Topics
Basic Biology
Cell - the Structure and Fundamental Unit of Life [For Revision Only]
- Cell: Structural and Functional Unit of Life
- Organisms Show Variety in Cell Number, Shape and Size
- Plant Cell and Animal Cell
- Structure of the Cell
- Semi-permeable Membrane (Cell Membrane)
- Plasma Membrane
- Cell Wall - “Supporter and Protector”
- Nucleus - “Brain” of the Cell
- Cytoplasm - “Area of Movement”
- Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
- Mitochondria - “Power House of the Cell”
- Golgi Apparatus - "The delivery system of the cell"
- Ribosomes - "The sites of protein synthesis"
- Lysosome - “Suicidal Bag”
- Centrosome and Centrioles
- Plastids
- Non-living Substances Or Cell Inclusion
- Microscopic examination of onion peel
Cell Cycle, Cell Division and Structure of Chromosomes
- Chromosomes - The Carriers of Heredity
- Chromatin
- Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) and Its Structure
- Histone Proteins
- Genes and Genetic
- Need for New Cells
- Cell Cycle - "Divide, Grow and Redivide"
- Cell Division: an Essential Life Process
- Mitosis and Its Phases
- Phases of Mitosis: Karyokinesis (Division of Nucleus)
- Phases of Mitosis: Cytokinesis (Division of Cytoplasm)
- Significance of Mitosis
- Meiosis as a Reduction Division
- Stages of Meiosis: Meiosis I
- Stages of Meiosis: Meiosis II
- Significance of Meiosis
Genetics – Some Basic Fundamentals
- Genes and Genetic
- Gregor Johann Mendel – Father of Genetics
- Heredity or Inheritance
- Variation
- Chromosomes - The Carriers of Heredity
- Types of Chromosomes
- Sex Determination
- Sex Linked Inheritance
- Mendelian Inheritance - Mendel’s Law of Heredity
- Monohybrid Cross
- Gregor Johann Mendel – Father of Genetics
- Mendel's Experiments Inheritance
- Mutation
- Genes and their Alleles
- Genotype and Phenotype
- From parents to children - tongue rolling - An example of inheritance
Plant Physiology
Absorption by Roots: The Processes Involved
- Plant Anatomy and Plant Physiology
- Water absorbing organ
- Need of Water and Minerals for Plant
- Characteristics of Roots for Absorbing Water
- Semi-permeable Membrane (Cell Membrane)
- Means of Transport in Plants
- Concept of Imbibition
- Simple Diffusion
- Concept of Osmosis
- Osmotic Pressure
- Active Transport
- Turgidity and Flaccidity (Plasmolysis)
- Root Pressure
- Translocation of Water (Ascent of Sap)
Transpiration
- Transpiration
- Measurement of Transpiration
- Types of Transpiration
- Factors Affecting the Rate of Transpiration
- Adaptations in Plants to Reduce Excessive Transpiration
- Significance of Transpiration
- Direct Loss of Water by Plants - Guttation and Bleeding
Photosynthesis: Provider of Food for All
- Photosynthesis: Food-Making Process in Plants
- Significance of Photosynthesis
- Chlorophyll: The Vital Plant Pigment
- Regulation of Stomatal Opening for Letting in Carbon Dioxide
- Process of Photosynthesis
- Role of Sunlight in Photosynthesis
- Light Dependent Reaction (Hill Reaction \ Light Reaction)
- Photophosphorylation
- Light Independent Reactions (Dark Reaction \ Biosynthetic Phase)
- Adaptations in Leaf to Perform Photosynthesis
- End Result of the Products of Photosynthesis
- Factors Affecting Photosynthesis
- Experiments on Photosynthesis
- The Carbon Cycle
- Respiration and Photosynthesis
- Photosynthesis: Food-Making Process in Plants
Chemical Coordination in Plants
- Plant Hormones
- Types of Plant Hormones: Auxins
- Types of Plant Hormones: Gibberellins
- Types of Plant Hormones: Cytokinins
- Types of Plant Hormones: Ethylene
- Types of Plant Hormones: Abscisic Acid (ABA)
- Coordination in Plant: Tropism in Plants
Human Anatomy and Physiology
The Circulatory System
- Circulation in Animals
- Fluids in Our Body
- Blood
- Functions of Blood
- Composition of Blood: Plasma (The Liquid Portion of Blood)
- Composition of Blood: Red Blood Cells (Erythrocytes)
- Composition of Blood: White Blood Cells (Leukocytes)
- Composition of Blood: Blood Platelets (Thrombocytes)
- Function of Platelets - Clotting of Blood (Coagulation)
- Blood Transfusion and Blood Groups (ABO and Rh system)
- Blood Circulatory System in Human
- Human Heart
- Circulation of Blood in the Heart (Functioning of Heart)
- Working mechanism of human heart
- Heart Beat - Heart Sounds "LUBB" and "DUP"
- Pacemaker
- Blood Vessels
- Types of Closed Circulation
- Blood Pressure (B.P.)
