Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
![Selina solutions for Concise Chemistry [English] Class 9 ICSE chapter 3 - Water Selina solutions for Concise Chemistry [English] Class 9 ICSE chapter 3 - Water - Shaalaa.com](/images/concise-chemistry-english-class-9-icse_6:3baa192b34e3498fa97ae56602d705f0.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 3: Water
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 3 of CISCE Selina for Concise Chemistry [English] Class 9 ICSE.
Selina solutions for Concise Chemistry [English] Class 9 ICSE 3 Water Exercise 3 (A) [Pages 36 - 37]
Water exists in all three states. Discuss.
Why is water considered a compound?
Why does temperature in Mumbai and Chennai not fall as low as it does in Delhi?
Give the properties of water responsible for controlling the temperature of our body.
'Water is the universal solvent'. Comment.
What causes the violence associated with torrential rain?
Which property of water enables it to modify the climate?
Density of water varies with temperature. What are its consequences?
What is the effect of impurities present in the water on the melting point and boiling point of water?
How do fishes and aquatic animals survive when the pond gets covered with thick ice?
The properties of water are different from the properties of the elements of which it is formed. Discuss.
How is aquatic life benefited by the fact that water has maximum density at 4oC?
What are the observations and conclusions when tap water is boiled and evaporated in watch glass?
What is the importance of dissolved salts in water?
State the importance of the solubility of CO2 and O2 in water.
How is air dissolved in water different from ordinary air?
Identify A, B, C and D; first one is done for you.
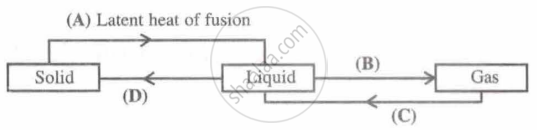
Explain why boiled or distilled water tastes flat.
Explain why:
Ice at zero degrees centigrade has greater cooling effect than water at 0oC.
Explain why:
Burns caused by steam are more severe than burns caused by boiling water.
Explain why:
Rivers and lakes do not freeze easily?
Explain why:
Air dissolved in water contains a higher proportion of oxygen.
Explain why:
If distilled water is kept in a sealed bottle for a long time, it leaves etchings on the surface of the glass.
Explain why:
Rain water does not leave behind concentric rings when boiled.
Selina solutions for Concise Chemistry [English] Class 9 ICSE 3 Water Exercise 3 (B) [Page 47]
Explain the terms:
Solution
Explain the terms:
Solute
Explain the terms:
Solvent
Explain why a hot saturated solution of potassium nitrate forms crystals as it cools.
Give three factors which affect the solubility of a solid solute in a solvent.
If you are given some copper sulphate crystals, how would you proceed to prepare its saturated solution at room temperature?
How can you show that your solution is really saturated?
Define
Henry's law
Define crystallisation.
Define
Seeding
State any three methods of crystallisation.
What would you observe when crystals of copper (II) sulphate and iron (II) sulphate are separately heated in two test tubes?
Give the names and formulae of two substances.
Hydrated substance
Give the names and formulae of two substances
Anhydrous substance
Give the names and formulae of two substances
Liquid drying agent
Give the names and formulae of two substances
A basic drying agent
What is the effect of temperature on solubility of KNO3 and CaSO4 in water?
Solubility of NaCl at 40oC is 36.5 g. What is meant by this statement?
Which test will you carry out to find out if a given solution is saturated or unsaturated or supersaturated?
What is the effect of pressure on solubility of gases? Explain with an example.
State the term: (Do not give examples)
A solution where solvent is a liquid other than water.
State the term:
When a substance absorbs moisture on exposure to moist air and dissolves in the absorbed water and turned to solution.
State the term:
A substance which contains water of crystallisation.
When a substance absorbs moisture from the atmosphere but does not form a solution.
When a compound loses its water of crystallisation on exposure to dry air.
The substance that can remove hydrogen and oxygen atoms in the ratio of 2:1(in the form of water) from the compound.
Explain why:
Water is an excellent liquid to use in cooling systems.
Explain why:
A solution is always clear and transparent.
Explain why:
Lakes and rivers do not suddenly freeze in the winters.
Explain why:
The solute cannot be separated from a solution by filtration.
Explain why:
Fused CaCl2 or conc. H2SO4 is used in a desiccator.
Explain why:
Effervescence is seen on opening a bottle of soda water.
Explain why:
Table salts become sticky on exposure to humid air during the rainy season.
