Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
2: Chemical Changes and Reactions
3: Water
▶ 4: Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding
5: The Periodic Table
6: Study of the First Element - Hydrogen
7: Study of Gas Laws
8: Atmospheric Pollution
9: Practical Work
![Selina solutions for Concise Chemistry [English] Class 9 ICSE chapter 4 - Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding Selina solutions for Concise Chemistry [English] Class 9 ICSE chapter 4 - Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding - Shaalaa.com](/images/concise-chemistry-english-class-9-icse_6:3baa192b34e3498fa97ae56602d705f0.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 4: Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 4 of CISCE Selina for Concise Chemistry [English] Class 9 ICSE.
Selina solutions for Concise Chemistry [English] Class 9 ICSE 4 Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding Exercise 4 (A) [Page 59]
What is the contribution of the following in atomic structure?
Maharshi Kanada
What is the contribution of the following in atomic structure?
Democritus
State Dalton's atomic theory.
What is an α (alpha) particle?
What are cathode rays? How are these rays formed?
What is the nature of the charge on Cathode rays .
What is the nature of the charge on Anode rays?
How are X-rays produced?
Why are anode rays also called as 'canal rays'?
How does cathode ray differ from as anode rays?
State one observation which shows that atom is not indivisible.
Name an element which does not contain neutron.
If an atom contains one electron and one proton, will it carry as a whole is neutral
On the basis of Thomson's model of an atom explain how an atom as a whole is neutral.
Which sub-atomic particle was discovered by Thomson?
Which sub-atomic particle was discovered by Goldstein.
Which sub-atomic particle was discovered by Chadwick.
Name the sub-atomic particle whose charge is +1.
Name the sub-atomic particle whose charge is -1.
Name the sub-atomic particle whose charge is 0.
Which metal did rutherford select for his `alpha` particle scattering experiment and why?
What do you think would be the observation of `alpha` particle scattering experiment if carried out on (i) heavy nucleus like platinum (ii) light nuclei like litheum.
On the basis of Rutherford's model of an atom, which subatomic particle is present in the nucleus of an atom?
Which part of atom was discovered by Rutherford?
How was it shown that atom has empty space?
State one major drawback of Rutherford's model.
In the figure given alongside
(a) Name the shells denoted by A,B, and C. Which shell has least energy
(b) Name X and state the charge on it
(c) The above sketch is of …………. Model of an atom
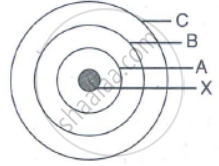
Give the postulates of Bohr's atomic model
Selina solutions for Concise Chemistry [English] Class 9 ICSE 4 Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding Exercise 4 (B) [Page 63]
Name the three fundamental particles of an atom.
Give the symbol and charge of each particle.
Complete the table given below by identifying P, Q, R and S.
|
Element |
Symbol |
No. of Protons |
No. of neutrons |
No. of Electrons |
|
Sodium |
`""_11^23"NA"` |
11 |
P |
11 |
|
Chlorine |
`""_17^35"CI"` |
Q |
18 |
17 |
|
Uranium |
R |
92 |
146 |
92 |
|
S |
`""_9^19"F"` |
9 |
10 |
9 |
The atom of an element is made up of 4 protons, 5 neutrons and 4 electrons. What are its atomic number and mass number?
The atomic number and mass number of sodium are 11 and 23 respectively. What information is conveyed by this statement?
Write down the names of the particles represented by the following symbols and explain the meaning of superscript and subscript numbers attached `""_1"p"^1, ""_0"n"^1,""_-1"e"^0`
From the symbol `""_12^24"Mg"`
, state the mass number, the atomic number and electronic configuration of magnesium.
Sulphur has an atomic number 16 and a mass of 32.
State the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of sulphur. Give a simple diagram to show the arrangement of electrons in an atom of sulphur.
Explain the rule according to which electrons are filled in various energy levels.
Draw the orbital diagram of `""_20^40"Ca"^(2+)` ion and state the number of three fundamental particles present in it.
Write down the electronic configuration of the following:
(a) `""_13^27"Y"`
(b) `""_17^35"Y"`
Write down the number of electrons in X and neutrons in Y.
Selina solutions for Concise Chemistry [English] Class 9 ICSE 4 Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding Exercise 4 (C) [Pages 66 - 67]
How does the Modern atomic theory contradict and correlate with Dalton's atomic theory?
What are inert elements?
Why do they exist as monoatoms in molecules?
