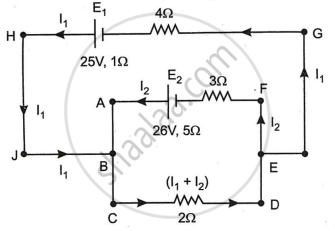
Concept: Kirchhoff’s Rules
