Advertisements
Chapters
2: Geometry
3: Integers
4: Fractions and Decimals
5: Data Handling
6: Mensuration
7: Algebra
8: Ratio and Proportion
▶ 9: Symmetry and Practical Geometry
![NCERT Exemplar solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 6 chapter 9 - Symmetry and Practical Geometry NCERT Exemplar solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 6 chapter 9 - Symmetry and Practical Geometry - Shaalaa.com](/images/mathematics-english-class-6_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 9: Symmetry and Practical Geometry
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 9 of CBSE NCERT Exemplar for Mathematics [English] Class 6.
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 6 9 Symmetry and Practical Geometry Exercise [Pages 136 - 145]
Choose the correct alternative:
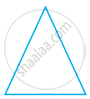
In the following figures, the figure that is not symmetric with respect to any line is ______.
The number of lines of symmetry in a scalene triangle is ______.
0
1
2
3
The number of lines of symmetry in a circle is ______.
0
2
4
More than 4
Which of the following letters does not have the vertical line of symmetry?
M
H
E
V
Which of the following letters have both horizontal and vertical lines of symmetry?
X
E
M
K
Which of the following letters does not have any line of symmetry?
M
S
K
H
Which of the following letters has only one line of symmetry?
H
X
Z
T
The instrument to measure an angle is a ______.
Ruler
Protractor
Divider
Compasses
The instrument to draw a circle is ______.
Ruler
Protractor
Divider
Compasses
Number of set squares in the geometry box is ______.
0
1
2
3
The number of lines of symmetry in a ruler is ______.
0
1
2
4
The number of lines of symmetry in a divider is ______.
0
1
2
3
The number of lines of symmetry in compasses is ______.
0
1
2
3
The number of lines of symmetry in a protractor is ______.
0
1
2
More than
The number of lines of symmetry in a 45° – 45° – 90° set-square is ______.
0
1
2
3
The number of lines of symmetry in a 30° – 60° – 90° set square is ______.
0
1
2
3
The instrument in the geometry box having the shape of a triangle is called a ______.
Protractor
Compasses
Divider
Set-square
Fill in the blank:
The distance of the image of a point (or an object) from the line of symmetry (mirror) is ______ as that of the point (object) from the line (mirror).
The number of lines of symmetry in a picture of Taj Mahal is ______.
The number of lines of symmetry in a rectangle and a rhombus are ______ (equal/unequal).
The number of lines of symmetry in a rectangle and a square are ______ (equal/unequal).
If a line segment of length 5 cm is reflected in a line of symmetry (mirror), then its reflection (image) is a ______ of length _______.
If an angle of measure 80° is reflected in a line of symmetry, then the reflection is an ______ of measure ______.
The image of a point lying on a line l with respect to the line of symmetry l lies on ______.
In figure, if B is the image of the point A with respect to the line l and P is any point lying on l, then the lengths of the line segments PA and PB are ______.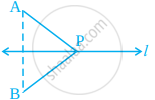
The number of lines of symmetry in given figure is ______.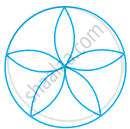
The common properties in the two set-squares of a geometry box are that they have a ______ angle and they are of the shape of a ______.
The digits having only two lines of symmetry are ______ and ______.
The digit having only one line of symmetry is ______.
The number of digits having no line of symmetry is ______.
The number of capital letters of the English alphabets having only vertical line of symmetry is ______.
The number of capital letters of the English alphabets having only horizontal line of symmetry is ______.
The number of capital letters of the English alphabets having both horizontal and vertical lines of symmetry is ______.
The number of capital letters of the English alphabets having no line of symmetry is ______.
The line of symmetry of a line segment is the ______ bisector of the line segment.
The number of lines of symmetry in a regular hexagon is ______.
The number of lines of symmetry in a regular polygon of n sides is ______.
A protractor has ______ line/lines of symmetry.
A 30° – 60° – 90° set-square has ______ line/lines of symmetry.
A 45° – 45° – 90° set-square has ______ line/lines of symmetry.
A rhombus is symmetrical about ______.