What are valence electrons?
In what respects do the three isotopes of hydrogen differ? Give their structures.
Match the atomic numbers 4, 14, 8, 15 and 19 with each of the following:
- A solid non-metal of valency 3.
- A gas of valency 2.
- A metal of valency 1.
- A non-metal of valency 4.
Draw diagrams representing the atomic structures of the following:
- Sodium atom
- Chlorine ion
- Carbon atom
- Oxygen ion
What is the significance of the number of protons found in the atoms of different elements?
Elements X, Y and Z have atomic numbers 6, 9 and 12 respectively. Which one:
- Forms an anion
- Forms a cation
- Has four electrons in its valence shell?
Element X has electronic configurations 2, 8, 18, 8, 1. Without identifying X,
- Predict the sign and charge on a simple ion of X.
- Write if X will be an oxidizing agent or a reducing agent. Why?
Define the term:
Mass number
Define the term:
Ion
Define the term: Cation
Define the term: Anion
Define the term: Element
Define the term:
orbit
From the symbol `""_2^4"He"` for the element helium, write down the mass number and the atomic number of the element.
Five atoms are labeled A to E
|
Atoms |
Mass No |
Atomic No. |
|
A |
40 |
20 |
|
B |
19 |
9 |
|
C |
7 |
3 |
|
D |
16 |
8 |
|
E |
14 |
7 |
(a) Which one of these atoms:
(i) contains 7 protons
(ii) has electronic configuration 2,7
(b) Write down the formula in the compound formed between C and D
(c) Predict : (i) metals (ii) non-metals
An atom of an element has two electrons in the M shell.
What is the (a) atomic number (b) number of protons in this element?
\[\ce{^24_12Mg}\] and \[\ce{^26_12Mg}\] are symbols of isotopes of magnesium.
(a) Compare the atoms of these isotopes with respect to :
i. the composition of their nuclei
ii. their electronic configurations
(b) Give reasons why the two isotopes of magnesium have different mass numbers.
What are nucleons? How many nucleons are present in phosphorus? Draw its structure.
What are isotopes? With reference to which fundamental particle do isotopes differ? Give two uses of isotopes.
Why do `""_17^35"CI"` and `""_17^37"CI"` have the same chemical properties? In what respect do these atoms differ?
Explain fractional atomic mass. What is the fractional mass of chlorine?
What is meant by the 'atomic number of an element'?
Complete the table given below
|
|
No. of protons |
No. of electrons |
No. of Neutrons |
Atomic Number |
Mass number |
| `""_17^35"CI"` |
|
|
|
|
|
| `""_17^37"CI"` |
|
|
|
|
|
Write down the electronic configuration of
(i) chlorine atom (ii) chlorine ion
Name the following:
The element which does not contain any neutron in its nucleus.
Name the following:
An element having valency 'zero'
Name the following:
Metal with valency 2
Name the following:
Two atoms having the same number of protons and electrons but different number of neutrons.
Name the following:
The shell closest to the nucleus of an atom
Give a reason
Physical properties of isotopes are different.
Give reason
Argon does not react.
Give reason
Actual atomic mass is greater than mass number.
Give reason
`""_17^35"CI"` and `""_17^37"CI"` do not differ in their chemical reactions.
An element A atomic number 7 mass numbers 14
B electronic configuration 2,8,8
C electrons 13, neutrons 14
D Protons 18 neutrons 22
E Electronic configuration 2,8,8,1
State Valency of each element
An element A atomic number 7 mass numbers 14
B electronic configuration 2,8,8
C electrons 13, neutrons 14
D Protons 18 neutrons 22
E Electronic configuration 2,8,8,1
State (i) Valency of each element (ii) which one is a metal (iii) which is non-metal (iv) which is an inert gas
Choose the correct option
Rutherford's alpha-particle scattering experiment discovered
Electron
Proton
Atomic nucleus
Neutron
Choose the correct option
The number of valence electrons in O2- is :
6
8
10
4
Choose the correct option
Which of the following is the correct electronic configuration of potassium?
