Topics
Heredity and Evolution
- Heredity or Inheritance
- Protein Synthesis
- Transcription, Translation and Translocation
- Protein Synthesis
- Protein Synthesis
- Organic Evolution
- Theories of Origin of Life
- Evolution and Classiffication
- Evidences for Biological Evolution
- Darwinism
- Lamarck’s Theory of Evolution
- Speciation
- Human Evolution
Life Processes in Living Organisms Part -1
- Living Organisms and Life Processes
- Living Organism and Energy Production
- Formation of ATP
- Energy Production in Living Organism
- Cell Division: an Essential Life Process
- Mitosis and Its Phases
- Phases of Mitosis: Karyokinesis (Division of Nucleus)
- Phases of Mitosis: Cytokinesis (Division of Cytoplasm)
- Significance of Mitosis
- Meiosis as a Reduction Division
- Stages of Meiosis: Meiosis I
- Stages of Meiosis: Meiosis II
- Significance of Meiosis
- Differences Between Mitosis and Meiosis
Life Processes in Living Organisms Part - 2
- Introduction to Life Processes in Living Organisms
- Asexual Reproduction in Animal
- Fission
- Fragmentation
- Regeneration
- Budding
- Sporulation (Sporogenesis)
- Asexual Reproduction in Plant
- Budding
- Vegetative Reproduction
- Reproduction
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
- Sexual Reproduction in Animals
- Human Reproduction
- The Male Reproductive System
- The Female Reproductive System
- Gametogenesis
- Fertilization in Human
- Embryonic Development in Human
- Implantation in Human
- Pregnancy in Humans
- Placenta (Growth) in Human
- Parturition (Birth) in Human
- Menstrual Cycle (Ovarian Cycle)
- Reproduction and Modern Technology
- Reproductive Health
Environmental Management
- Our needs and the Environment
- Ecosystem
- Structure and function of an Ecosystem
- Relationship Between Environment and Ecosystem
- Environmental Balance
- Environmental Conservation
- Environmental Conservation and Biodiversity
- Endangered Species
Towards Green Energy
- Energy and Use of Energy
- Generation of Electrical Energy
- Heat Energy (Thermal Energy)
- Nuclear Energy
- Natural Gas Energy
- Electric Energy Generation and Environment
- Hydroelectric Energy
- Wind Energy
- Solar Energy
- Solar Energy
Animal Classification
- Biological Classification
- Classification of Living Organisms
- Taxonomic Hierarchy of Living Organisms: Unit of Classification
- New Criteria for Basis of Classification
- History of Animal Classification
- Traditional Method of Animal Classification
- Five Kingdom Classification
- Phylum: Porifera
- Phylum: Cnidaria/Coelenterata
- Phylum: Platyhelminthes
- Phylum: Aschelminthes
- Phylum: Annelida
- Phylum: Arthropoda
- Phylum: Mollusca
- Phylum: Echinodermata
- Phylum: Hemichordata
- Phylum: Chordata
- Kingdom Animalia
- Chordata: Vertebrata
Introduction to Microbiology
- Microorganisms (Microbes) and Microbiology
- Applied Microbiology
- Industrial Microbiology
- Useful micro-organisms
Cell Biology and Biotechnology
- Cell Biology (Cytology)
- Stem Cells
- Organ Transplantation
- Organ and Body Donation
- Biotechnology
- Commercial Applications of Biotechnology
- Modern Agricultural Practices and Crop Improvement
- Important Stages in Agricultural Development
Social Health
- Social Health
- Factors Disturbing the Social Health
- Communication Media and Excessive Use of Modern Technology
- Stress Management
Disaster Management
- Disaster
- Effects of Disaster
- Nature and Scope of Disaster
- Disaster Management
- Classification of Disaster Management
- Disaster Management Cycle
- Structure of Disaster Management Authority
- First Aid and Emergency Action
- Mock Drill
Life's Internal Secrets
The Regulators of Life
- Coordination in Plants - Introduction
- Control and Co-ordination in Plants
- Human Nervous System
- Central Nervous System (CNS)
- Chemical Control
The Life Cycle
Mapping Our Genes
Striving for Better Environment 2
- Use of Efficient and Eco-friendly Technology
- Sustainable Use of Resources
- Enforcement of Acts, Laws and Policies
Understanding Metals and Non-Metals
Amazing World of Carbon Compounds
- First Aid
- Basic Principles of First Aid
- Simple Steps for Providing First Aid in Different Situations
First Aid:
First aid is the immediate help given to someone who is injured or ill before professional medical help arrives. The main objective of first aid is the prevention of death, the prevention of deterioration of health, and the starting of the process of rehabilitation. Hence, it is important to know about the emergency measures or first aid practices to be followed.
