Topics
Chemical Substances - Nature and Behaviour (Chemistry)
Chemical Reactions and Equations
- Chemical Equation
- Balancing Chemical Equation
- Types of Chemical Change or Chemical Reaction
- Direct Combination (or Synthesis) Reaction
- Decomposition Reactions
- Single Displacement Reactions
- Double Displacement Reaction
- Oxidation, Reduction and Redox Reactions
- Corrosion of Metals
- Rancidity of Food and Its Prevention
World of Living (Biology)
Acids, Bases and Salts
- Acids
- Bases (Alkalis)
- Indicators
- Properties of Acids
- Properties of Bases (Alkalis)
- Acid or a Base in a Water Solution
- Similarities and Differences Between Acids and Bases
- Strength of Acidic or Basic Solutions
- Salts
- Important Salts in Daily Life
- Preparation and Uses of Sodium Hydroxide
- Preparation and Uses of Bleaching Powder
- Preparation and Uses of Baking Soda
- Preparation and Uses of Washing Soda
- Preparation and Uses of Plaster of Paris
Metals and Non Metals
- Types of Element: Metals
- Physical Properties of Metals
- Chemical Properties of Metal
- Types of Element: Non-metal
- Physical Properties of Non-metal
- Chemical Properties of Non-metal
- Ionic or Electrovalent Bond
- Reactivity Series of Metals
- Extraction of Reactive Metals
- Refining of Metals
- Corrosion of Metals
- The Covalent Bond
- Prevention of Corrosion
Natural Phenomena (Physics)
Carbon and its Compounds
- Carbon: a Versatile Element
- The Covalent Bond
- Saturated and Unsaturated Carbon Compounds
- Allotropy and Allotropes of Carbon
- Crystalline Allotropes of Carbon: Diamond
- Crystalline Allotropes of Carbon: Graphite
- Crystalline Allotropes of Carbon: Fullerene
- Chains, Branches and Rings of Carbon Compound
- Functional Groups in Carbon Compounds
- Homologous Series of Carbon Compound
- Nomenclature of Organic Compounds
- Properties of Carbon
- Ethanol
- Ethanoic Acid
- Soap
- Detergents
- Cleansing Action of Soap
Effects of Current (Physics)
Life Processes
- Living Organisms and Life Processes
- Nutrients and Nutrition
- Mode of Nutrition in Plant
- Autotrophic Plants
- Heterotrophic Plants
- Different Ways of Taking Food
- Human Digestive System
- The Mouth and Buccal Cavity
- The Teeth and Its Structure
- The Salivary Glands
- Swallowing and Peristalsis
- The Food Pipe/Oesophagus
- The Stomach
- The Small Intestine
- Pancreas
- Absorption of Food
- The Large Intestine
- Assimilation of Food
- Liver
- Respiration
- Respiration
- Breathing in Other Animals
- Osmoregulation
- Types of Respiration: Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration
- Human Respiratory System
- Circulation in Animals
- Blood
- Composition of Blood: Plasma (The Liquid Portion of Blood)
- Composition of Blood: Red Blood Cells (Erythrocytes)
- Composition of Blood: White Blood Cells (Leukocytes)
- Composition of Blood: Blood Platelets (Thrombocytes)
- Blood Circulatory System in Human
- Human Heart
- Blood Vessels
- Circulation of Blood in the Heart (Functioning of Heart)
- Types of Closed Circulation
- Heart Beat - Heart Sounds "LUBB" and "DUP"
- Function of Platelets - Clotting of Blood (Coagulation)
- Lymph and Lymphatic System
- Blood Pressure (B.P.)
