Topics
Basic Biology
Cell - the Structure and Fundamental Unit of Life [For Revision Only]
- Cell: Structural and Functional Unit of Life
- Organisms Show Variety in Cell Number, Shape and Size
- Plant Cell and Animal Cell
- Structure of the Cell
- Semi-permeable Membrane (Cell Membrane)
- Plasma Membrane
- Cell Wall - “Supporter and Protector”
- Nucleus - “Brain” of the Cell
- Cytoplasm - “Area of Movement”
- Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
- Mitochondria - “Power House of the Cell”
- Golgi Apparatus - "The delivery system of the cell"
- Ribosomes - "The sites of protein synthesis"
- Lysosome - “Suicidal Bag”
- Centrosome and Centrioles
- Plastids
- Non-living Substances Or Cell Inclusion
- Microscopic examination of onion peel
Cell Cycle, Cell Division and Structure of Chromosomes
- Chromosomes - The Carriers of Heredity
- Chromatin
- Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) and Its Structure
- Histone Proteins
- Genes and Genetic
- Need for New Cells
- Cell Cycle - "Divide, Grow and Redivide"
- Cell Division: an Essential Life Process
- Mitosis and Its Phases
- Phases of Mitosis: Karyokinesis (Division of Nucleus)
- Phases of Mitosis: Cytokinesis (Division of Cytoplasm)
- Significance of Mitosis
- Meiosis as a Reduction Division
- Stages of Meiosis: Meiosis I
- Stages of Meiosis: Meiosis II
- Significance of Meiosis
Genetics – Some Basic Fundamentals
- Genes and Genetic
- Gregor Johann Mendel – Father of Genetics
- Heredity or Inheritance
- Variation
- Chromosomes - The Carriers of Heredity
- Types of Chromosomes
- Sex Determination
- Sex Linked Inheritance
- Mendelian Inheritance - Mendel’s Law of Heredity
- Monohybrid Cross
- Gregor Johann Mendel – Father of Genetics
- Mendel's Experiments Inheritance
- Mutation
- Genes and their Alleles
- Genotype and Phenotype
- From parents to children - tongue rolling - An example of inheritance
Plant Physiology
Absorption by Roots: The Processes Involved
- Plant Anatomy and Plant Physiology
- Water absorbing organ
- Need of Water and Minerals for Plant
- Characteristics of Roots for Absorbing Water
- Semi-permeable Membrane (Cell Membrane)
- Means of Transport in Plants
- Concept of Imbibition
- Simple Diffusion
- Concept of Osmosis
- Osmotic Pressure
- Active Transport
- Turgidity and Flaccidity (Plasmolysis)
- Root Pressure
- Translocation of Water (Ascent of Sap)
Transpiration
- Transpiration
- Measurement of Transpiration
- Types of Transpiration
- Factors Affecting the Rate of Transpiration
- Adaptations in Plants to Reduce Excessive Transpiration
- Significance of Transpiration
- Direct Loss of Water by Plants - Guttation and Bleeding
Photosynthesis: Provider of Food for All
- Photosynthesis: Food-Making Process in Plants
- Significance of Photosynthesis
- Chlorophyll: The Vital Plant Pigment
- Regulation of Stomatal Opening for Letting in Carbon Dioxide
- Process of Photosynthesis
- Role of Sunlight in Photosynthesis
- Light Dependent Reaction (Hill Reaction \ Light Reaction)
- Photophosphorylation
- Light Independent Reactions (Dark Reaction \ Biosynthetic Phase)
- Adaptations in Leaf to Perform Photosynthesis
- End Result of the Products of Photosynthesis
- Factors Affecting Photosynthesis
- Experiments on Photosynthesis
- The Carbon Cycle
- Respiration and Photosynthesis
- Photosynthesis: Food-Making Process in Plants
Chemical Coordination in Plants
- Plant Hormones
- Types of Plant Hormones: Auxins
- Types of Plant Hormones: Gibberellins
- Types of Plant Hormones: Cytokinins
- Types of Plant Hormones: Ethylene
- Types of Plant Hormones: Abscisic Acid (ABA)
- Coordination in Plant: Tropism in Plants
Human Anatomy and Physiology
The Circulatory System
- Circulation in Animals
- Fluids in Our Body
- Blood
- Functions of Blood
- Composition of Blood: Plasma (The Liquid Portion of Blood)
- Composition of Blood: Red Blood Cells (Erythrocytes)
- Composition of Blood: White Blood Cells (Leukocytes)
- Composition of Blood: Blood Platelets (Thrombocytes)
- Function of Platelets - Clotting of Blood (Coagulation)
- Blood Transfusion and Blood Groups (ABO and Rh system)
- Blood Circulatory System in Human
- Human Heart
- Circulation of Blood in the Heart (Functioning of Heart)
- Working mechanism of human heart
- Heart Beat - Heart Sounds "LUBB" and "DUP"
- Pacemaker
- Blood Vessels
- Types of Closed Circulation
- Blood Pressure (B.P.)