2,8,9
8,2,9
2,8,8,1
1,2,8,8
Choose the correct option:
The mass number of an atom whose unipositive ion has 10 electrons and 12 neutrons is :
22
23
21
20
Explain
Octet rule for the formation of sodium chloride
Explain
Duplet rule for the formation of hydrogen
Complete the following table relating to the atomic structure of some elements.
|
Element Symbol |
Atomic Number |
Mass Number |
Numbers of neutrons |
Number of Electrons |
Number of Protons |
|
Li |
3 |
6 |
|
|
|
|
Cl |
17 |
|
20 |
|
|
|
Na |
|
|
12 |
|
11 |
|
Al |
|
27 |
|
|
13 |
|
S |
|
32 |
16 |
|
|
Selina solutions for Concise Chemistry [English] Class 9 ICSE 4 Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding Exercise 4 (D) [Page 71]
How do atoms attain noble gas configurations?
Define electrovalent bond.
Elements are classified as metals, non-metal, metalloids, and inert gases. Which of them form an electrovalent bond?
An atom X has three electrons more than the noble gas configuration. What type of ion will it form?
Write the formula of its (X)
sulphate
nitrate
phosphate
carbonate
hydroxide.
Mention the basic tendency of an atom which makes it combine with other atoms
What type of compounds are usually formed between metals and non-metals and why?
In the formation of the compound XY2, an atom X gives one electron to each Y atom. What is the nature of the bond in XY2?
Draw the electron dot structure of this compound.
An atom X has 2, 8, 7 electrons in its shell. It combines with Y having 1 electron in its outermost shell.
What type of bond will be formed between X and Y?
An atom X has 2, 8, 7 electrons in its shell. It combines with Y having 1 electron in its outermost shell.
Write the formula of the compound formed.
Draw orbit structure diagram of sodium chloride (NaCl).
Draw orbit structure diagram of calcium oxide (CaO).
Compare :
Sodium atom and sodium ion
Compare:
Chlorine atom and chloride ion, with respect to
Atomic structure
Electrical state
The electronic configuration of fluoride ion is the same as that of the neon atom. What is the difference between the two?
What do you understand by redox reactions?
Explain oxidation and reduction in terms of loss or gain of electrons.
Potassium (at No.19) and chlorine (at No.17) react to form a compound. Explain the formation of the compound on the basis of oxidation.
Potassium (at No.19) and chlorine (at No.17) react to form a compound. Explain the formation of the compound on the basis of reduction.
Potassium (at No.19) and chlorine (at No.17) react to form a compound. Explain the formation of the compound on the basis of oxidizing agent.
Potassium (at No.19) and chlorine (at No.17) react to form a compound. Explain the formation of the compound on the basis of reducing agent.
Selina solutions for Concise Chemistry [English] Class 9 ICSE 4 Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding Exercise 4 (E) [Pages 76 - 77]
Define a covalent bond.
Covalent bonds can be single, double or triple covalent bonds. How many electrons are shared in each? Give an example of each type.
Show number of bonds in ethene molecule.
Show number of bonds in ethyne molecule.
An element A has 1 electron in its first shell. It combines with element B having 7 electrons in its third shell. What type of bond is formed?
Match the atomic numbers 4,8,10,15 and 19 with the following:
Element which can form trivalent ion
Match the atomic numbers 4,8,10,15 and 19 with the following:
Element with four shells
Match the atomic numbers 4,8,10,15 and 19 with the following:
Element with 6 valence electrons
Match the atomic numbers 4,8,10,15 and 19 with each of the following:
An element which does not form ion
If electrons are getting added to en element Y; then
Is Y getting oxidized or reduced?
If electrons are getting added to en element Y; then
What charge will Y migrate to during the process of electrolysis?
Elements X, Y and Z have atomic numbers 6,9 and 12 respectively. Which one:
- Forms an anion
- Forms a cation
State the type of bond between Y and Z and give its molecular formula.
Taking MgCl2 as an electrovalent compound, CCl4 as a covalent compound, give four difference between electrovalent and covalent compounds
Potassium chloride is an electrovalent compound, while hydrogen chloride is a covalent compound, But, both conduct electricity in their aqueous solutions. Explain.
Name two compounds that are covalent when taken pure but produce ions when dissolved in water.
An element M burns in oxygen to form an ionic compound MO. Write the formula of the compounds formed if this element is made to continue with chlorine and sulfur separately.
Give the orbital diagram of the following:
Magnesium chloride
Give the orbital diagram of the following:
Nitrogen
Give the orbital diagram of the following:
Methane
Give the orbital diagram of the following:
Hydrogen chloride
State the type of bonding in the following molecules.
Water,
State the type of bonding in the following molecules.
Calcium oxide
State the type of bonding in the following molecules.
Hydrogen chloride
Element M forms a chloride with the formula MCl2 which is solid with a high melting point. What type of bond is in MCl2. Write the formula of the compound when M combines with sulphur, oxygen, and nitrogen.