- Tissue Fluid (Or Intercellular Fluid)
- Lymph and Lymphatic System
- The Spleen
The Excretory System (Elimination of Body Wastes)
Nervous System and Sense Organs
- Human Nervous System
- Neuron (Or Nerve Cell) and Its Types
- Nerve Fibres
- Transmission of Nerve Impulse
- Synapse - Properties of nerve fibres
- Major Division of the Nervous System
- The Human Brain - Forebrain
- Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
- The Spinal Cord
- Reflex and Reflex Action
- Types of Reflexes
- Nervous Pathways in Reflexes
- Reflex Arc
- Complex Reflex Action
- Sense Organ
- The Eyes
- Human Eye
- Working of the Human Eye
- Eye Defect and Its Correction: Myopia Or Near-sightedness
- Eye Defect and its Correction: Hypermetropia or Far-sightedness
- Eye Defect and Its Correction: Presbyopia
- Eye Defect and Its Correction: Astigmatism
- Some Common Defects of the Eye
- Stereoscopic (Binocular) Vision
- Functions of the Ear
- Human Ear
The Endocrine System
- Need for the Regulation of Body Activities
- Chemical Coordination
- Human Endocrine System
- Adrenal Gland (Suprarenal Gland)
- Pancreas (Islets of Langerhans)
- Thyroid Gland
- Pituitary Gland or Hypophysis Gland
- Control of Hormonal Secretions
- Difference in Endocrine and Exocrine Glands
Sense Organs
- Sense Organ
- The Eyes
- Human Eye
- Working of the Human Eye
- Eye Defect and Its Correction: Myopia Or Near-sightedness
- Eye Defect and its Correction: Hypermetropia or Far-sightedness
- Eye Defect and Its Correction: Presbyopia
- Eye Defect and Its Correction: Astigmatism
- Some Common Defects of the Eye
- Stereoscopic (Binocular) Vision
- Functions of the Ear
- Human Ear
The Reproductive System
- Reproduction
- Mode of Reproduction in Animal
- Asexual Reproduction in Animal
- Sexual Reproduction in Animals
- Human Reproduction
- The Male Reproductive System
- The Female Reproductive System
- Role of Hormones in Reproduction
- Menstrual Cycle (Ovarian Cycle)
- Fertilization in Human
- Implantation in Human
- Pregnancy in Humans
- Placenta (Growth) in Human
- Embryonic Development in Human
- Parturition (Birth) in Human
Population
- Population Explosion - Rising Population a Global Threat
- World Population Through the Ages
- Rapid Rise in Population
- A Highly Simplified Model of Population Growth
- Population
- Factors Responsible for Population Explosion in India
- Problems of Over Population
- Rising Population - Pressure on Natural Resources
- Population Growth
- Consequences of Urbanisation
- Terms Related to the Population
- Population Control
- Family Planning
Human Evolution
Pollution
- Waste and Its Categories
- Pollution and Its Types
- Air Pollution and Its Causes
- Prevention of Air Pollution
- Water Pollution and Its Causes
- Soil Pollution and its Causes
- Radiation
- Noise Pollution
- Measures to Limit Noise Pollution
- Acid Rain
- Causes of Acid Rain
- Green House Effect
- Global Warming
- Ozone
- Ozone Layer Depletion
- Effects of Air Pollution
- Effects of Water Pollution
- Effects of Soil Pollution
- Control of Pollution
Physical Health and Hygiene
Health Organisations
- International Bodies: WHO (World Health Organisation)
- Common Health Problems in India
Aids to Health
- Health
- First Aid and Emergency Action
- Antiseptics and Disinfectants
- Antibiotics
- Cell Inclusion
- Granule
- Vacuole
- Functions of Vacuole
Cell Inclusion:
The inclusion bodies are tiny particles freely suspended and floating within the cytoplasmic matrix. Therefore, they are also referred to as cytoplasmic inclusions. These cell inclusions are formed with decreasing pH and from the pool of soluble fusion proteins within the cell. They are the elementary bodies formed during infectious diseases or within the virus-infected cells, such as rabies, herpes, measles, etc.