A rectangle is symmetrical about the lines joining the ______ of the opposite sides.
State whether the following statement is True or False:
A right triangle can have at most one line of symmetry.
True
False
A kite has two lines of symmetry.
True
False
A parallelogram has no line of symmetry.
True
False
If an isosceles triangle has more than one line of symmetry, then it need not be an equilateral triangle.
True
False
If a rectangle has more than two lines of symmetry, then it must be a square.
True
False
With ruler and compasses, we can bisect any given line segment.
True
False
Only one perpendicular bisector can be drawn to a given line segment.
True
False
Two perpendiculars can be drawn to a given line from a point not lying on it.
True
False
With a given centre and a given radius, only one circle can be drawn.
True
False
Using only the two set-squares of the geometry box, an angle of 40° can be drawn.
True
False
Using only the two set-squares of the geometry box, an angle of 15° can be drawn.
True
False
If an isosceles triangle has more than one line of symmetry, then it must be an equilateral triangle.
True
False
A square and a rectangle have the same number of lines of symmetry.
True
False
A circle has only 16 lines of symmetry.
True
False
A 45° – 45° – 90° set-square and a protractor have the same number of lines of symmetry.
True
False
It is possible to draw two bisectors of a given angle.
True
False
A regular octagon has 10 lines of symmetry.
True
False
Infinitely many perpendiculars can be drawn to a given ray.
True
False
Infinitely many perpendicular bisectors can be drawn to a given ray.
True
False
Is there any line of symmetry in the figure? If yes, draw all the lines of symmetry.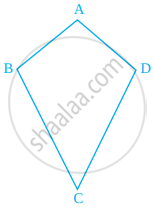
In figure, PQRS is a rectangle. State the lines of symmetry of the rectangle.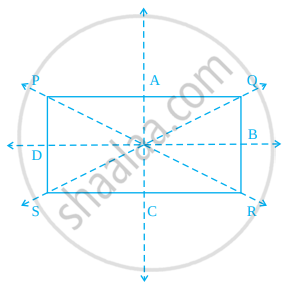
Write all the capital letters of the English alphabets which have more than one lines of symmetry.
Write the letters of the word ‘MATHEMATICS’ which have no line of symmetry.
Write the number of lines of symmetry in each letter of the word ‘SYMMETRY’.
Match the following
| Shape | Number of lines of symmetry |
| (i) Isosceles triangle | (a) 6 |
| (ii) Square | (b) 5 |
| (iii) Kite | (c) 4 |
| (iv) Equilateral triangle | (d) 3 |
| (v) Rectangle | (e) 2 |
| (vi) Regular hexagon | (f) 1 |
| (vii) Scalene triangle | (g) 0 |
Open your geometry box. There are some drawing tools. Observe them and complete the following table:
| Name of the tool | Number of lines of symmetry |
| (i) The Ruler | ______ |
| (ii) The Divider | ______ |
| (iii) The Compasses | ______ |
| (iv) The Protactor | ______ |
| (v) Triangular piece with two equal sides | ______ |
| (vi) Triangular piece with unequal sides | ______ |
Draw the images of points A and B in line l of figure and name them as A’ and B’, respectively. Measure AB and A’B’. Are they equal?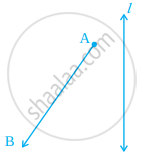
In figure, the point C is the image of point A in line l and line segment BC intersects the line l at P.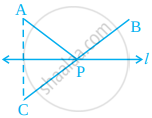
(a) Is the image of P in line l the point P itself?
(b) Is PA = PC?
(c) Is PA + PB = PC + PB?
(d) Is P that point on line l from which the sum of the distances of points A and B is minimum?