Explain the following:
Mass of an atom is concentrated inside the nucleus of the atom.
Explain the following:
Atoms combine by transfer and sharing of an electron(s).
Explain the following:
An element has atoms with different mass numbers.
Explain the following:
Carbon-12 and carbon-14 both show similar chemical properties.
Choose the correct answer from A, B, C and D:
The characteristic of an electrovalent compound is that:
They are formed by the sharing of electrons.
They are formed between metals and non-metals.
They are formed between two non-metals.
They often exist as a liquid.
Choose the correct answer from A, B, C and D:
When a metal atom becomes an ion:
It loses electrons and is oxidised.
It gains electrons and is reduced.
It gains electrons and is oxidised.
It loses electrons and is reduced.
Identify the following reaction as either oxidation or reduction:
O + 2e- → O2-
Identify the following reaction as either oxidation or reduction:
K - e- → K+
Identify the following reaction as either oxidation or reduction:
Fe3+ + e- → Fe2+
Identify the following reaction as either oxidation or reduction:
Zn → Zn2+ + 2e-
Name the charged particles which attract one another to form electrovalent compound?
In the formation of electrovalent compounds, electrons are transferred from one element to another. How are electrons involved in the formation of a covalent compound?
The electronic configuration of nitrogen is (2, 5). How many electrons in the outer shell of a nitrogen atom are not involved in the formation of a nitrogen molecule?
In the formation of magnesium chloride (by direct combination between magnesium and chlorine), name the substance that is oxidized and the substance that is reduced.
What is the term defined below?
A bond formed by a shared pair of electrons, each bonding atom contributing one electron to the pair.
What is the term defined below?
A bond formed by transfer of electron(s).
Name or state the following:
An element having valency zero
Name or state the following:
Metal with valency one
Name or state the following:
Atoms of the same element differing in mass number
Name or state the following:
Elements having same mass number but different atomic number
Name or state the following:
A bond formed by transfer of electron(s)
Name or state the following:
Ion formed by the gain of an electron(s)
An element X has 2 electrons in its M shell, it forms a bond with an element Y which has 7 electrons in its third orbit.
- Write the formula of the compound formed.
- Which nearest inert gas electronic configuration will element X and Y acquire.
- Show by orbital diagram the formation of the compound between X and Y.
In the formation of (i) oxygen molecule (ii) carbon tetrachloride molecule, state the following:
- Electronic configuration of nearest inert gas attained.
- How many electrons are shared/transferred in bond formation
- Which type of bonds these compounds form?
- Draw their orbital diagrams.
Solutions for 4: Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding
![Selina solutions for Concise Chemistry [English] Class 9 ICSE chapter 4 - Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding Selina solutions for Concise Chemistry [English] Class 9 ICSE chapter 4 - Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding - Shaalaa.com](/images/concise-chemistry-english-class-9-icse_6:3baa192b34e3498fa97ae56602d705f0.jpg)
Selina solutions for Concise Chemistry [English] Class 9 ICSE chapter 4 - Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding
Shaalaa.com has the CISCE Mathematics Concise Chemistry [English] Class 9 ICSE CISCE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. Selina solutions for Mathematics Concise Chemistry [English] Class 9 ICSE CISCE 4 (Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. Selina textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Concise Chemistry [English] Class 9 ICSE chapter 4 Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding are Chemical Bond, History of Atom, Elements, Atoms: Building Blocks of Matter, Discovery of Charged Particles in Matter, Electrons (e), Protons (p), Nucleus, Neutrons (n), J. J. Thomson’s Atomic Model, Lord Rutherford’s Atomic model, Neils Bohr’s Model of an Atom, Structure of an Atom, Atomic Number (Z), Mass Number (A), and Number of Neutrons (n), Atomic Mass, Electronic Configuration of Atom, Reason for Chemical Activity of an Atom, Isotopes, Isobars, Types of Covalent Bond, Formation of Covalent Bond, The Covalent Bond, Ionic or Electrovalent Bond, Ionic or Electrovalent Bond, Valency, Dalton’s Atomic Theory.
Using Selina Concise Chemistry [English] Class 9 ICSE solutions Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in Selina Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CISCE Concise Chemistry [English] Class 9 ICSE students prefer Selina Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 4, Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding Concise Chemistry [English] Class 9 ICSE additional questions for Mathematics Concise Chemistry [English] Class 9 ICSE CISCE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
