Topics
Living World
- What is ‘Living’?
- Taxonomical Aids
Systematics of Living Organisms
- Systematics of Living Organisms (Introduction)
- Systematics of Living Organisms (Introduction)
- Concept of Systematics
- Concept of Systematics
- Classification of Taxonomy
- Classification of Taxonomy
- Three Domains of Life
- Three Domains of Life
- Chemotaxonomy
- Chemotaxonomy
- Numerical Taxonomy
- Numerical Taxonomy
- Cladogram
- Cladogram
- Phylogeny
- Phylogeny
- DNA Barcoding
- DNA Barcoding
- Taxonomic Hierarchy of Living Organisms: Unit of Classification
- Taxonomic Hierarchy of Living Organisms: Unit of Classification
- Taxonomic Hierarchy
- Taxonomic Hierarchy
- Units of Classification
- Units of Classification
- Binomial Nomenclature
- Binomial Nomenclature
- Salient Features of Five Kingdoms
- Salient Features of Five Kingdoms
- Acellular Organisms
- Acellular Organisms
Kingdom Plantae
- Classification of Kingdom Plantae
- Salient Features of Major Plant Groups Under Cryptogams
- Salient Features of Major Plant Groups Under Phanerogams
- Plant Life Cycle and Alternation of Generations
Kingdom Animalia
- Criteria Used for Animal Classification
- Animal Body Plan
- Animal Classification
Cell Structure and Organization
- Cell: Structural and Functional Unit of Life
- Types of Cells
- Components of Eukaryotic Cell
Biomolecules
- Biomolecules in Living System
- Biomolecules in the Cell
- Carbohydrates
- Lipids
- Proteins
- Nucleic Acids
- Enzymes
- Nature of Enzyme Action
- Nomenclature of Enzymes
- Classification of Enzymes
- Mechanism of Enzyme Action
- Enzyme - Substrate Interactions
- Factors Affecting Enzyme Activity
- Metabolism
- Metabolic Pool
- Secondary metabolites (SMs)
Cell Division
- Introduction of Cell Division
- Cell Cycle
- Types of Cell Division
- Significance of Mitosis
- Significance of Mitosis
Plant Tissues and Anatomy
- Tissues - “The Teams of Workers”
- Meristems or Meristematic Tissues
- Permanent Tissue
- Tissue System
- Secondary Growth in Plants
- Wood
- Cork Cambium and Secondary Growth
- Anatomy of Root, Stem and Leaf
Morphology of Flowering Plants
- Division II- Angiosperms
- Morphology
- Study of Some Important Families
Animal Tissue
Study of Animal Type : Cockroach
- Habit and Habitat
- Systematic Position
- External Morphology
- Body Cavity
- Digestive System of Cockroach
- Circulatory System Or Blood Vascular System
- Human Respiratory System
- Reproduction System
- Interactions with Mankind
Photosynthesis
- Photosynthesis: Food-Making Process in Plants
- Chloroplasts
- Nature of Light
- Mechanism of Photosynthesis
- Light Dependent Reaction (Hill Reaction \ Light Reaction)
- Photophosphorylation
- Light Independent Reactions (Dark Reaction \ Biosynthetic Phase)
- Photorespiration
- C4 Pathway Or Hatch-slack Pathway
- Cam - Crassulacean Acid Metabolism
- Factors Affecting Photosynthesis
Respiration and Energy Transfer
- Formation of ATP
- Respiration
- Types of Respiration: Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration
- Phases of Respiration: Glycolysis
- Phases of Respiration: Pyruvate Oxidation (Link Reaction)
- Phases of Respiration: Electron Transport System (Ets) and Oxidative Phosphorylation
- Phases of Respiration: Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle (Citric Acid Cycle Or Kreb’s Cycle)
- Phases of Respiration: Electron Transport Chain (Electron Transfer System)
- Phases of Respiration: Fermentation
- Respiratory Balance Sheet
- Amphibolic Pathways
- Utility of Stepwise Oxidation
- Respiratory Quotient (R.Q.)
Human Nutrition
- Nutrients and Nutrition
- Component of Food
- Human Digestive System
- The Mouth and Buccal Cavity
- The Salivary Glands
- The Teeth and Its Structure
- Tongue
- The Food Pipe/Oesophagus
- The Stomach
- The Small Intestine
- Pancreas
- The Large Intestine
- Liver
- Physiology of Digestion
- Absorption of Food
- Assimilation of Food
- Egestion of Food
- Nutritional and Digestive Tract Disorders
Excretion and Osmoregulation
- Excretion
- Modes of Excretion: Ammonotelism, Ureotelism, and Uricotelism
- Human Excretory System
- Kidney and Its Internal Structure
- Kidney Tubule (Nephrons)
- Function of the Kidney - “Production of Urine”
- Concentration of Urine
- Composition of Urine
- Accessory Excretory Organs
- Common Disorders of the Urinary System
Skeleton and Movement
- Movements and Locomotion
- Location and Structure of Skeletal Muscles
- Working of Skeletal Muscles
- Mechanism of Muscle Contraction
- Physiology of Muscle Relaxation
- Relaxation of Muscle Fibres
- Skeletal System
- Group of Skeleton
- Types of Joints
- Disorders Related to Muscles
- Disorders Related to Bones
- Introduction
- Simple Epithelium Tissue
- Compound Epithelial Tissue
Introduction:
Epithelial tissues are characterised by the absence of blood vessels. Instead, it receives the required nutrition through diffusion. They form the outer covering as well as the inner lining of many organs. In epithelial tissues, all cells are densely packed with little intercellular matrix between them.