Normally, solubility of crystalline solid increases with temperature. Does it increase uniformly in all cases? Name a substance whose solubility:
Increases rapidly with temperature
Normally, solubility of crystalline solid increases with temperature. Does it increase uniformly in all cases? Name a substance whose solubility:
Increases gradually with temperature.
Normally, solubility of crystalline solid increases with temperature. Does it increase uniformly in all cases? Name a substance whose solubility:
Increases slightly with temperature.
Normally, solubility of crystalline solid increases with temperature. Does it increase uniformly in all cases? Name a substance whose solubility:
Initially increases then decreases with rise in temperature.
What are drying or desiccating agents? Give examples.
Complete the following table:
|
Common Name |
Chemical Name |
Formula |
Acid, base or salt |
Efflorescent, hygroscopic or deliquescent substance |
|
Solid caustic potash |
|
|
|
|
|
Quick lime |
|
|
|
|
|
Oil of vitriol |
|
|
|
|
|
Washing soda |
|
|
|
|
|
Solid caustic soda |
|
|
|
|
|
Blue vitriol |
|
|
|
|
In which of the following substances will there be
Decrease in mass
In which of the following substances will there be
Increase in mass
In which of the following substances will there be
No change in mass when they are exposed to air?
Sodium chloride
Iron
Conc. sulphuric acid
Table salt
Sodium carbonate crystals
State the methods by which hydrated salts can be made anhydrous.
Selina solutions for Concise Chemistry [English] Class 9 ICSE 3 Water Exercise 3 (C) [Page 52]
What is the composition of water? In what volume its elements combine?
What is the use of solubility of oxygen and carbon dioxide in water?
Hot saturated solution of sodium nitrate forms crystals as it cools. Why?
What are hydrous substances? Explain with examples.
Name three methods by which hydrous substances can be made anhydrous.
What is the importance of dissolved impurities in water?
State two ways by which a saturated solution can be changed to unsaturated solution.
What do you understand by
Soft water
What do you understand by
Hard water
What do you understand by
Temporary hard water
What do you understand by
Permanent hard water
What are the causes for:
Temporary hardness
What are the causes for
Permanent hardness
What are the advantages of soft water.
What are the advantages of hard water.
What are stalgmites and stalactites? How are they formed?
Name the substance which makes water temporarily hard
Name the substance which makes water permanently hard.
Give equations to show what happens when temporary hard water is
Boiled
Give equations to show what happens when temporary hard water is
Treated with slaked lime
State the disadvantages of using hard water.
What is soap? For what is it used?
What is the advantage of a detergent over soap?
Why does the hardness of water render it unfit for use in a boiler.
Why does the hardness of water render it unfit for use in a washing purposes.
Explain with equation, what is noticed when permanent hard water is treated with
Slaked time
Explain with equation, what is noticed when permanent hard water is treated with Washing soda.
Explain the permutit method for softening hard water.
Solutions for 3: Water
![Selina solutions for Concise Chemistry [English] Class 9 ICSE chapter 3 - Water Selina solutions for Concise Chemistry [English] Class 9 ICSE chapter 3 - Water - Shaalaa.com](/images/concise-chemistry-english-class-9-icse_6:3baa192b34e3498fa97ae56602d705f0.jpg)
Selina solutions for Concise Chemistry [English] Class 9 ICSE chapter 3 - Water
Shaalaa.com has the CISCE Mathematics Concise Chemistry [English] Class 9 ICSE CISCE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. Selina solutions for Mathematics Concise Chemistry [English] Class 9 ICSE CISCE 3 (Water) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. Selina textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Concise Chemistry [English] Class 9 ICSE chapter 3 Water are Water: Our Lifeline, Water - a Universal Solvent, Salts, Removal of Hardness of Water, Efflorescence, Hygroscopic, and Deliquescence Substances, Drying and Dehydrous Substances, Classification of water: Soft and Hard Water, Causes of Hardness, Advantage and Disadvantage of Hard Water, Physical Properties of Water, Chemical Properties of Water, Solutions as 'Mixtures' of Solids in Water, Components of Solutions, Different Types of Solutions, Saturated Solutions, Concentration of a Solution, Solubility, Crystals and Crystallisation, Hydrated and Anhydrous Substances, Prevention of Water Pollution.
Using Selina Concise Chemistry [English] Class 9 ICSE solutions Water exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in Selina Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CISCE Concise Chemistry [English] Class 9 ICSE students prefer Selina Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 3, Water Concise Chemistry [English] Class 9 ICSE additional questions for Mathematics Concise Chemistry [English] Class 9 ICSE CISCE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
