Topics
Historiography : Development in the West
History : Applied History
Working of the Constitution
Historiography : Indian Tradition
The Electoral Process
Political Science : Working of the Indian Constitution
Applied History
Political Parties
History of Indian Arts
- What is ‘Art’?
- Indian Traditions of Visual Arts (Drik Kala): Painting
- Prehistoric Paintings
- Mural Paintings and Cave Painting
- Folk Styles of Paintings
- Classical Styles of Painting
- Miniature Paintings in Manuscripts
- Modern Indian Paintings
- Indian Traditions of Visual Arts (Drik Kala): Sculpture Art
- Indus Civilization Sculpture
- Folk Styles of Sculptural Art
- Classical Styles of Sculptural Art
- Indian Iconography
- Indian Traditions of Visual Arts (Drik Kala): Architecture and Sculpture
- Rock-cut Architecture
- Temple Architecture
- Indo-Islamic Architecture
- Indo-Gothic architecture
- Indian Traditions of Performing Arts
- Indian Theatre
- Indian Music
- Indian Dance
- Present Scenario of the Performing Arts
- Art, Applied Art, and Professional Opportunities
Social and Political Movements
- Movement
- Important Movements in India
- Tribal Movement
- Farmers Movement
- Worker's Movements
- Women’s Movement
- Environment Movements
- Consumer Movement
Mass Media and History
Challenges Faced by Indian Democracy
Entertainment and History
Sports and History
Tourism and History
Heritage Management
History - Imperialism
History - 20th Century Age of conflict
History - Emancipation of Asia and Africa
History - World after World War 2
Political Science
Geographical discoveries and colonization
- Concept for Geographical Discoveries and Colonization
Africa
- Imperialism - Africa
Asia: India, China, Japan
- Concept for Asia: India, China, Japan
Dictatorships in Europe, Second World War and world
- Concept on Dictatorships in Europe
- Concept for Second World War and World
First world war
- Concept on First World War
The League of Nations
- Concept for the League of Nations
Russian Revolution
- Concept for Russian Revolution
United Nations Organization
- Concept for United Nations Organization
Africa
- Emancipation of Africa
Asia
- Emancipation of Asia
Globalization
- Globalization After World War II
Scientific and Technological Progress
- Scientific and Technological Progress After World War II
Cold war
- Formation of the Cold War
Social Diversity and Democracy
- Social Diversity
- Coccept for Caste/Race and Democracy
- Concept for Language and Democracy
- Cocnept for Religion and Democracy
- Concept for Gender and Democracy
- Concept for Democracy and Diversity
Challenges to Democracy Remedial Measures to the Challenges
- Concept for Challenges to Democracy Remedial Measures to the Challenges
Internal work
Democracy
- Democracy - Meaning, Types and Characteristics
Political Parties and Types
- Political Parties
- Importance of Political Parties
- Major National and Regional Parties in India/ Types of Political Parties
Notes
Historiography in the Medieval Period:
Medieval India refers to a long period of Post-Classical history of the Indian subcontinent between the "ancient period" and "modern period". It is usually regarded as running approximately from the breakup of the Gupta Empire in the 6th century CE and the start of the Early modern period in 1526 with the start of the Mughal Empire, although some historians regard it as both starting and finishing later than these points. The medieval period is itself subdivided into the Early Medieval and Late Medieval eras.
Sources of Medieval Indian History:
- The writing style of Kalhana's history of Kashmir, ‘Rajtarangini’, from the 12th century C.E., is strikingly similar to that of contemporary historiography. According to Kalhana, he penned this book after carefully researching a variety of sources, including inscriptions, coins, the remnants of ancient structures, dynastic documents, and regional customs.

Kalhana's Rajtarangini
- Arabic and Persian historiography had an impact on the court historians of Muslim kings in medieval India. Ziauddin Barani occupies a significant position among them. In a book he wrote titled ‘Tarikh-i-Phiruz Shahi,’ he outlined the goal of history. He contends that the historian's obligation extends beyond simply documenting the heroism and welfare policies of the ruler and requires him to also write about the monarch's flaws and bad decisions.

Tarikh-i-Phiruz Shahi
- The Mughal empire's founder Babur authored an autobiography titled ‘Tuzuk-i-Babari.’ It includes accounts of the conflicts he was involved in. Babur also kept a detailed journal of his observations of the plants and trees, culture, and economy of the different places and cities he visited.

Tuzuk-i-Babari
- The ‘Akbarnama’ by Abul Fazl is crucial from the perspective of critical historiography. His approach to gathering real historical materials and studying them is seen as objective and so realistic.

Akbarnama
-
Alberuni discussed Indian culture and society in his Arabic writings. Many works about India were written by foreign academics in the years that followed.
The experiences of international visitors to India are very crucial. Ibn Battuta, Abdul Razzaq, Marco Polo, Nicolo Conti, Barbosa, and Domingos Paes are a few of them. Their writings give us historical details about medieval India. Among the Aurangzeb era historians whose writings are significant sources of Mughal history are Ishwardas Nagar, Bhimsen Saxena, Khafi Khan, and Niccolo Manucci.Author Book Hasan Nizami Tajul-Ma’asir Minhaj-i-Siraj Tabaqat-i-Nasiri Amir Khusrau Tuzuk-i-Timuri, The autobiography of Timur (-i) Lang, who was also known as Amir Timur who invaded India Yahya Bin Ahmad Sirhindi
Tarikh-i- Mubarakshahi - Bakhar:
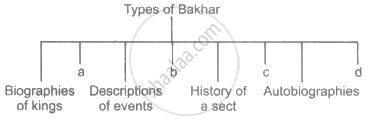
- A significant category of historical writing from the Middle Ages is called ‘Bakhar.’ It includes tributes to the heroes as well as accounts of historical occasions, conflicts, and the lives of famous persons.
- Bakhars can be categorized into a variety of types, including king biographies, dynasty histories, event summaries, sect histories, autobiographies, about grievances, based on mythology, and state management by a monarch.
- There are several kinds of Marathi bakhars. During the rule of Chhatrapati Rajaram Maharaj, Krishnaji Anant Sabhasad penned ‘Sabhasad Bakhar.’ It is an important source of knowledge regarding Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj's reign.
- The Battle of Panipat is described in ‘Bhausahebanchi Bakhar.’ The same event is also covered in another bakhar, titled ‘Panipatachi Bakhar.’ Information on the Holkars and their contributions to the Maratha rule can be found in ‘Holkaranchi Kaiphiyat.’

Page of Sabhasad Bakhar
Related QuestionsVIEW ALL [4]
Read the following extract and answer the questions:
|
For the historians in the Mughal courts, praising the emperors and exhibiting loyalty became more important. The custom of adding suitable poetic quotes and beautiful pictures was also introduced. Babur, the founder of the Mughal empire wrote an autobiography, entitled, 'Tuzuk-i-Baburi'. It contains descriptions of the battles fought by him. Babur also recorded his minute observations of various regions and cities travelled by him including the local economy, customs, and flora. Abul Fazl's 'Akbarnama' is very important from the viewpoint of critical historiography. His method of collecting authentic historical documents and their scrutiny is looked upon as devoid of bias a hence realistic. |
- Which issues got more important in historiography during the Mughal period?
- Why is 'Tuzuk-i-Baburi' an important source of history?
- Why is 'Akbarnama' important from a critical point of view?