- Transport System in Plants
- Water absorbing organ
- Translocation of Water (Ascent of Sap)
- Transport of Mineral Ions
- Transport of Food
- Transpiration
- Excretion
- Human Excretory System
- Function of the Kidney - “Production of Urine”
- Excretion
Natural Resources
Periodic Classification of Elements
- History of Periodic Table: Early Attempts at the Classification of Elements
- Dobereiner’s Triads
- Newland's Law of Octaves
- Mendeleev’s Periodic Table
- Merits and Demerits of Mendeleev’s Periodic Table
- The Modern Periodic Table
- Periodic Properties
- Valency
- Atomic Radius Or Atomic Size
- Metallic and Non-metallic Characters
Control and Co-ordination
- Control and Co-ordination in Human Being
- Human Nervous System
- Neuron (Or Nerve Cell) and Its Types
- Neuron (Or Nerve Cell) and Its Types
- Nerve Fibres
- Major Division of the Nervous System
- Central Nervous System (CNS)
- Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
- The Human Brain - Forebrain
- The Human Brain - Forebrain
- Reflex and Reflex Action
- Nervous Pathways in Reflexes
- Reflex Arc
- Coordination in Plant: Tropism in Plants
- Chemical Coordination
- Plant Hormones
- Types of Plant Hormones: Auxins
- Types of Plant Hormones: Gibberellins
- Types of Plant Hormones: Ethylene
- Types of Plant Hormones: Cytokinins
- Types of Plant Hormones: Abscisic Acid (ABA)
- Types of Plant Hormones: Ethylene
- Hormones in Animals
- Human Endocrine System
- Pituitary Gland or Hypophysis Gland
- Thyroid Gland
- Parathyroid Gland
- Pancreas (Islets of Langerhans)
- Adrenal Gland (Suprarenal Gland)
- Reproductive Glands (Gonads)
- Thymus Gland
Internal assessment
How do Organisms Reproduce?
- Accumulation of Variation During Reproduction
- Reproduction
- Mode of Reproduction in Plant
- Asexual Reproduction in Plant
- Natural Vegetative Reproduction
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
- Sexual Reproduction in Animals
- Human Reproduction
- The Male Reproductive System
- The Female Reproductive System
- Menstrual Cycle (Ovarian Cycle)
- Reproductive Health
- Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STD)
Heredity
- Accumulation of Variation During Reproduction
- Heredity or Inheritance
- Gregor Johann Mendel – Father of Genetics
- Monohybrid Cross
- Gregor Johann Mendel – Father of Genetics
- Mendelian Inheritance - Mendel’s Law of Heredity
- Sex Determination
- Organic Evolution
- Lamarck’s Theory of Evolution
- Darwinism
- Theories of Origin of Life
- Speciation
- Evolution and Classiffication
- Evidences for Biological Evolution
- Paleobotany
- Evolution by Stages
- Human Evolution
Light - Reflection and Refraction
- Reflection of Light
- Law of Reflection of Light
- Mirrors
- Plane Mirror
- Spherical Mirrors
- Rules for the Construction of Image Formed by a Spherical Mirror
- Images Formed by Spherical Mirrors
- Concave Mirror
- Image Formation by Concave Mirror
- Convex Mirror
- Image Formation by Convex Mirror
- Sign Convention
- Mirror Equation/Formula
- Linear Magnification (M) Due to Spherical Mirrors
- Introduction to Refraction of Light
- Refraction of Light Through a Rectangular Glass Slab
- Refractive Index
- Spherical Lens
- Images Formed by Sperical Lenses
- Guideline for Image Formation Due to Refraction Through a Convex and Concave Lens
- Concave Lens
- Images Formed by Concave Lenses
- Convex Lens
- Images Formed by Convex Lenses
- Sign Convention
- Lens Formula
- Magnification Due to Spherical Lenses
- Power of a Lens
The Human Eye and the Colourful World
- Human Eye
- Working of the Human Eye
- Eye Defect and Its Correction: Myopia Or Near-sightedness
- Eye Defect and its Correction: Hypermetropia or Far-sightedness
- Eye Defect and Its Correction: Presbyopia
- Care of the Eyes
- Refraction of Light Through a Prism
- Prism
- Dispersion of Light Through Prism and Formation of Spectrum
- Atmospheric Refraction
- Application of Atmospheric Refraction
- Scattering of Light and Its Types
- Applications of Scattering of Light
Electricity
- Electricity
- Electric Current
- Electric Circuit
- Potential and Potential Difference
- Symbols and Functions of Various Components of an Electric Circuits
- Ohm's Law (V = IR)
- Factors Affecting the Resistance of a Conductor
- Electrical Resistivity and Electrical Conductivity
- Resistors in Series
- Resistors in Parallel
- Effects of Electric Current
- Heating Effect of Electric Current
- Electrical Power
Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
- Magnetic Effect of Electric Current
- Magnetic Field
- Properties of magnetic lines of force
- Magnetic Field Due to a Current Carrying Straight Conductor
- Right-hand Thumb Rule
- Magnetic Field Due to Current in a Loop (Or Circular Coil)
- Magnetic Field Due to a Current Carving Cylindrical Coil (or Solenoid)
- Force on a Current Carrying Conductor in a Magnetic Field
- Electric Motor
- Electromagnetic Induction
- Faraday's Laws of Electromagnetic Induction
- Electric Generator
- Alternating Current (A.C.) Generator
- Direct Current Motor
- Household Electrical Circuits
- Distinction Between an A.C. Generator and D.C. Motor
- Types of Current
Our Environment
Sources of Energy
- Source of Energy
- Conventional energy resources or non-renewable energy resources
- Fossil Fuels
- Heat Energy (Thermal Energy)
- Hydroelectric Energy
- Bio-energy
- Wind Energy
- Solar Energy
- Solar Energy Devices
- Energy from the Sea
- Geothermal Energy
- Nuclear Energy
- Nuclear Fission
- Forms of Energy
- Environmental Consequences
- How Long Will an Energy Source Last Us?
