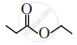
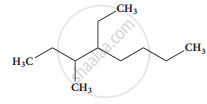
IUPAC provides a standardised naming system for organic and inorganic compounds to ensure global consistency and avoid confusion.
Key Components:
- Substituents: Functional groups attached to the main carbon chain.
- Parent Chain: The longest continuous carbon chain in the molecule.
- Chemical Ending: Represents the functional group type (e.g., -ol for alcohol, -al for aldehyde).
Methods for Modifying the Root Name:
- Substitutive: The highest-priority functional group modifies the suffix, while other groups act as prefixes.
- Functional Group-Based: Named according to the most significant functional group (e.g., ketones, alcohols).
- Replacement: When a carbon atom is replaced by another atom.
- Conjunctive: Combines different named subunits.
- Trivial Naming: Some widely used compounds retain their common (trivial) names under IUPAC rules.