Basic Principles of First Aid
Life and Resuscitation: ABC
1. Airway
If the victim has difficulty breathing, ensure their airway is clear. Gently tilt the head backward and lift the chin upward to open the respiratory passage. This position prevents the tongue from blocking the airway, allowing smooth airflow.
2. Breathing
If the victim has stopped breathing, provide mouth-to-mouth resuscitation. Pinch the victim's nose shut, take a deep breath, and seal your mouth over the victim's mouth. Blow air into the lungs until the chest rises, then allow the chest to fall naturally. Repeat this process every 4–5 seconds until normal breathing resumes or professional help arrives.
3. Circulation
If the victim is unconscious and has no pulse, perform cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR). Start by giving two mouth-to-mouth breaths. Place both palms one over the other in the centre of the chest (just above the sternum). Press down firmly and quickly, compressing the chest about 2 inches deep. Repeat chest compressions about 15 times at a steady rhythm (around 100-120 compressions per minute). Alternate between 2 breaths and 15 chest compressions until help arrives or the person shows signs of recovery.
Simple Steps for Providing First Aid in Different Situations:
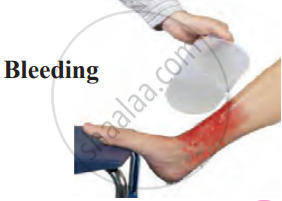
1. External Bleeding: If a person is bleeding, the first step is to help them sit or lie down comfortably. Keep the bleeding part of the body elevated (above the heart level) to reduce blood flow. Clean the wound with clean water and apply pressure with a clean cloth to stop the bleeding.
2. Burns and Scalds
Minor Burns:
- Wash the burn with cool water or hold it under running water to reduce the heat.
- Give the person water to drink to keep them hydrated.
- Clean the burn with a cotton swab soaked in an antiseptic solution.
- Do not apply oily ointments like ghee or butter to the burn. Cover the burn with a clean, dry cloth or dressing.
Serious Burns:
- Give the person emotional support to keep them calm. Cover the burn with a sterilised cloth or clean fabric.
- Remove jewellery or shoes if it can be done easily without hurting the burn.
- Do not burst blisters or touch the burnt skin. Do not apply oily ointments or try to remove any cloth stuck to the burn.
- If the person is conscious, give them water to drink, but avoid tea or coffee.
- Get medical help immediately.

Immediate steps for burns
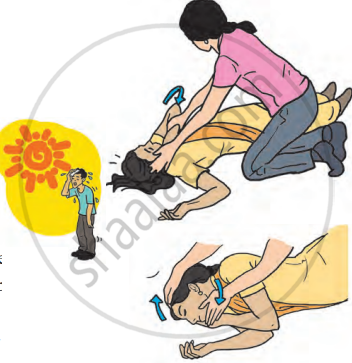
3. Sunstroke: Sunstroke occurs when someone has been in the sun for too long and their body loses water and minerals.
Remedial Measures:
- Take the person to a cool place or the shade.
- Sponge their body with cold water to cool them down.
- Put a cold cloth on their neck to reduce their body temperature.
- Give them plenty of water or liquids like sherbet to drink.
- If the person feels like vomiting, make them lie on their stomach with their head turned to one side.
- Get medical help or take the person to a hospital.
First aid for sunstroke
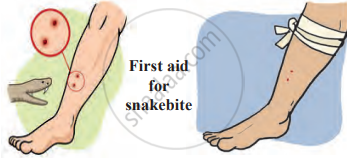
4. Snakebite: There are about 2000 species of snakes, but only a few, like cobras, kraits, vipers, and sea snakes, are poisonous. Not all snakebites are deadly, but the fear of the bite can cause a lot of stress.
Remedial Measures:
- Wash the wound with clean water.
- Give the person emotional support to calm them down.
- Tie a cloth tightly above the bite to slow the spread of venom.
- Get immediate medical help for treatment.
5. Dog Bite: A dog bite can cause infection, so it’s important to give first aid and seek medical help.
Remedial Measures:
- Wash the wound with an antiseptic solution like potassium permanganate.
- Cover the wound with a clean, dry cloth.
- Get medical help immediately and make sure the person receives an anti-rabies vaccine to prevent infection.