- Tissue Fluid (Or Intercellular Fluid)
- Lymph and Lymphatic System
- The Spleen
The Excretory System (Elimination of Body Wastes)
Nervous System and Sense Organs
- Human Nervous System
- Neuron (Or Nerve Cell) and Its Types
- Nerve Fibres
- Transmission of Nerve Impulse
- Synapse - Properties of nerve fibres
- Major Division of the Nervous System
- The Human Brain - Forebrain
- Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
- The Spinal Cord
- Reflex and Reflex Action
- Types of Reflexes
- Nervous Pathways in Reflexes
- Reflex Arc
- Complex Reflex Action
- Sense Organ
- The Eyes
- Human Eye
- Working of the Human Eye
- Eye Defect and Its Correction: Myopia Or Near-sightedness
- Eye Defect and its Correction: Hypermetropia or Far-sightedness
- Eye Defect and Its Correction: Presbyopia
- Eye Defect and Its Correction: Astigmatism
- Some Common Defects of the Eye
- Stereoscopic (Binocular) Vision
- Functions of the Ear
- Human Ear
The Endocrine System
- Need for the Regulation of Body Activities
- Chemical Coordination
- Human Endocrine System
- Adrenal Gland (Suprarenal Gland)
- Pancreas (Islets of Langerhans)
- Thyroid Gland
- Pituitary Gland or Hypophysis Gland
- Control of Hormonal Secretions
- Difference in Endocrine and Exocrine Glands
Sense Organs
- Sense Organ
- The Eyes
- Human Eye
- Working of the Human Eye
- Eye Defect and Its Correction: Myopia Or Near-sightedness
- Eye Defect and its Correction: Hypermetropia or Far-sightedness
- Eye Defect and Its Correction: Presbyopia
- Eye Defect and Its Correction: Astigmatism
- Some Common Defects of the Eye
- Stereoscopic (Binocular) Vision
- Functions of the Ear
- Human Ear
The Reproductive System
- Reproduction
- Mode of Reproduction in Animal
- Asexual Reproduction in Animal
- Sexual Reproduction in Animals
- Human Reproduction
- The Male Reproductive System
- The Female Reproductive System
- Role of Hormones in Reproduction
- Menstrual Cycle (Ovarian Cycle)
- Fertilization in Human
- Implantation in Human
- Pregnancy in Humans
- Placenta (Growth) in Human
- Embryonic Development in Human
- Parturition (Birth) in Human
Population
- Population Explosion - Rising Population a Global Threat
- World Population Through the Ages
- Rapid Rise in Population
- A Highly Simplified Model of Population Growth
- Population
- Factors Responsible for Population Explosion in India
- Problems of Over Population
- Rising Population - Pressure on Natural Resources
- Population Growth
- Consequences of Urbanisation
- Terms Related to the Population
- Population Control
- Family Planning
Human Evolution
Pollution
- Waste and Its Categories
- Pollution and Its Types
- Air Pollution and Its Causes
- Prevention of Air Pollution
- Water Pollution and Its Causes
- Soil Pollution and its Causes
- Radiation
- Noise Pollution
- Measures to Limit Noise Pollution
- Acid Rain
- Causes of Acid Rain
- Green House Effect
- Global Warming
- Ozone
- Ozone Layer Depletion
- Effects of Air Pollution
- Effects of Water Pollution
- Effects of Soil Pollution
- Control of Pollution
Physical Health and Hygiene
Health Organisations
- International Bodies: WHO (World Health Organisation)
- Common Health Problems in India
Aids to Health
- Health
- First Aid and Emergency Action
- Antiseptics and Disinfectants
- Antibiotics
- Kidney tubule
- Structure of a Kidney tubule
- Blood supply to the kidney tubules
If you would like to contribute notes or other learning material, please submit them using the button below.
Shaalaa.com | Excretory system - Nephron
to track your progress
Related QuestionsVIEW ALL [34]
The figure given below represents a kidney tubule in humans and its blood supply. Study the figure and answer the questions that follow. Write specific name and numbers shown in the diagram for each answer.
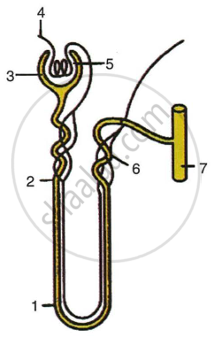 |
- Name the part which consists of a knot - like mass of blood capillaries.
- What is the specific name for the combination of parts shown as 5 and 3?
- Name the part which collects the glomerular filtrate.
- Where is the most water reabsorbed?
- Name the part which collects urine in the diagram shown.
- Which part lies in the medulla of the kidney?
- Which of the above parts is involved in the process of tubular secretion?
- How is hydrostatic pressure created?
- Where does ultrafiltration take place?
- Name two important constituents of urine.
Match the items in Column I with those in Column II and write down the matching pairs.
| Column I | Column II | ||
| (a) | Bowman's capsule | (i) | Renal artery |
| (b) | Contains more CO2 and less urea | (ii) | Regulates amount of water excreted |
| (c) | Antidiuretic hormone | (iii) | Renal vein |
| (d) | Contains more urea | (iv) | Glomerulus |