Complete the figure so that line l becomes the line of symmetry of the whole figure.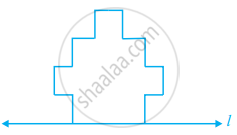
Draw the images of the points A, B and C in the line m (figure). Name them as A’,B’ and C respectively and join them in pair. Measure AB, BC, CA, A’B’, B’C’ and C’A’. Is AB = A’B’, BC = B’C’ and CA = C’A’?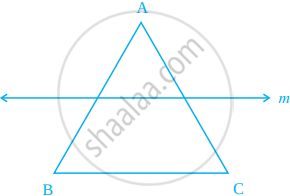
Draw the images P’, Q’ and R’ of the points P, Q and R respectively in the line n. Join P’Q’ and Q’ R’ to form an angle P’Q’R’. Measure ∠PQR and ∠P’Q’R’. Are the two angles equal?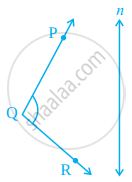
Complete the figure by taking l as the line of symmetry of the whole figure.
Draw a line segment of length 7 cm. Draw its perpendicular bisector, using ruler and compasses.
Draw a line segment of length 6.5 cm and divide it into four equal parts, using ruler and compasses.
Draw an angle of 140° with the help of a protractor and bisect it using ruler and compasses.
Draw an angle of 65° and draw an angle equal to this angle, using ruler and compasses.
Draw an angle of 80° using a protractor and divide it into four equal parts, using ruler and compasses.Check your construction by measurement.
Copy figure on your notebook and draw a perpendicular to l through P, using (i) set squares (ii) protractor (iii) ruler and compass. How many such perpendiculars are you able to draw?
Copy figure on your notebook and draw a perpendicular from P to line m using (i) set squares (ii) protractor (iii) ruler and compass. How many such perpendicular are you able to draw?
Draw a circle of radius 6 cm using ruler and compasses. Draw one of its diameters. Draw the perpendicular bisector of this diameter. Does this perpendicular bisector contain another diameter of the circle?
Bisect ∠XYZ of figure.
Draw an angle of 60° using ruler and compasses and divide it into four equal parts. Measure each part.
Bisect a straight angle, using ruler and compasses. Measure each part.
Bisect a right angle, using ruler and compasses. Measure each part. Bisect each of these parts. What will be the measure of each of these parts?
Draw an angle ABC of measure 45°, using ruler and compasses. Now draw an angle DBA of measure 30o , using ruler and compasses as shown in figure. What is the measure of ∠DBC?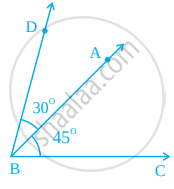
Draw a line segment of length 6 cm. Construct its perpendicular bisector. Measure the two parts of theline segment.
Draw a line segment of length 10 cm. Divide it into four equal parts. Measure each of these parts.
Solutions for 9: Symmetry and Practical Geometry
![NCERT Exemplar solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 6 chapter 9 - Symmetry and Practical Geometry NCERT Exemplar solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 6 chapter 9 - Symmetry and Practical Geometry - Shaalaa.com](/images/mathematics-english-class-6_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 6 chapter 9 - Symmetry and Practical Geometry
Shaalaa.com has the CBSE Mathematics Mathematics [English] Class 6 CBSE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. NCERT Exemplar solutions for Mathematics Mathematics [English] Class 6 CBSE 9 (Symmetry and Practical Geometry) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. NCERT Exemplar textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Mathematics [English] Class 6 chapter 9 Symmetry and Practical Geometry are Concept of Symmetry, Making Symmetric Figures: Ink-blot Devils, Concept of Lines Symmetry, Concept of Reflection Symmetry, Introduction to Geometric Tool, Construction of a Circle When Its Radius is Known, Construction of a Line Segment of a Given Length, Constructing a Copy of a Given Line Segment, Drawing a Perpendicular to a Line at a Point on the Line, Drawing a perpendicular to a line from a point outside the line, The Perpendicular Bisector, Constructing an Angle of a Given Measure, Construction of an angle bisector using a compass, Concept of Angle Bisector, Angles of Special Measures - 30°, 45°, 60°, 90°, and 120°.
Using NCERT Exemplar Mathematics [English] Class 6 solutions Symmetry and Practical Geometry exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in NCERT Exemplar Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CBSE Mathematics [English] Class 6 students prefer NCERT Exemplar Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 9, Symmetry and Practical Geometry Mathematics [English] Class 6 additional questions for Mathematics Mathematics [English] Class 6 CBSE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.