Sustainable Management of Natural Resources
- Sustainability of Natural Resources
- Case Study: Ganga Pollution and Ganga Action Plan
- Solid Waste Management
- Five R’s of Waste Management
- Protecting our environment
- Forests: Our Lifeline
- Stakeholders of Forest
- Conservation of Forest
- Conservation of Wildlife
- Water Management (Conservation of Water)
- Fresh Water Management
- Non-crystalline/Amorphous Forms: Coal
- Petroleum
- Conservation of Coal, Petroleum, and Natural Resources
- Overview of Natural Resource Management
- Introduction
- Experiment
Introduction:
A decomposition reaction is a chemical process in which a single compound breaks down into two or more simpler substances. This reaction is the opposite of a combination reaction and often requires an external energy source such as heat, light, or electricity.
For example, in the electrolysis of water, water (H₂O) decomposes into hydrogen (H₂) and oxygen (O₂) when an electric current is passed through it. This can be represented by the following chemical equation:
\[2H_2O\xrightarrow{\text{electricity}}2H_2+O_2\]
Experiment
1. Aim: To observe and understand decomposition reactions, where a single reactant breaks down into two or more simpler substances.
2. Requirements
- Apparatus: evaporating dish, test tubes, bent tube, rubber cork, Bunsen burner.
- Chemicals: sugar, calcium carbonate (CaCO₃), sulphuric acid, freshly prepared lime water.
4. Procedure
Experiment 1: Decomposition of Sugar
- Take some sugar in an evaporating dish.
- Heat it using a Bunsen burner and observe the changes.
- A black residue (carbon) forms, and water (H₂O) vapour is released.
\[\mathrm{C}_{12}\mathrm{H}_{22}\mathrm{O}_{11}\xrightarrow{\mathrm{Heat}}12C+11H_2O\]
Experiment 2: Decomposition of Calcium Carbonate
- Take some calcium carbonate (CaCO₃) in a test tube.
- Fit a bent tube into the test tube using a rubber cork.
- Insert the other end of the bent tube into another test tube containing freshly prepared lime water.
- Heat the calcium carbonate strongly. The lime water turns milky, indicating the presence of carbon dioxide (CO₂) gas.
\[\mathrm{CaCO}_3(s)\xrightarrow{\Delta}\mathrm{CaO}(s)+\mathrm{CO}_2\uparrow\]
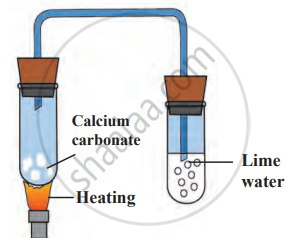
Decomposition of calcium carbonate
Experiment 3: Electrolysis of Water
- Pass electric current through acidulated water.
- Observe the formation of hydrogen (H₂) and oxygen (O₂) gases.
\[2H_2O(l)\xrightarrow{\text{Electrical Energy}}2H_2\uparrow+O_2\uparrow\]
5. Conclusion: A decomposition reaction occurs when a single reactant breaks down into two or more simpler substances. These reactions can be thermal (heat-driven), electrolytic (electricity-driven), or biological (natural degradation by microorganisms). Decomposition reactions are crucial in nature, industry, and energy production, such as in the formation of biogas from organic waste.