It is classified into two types: simple epithelium and compound epithelium.
Where are the epithelial tissues found in the human body?
- The lining of the blood vessels
- The lining of the mouth
- Kidney tubules
- Skin
- Lung alveoli
Simple Epithelium Tissue:
| Name | Appearance (Diagrammatic) | Location | Structure | Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Squamous Epithelium | 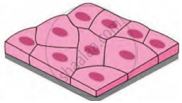 |
Inner surface of mouth, oesophagus, blood-vessels, alveoli | Thin, small, flat cells form a semipermeable membrane | Selective transport of substances |
| Glandular Epithelium | 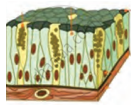 |
Inner layer of skin, etc. | Cells contain vesicles packed with secretory material | Secretion of sweat, oil (sebum), mucus, etc. |
| Columnar Epithelium | 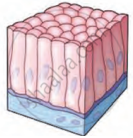 |
Inner surface (mucosa) of intestine, alimentary canal | Column-like tall cells. Upper free surface bears folds at places of absorption | Secretion of digestive juice, absorption of nutrients |
| Simple Pseudostratified Epithelium | 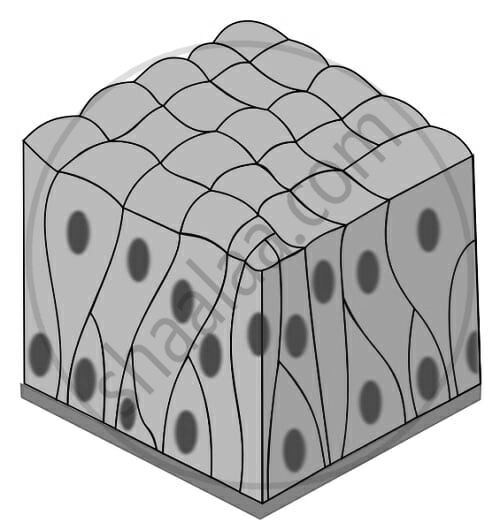 |
Lining of the trachea and upper respiratory tract. | It appears multilayered due to nuclei at different levels but is a single layer. Often has cilia and goblet cells. | Secretion and movement of mucus. |
| Ciliated Epithelium | 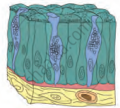 |
Inner surface of respiratory tract | The upper free surface of cells bears minute hair-like processes | Push mucus and air forward to keep the air passage free |
| Cuboidal Epithelium | 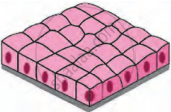 |
Tubules of kidney (nephron), salivary gland | Cells are cuboidal | Reabsorption of useful materials from urine, secretion of saliva |
| Germinal Epithelium | 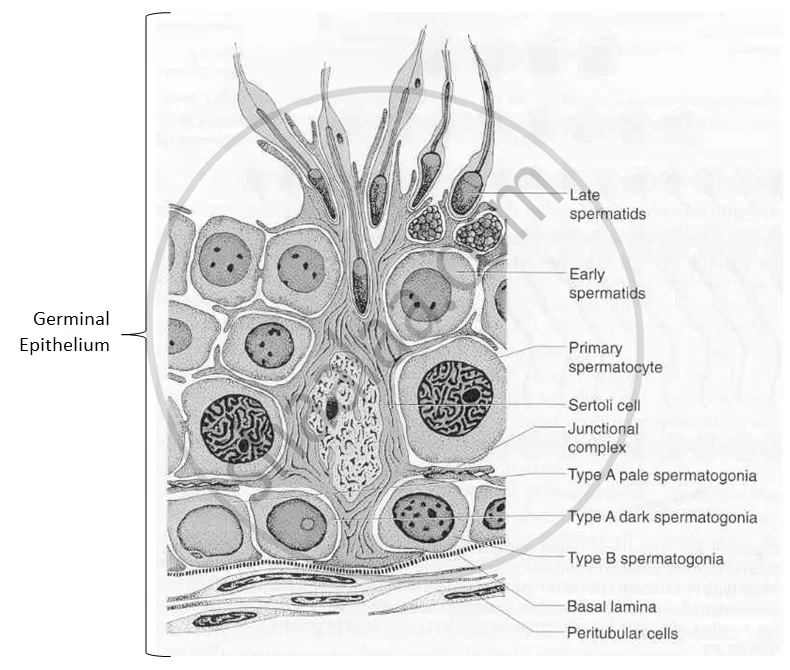 |
Testes (seminiferous tubules), ovaries (outer layer). | Covers reproductive organs; produces sperm/ova. | Production of gametes (sperm in males, ova in females). |
Compound Epithelial Tissue:
| Name | Appearance (Diagrammatic) | Location | Structure | Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stratified Epithelium | 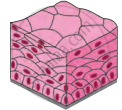 |
Outer layer of skin | Many layers of cells | Prevention of wearing of organs, protection of organs |
| Transitional Epithelium |  |
Ureters, urinary bladder, part of urethra. | Specialised stratified epithelium that can stretch and change shape. | Allows organs like the bladder to expand and contract. |
If you would like to contribute notes or other learning material, please submit them using the button below.
Video Tutorials
Shaalaa.com | Structural Organization Animals part 3 (Types Animal tissues: Epithelial)
to track your progress