- Inclusion bodies are abnormal structures of distinct size and shape, usually observed in nerve, epithelial, or endothelial cells.
- They have a characteristic staining property and are typically composed of proteins.
- Inclusion bodies are nonliving chemical compounds and by-products of cellular metabolism. They are found in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
- There are a wide variety of inclusion bodies in different types of cells. In prokaryotic cells, they are mainly formed to store reserve materials.
- In animal cells, they store fats and sugars ready for cellular respiration; in plant cells, they store granules of materials like glycogen, starch, etc.
- Examples of inclusion particles include gas vacuoles, cyanophycean granules, phosphate granules, and glycogen granules.
Granule:
Granules are tiny particles found in the cytoplasm of both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Granules act as storage units for energy-rich compounds. They store important materials that the cell needs for energy production and other functions. In some cases, granules store waste materials. There are different types of granules:
- Glycogen Granules: Found in animal and bacterial cells. Store glycogen, a form of sugar used for energy during cellular respiration.
- Starch Granules: Found in plant cells. Store starch, which is broken down into glucose, to provide energy for the plant.
- Phosphate Granules: Found in bacteria and other cells. Store phosphate to help the cell make DNA, RNA, and ATP (an energy molecule).
- Cyanophycean Granules: It is found in blue-green algae (cyanobacteria). Store proteins and nutrients needed for the organism’s growth.
Vacuole:
Vacuoles are storage sacs for solid or liquid contents. The central vacuole of some plant cells may occupy 50–90% of the cell volume. Found mainly in eukaryotic cells (both animal and plant cells). Vacuoles are full of cell sap and provide turgidity and rigidity to the plant cell. A vacuole is bound by a single membrane.
- Amino acids, sugars, various organic acids, and some proteins are stored in them.
- They are also present in unicellular organisms. E.g., food vacuoles in amoeba.
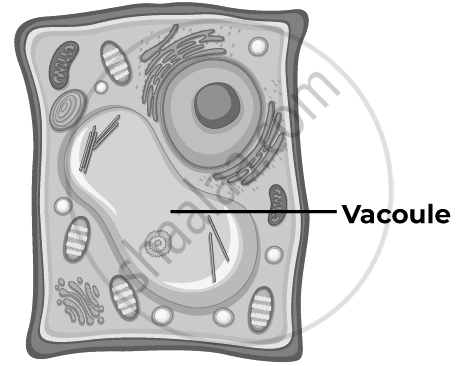
Functions of Vacuole:
- Vacuoles maintain the osmotic pressure of the cell.
- They store metabolic byproducts and end products like glycogen, proteins, and water.
- In animal cells, they store waste products and food.
- In amoebae, vacuoles store food before digestion.
- In plant cells, vacuoles are filled with cell sap, which provides turgidity and rigidity.
