Topics
Historiography : Development in the West
History : Applied History
Working of the Constitution
Historiography : Indian Tradition
The Electoral Process
Political Science : Working of the Indian Constitution
Applied History
Political Parties
History of Indian Arts
- What is ‘Art’?
- Indian Traditions of Visual Arts (Drik Kala): Painting
- Prehistoric Paintings
- Mural Paintings and Cave Painting
- Folk Styles of Paintings
- Classical Styles of Painting
- Miniature Paintings in Manuscripts
- Modern Indian Paintings
- Indian Traditions of Visual Arts (Drik Kala): Sculpture Art
- Indus Civilization Sculpture
- Folk Styles of Sculptural Art
- Classical Styles of Sculptural Art
- Indian Iconography
- Indian Traditions of Visual Arts (Drik Kala): Architecture and Sculpture
- Rock-cut Architecture
- Temple Architecture
- Indo-Islamic Architecture
- Indo-Gothic architecture
- Indian Traditions of Performing Arts
- Indian Theatre
- Indian Music
- Indian Dance
- Present Scenario of the Performing Arts
- Art, Applied Art, and Professional Opportunities
Social and Political Movements
- Movement
- Important Movements in India
- Tribal Movement
- Farmers Movement
- Worker's Movements
- Women’s Movement
- Environment Movements
- Consumer Movement
Mass Media and History
Challenges Faced by Indian Democracy
Entertainment and History
Sports and History
Tourism and History
Heritage Management
History - Imperialism
History - 20th Century Age of conflict
History - Emancipation of Asia and Africa
History - World after World War 2
Political Science
Geographical discoveries and colonization
- Concept for Geographical Discoveries and Colonization
Africa
- Imperialism - Africa
Asia: India, China, Japan
- Concept for Asia: India, China, Japan
Dictatorships in Europe, Second World War and world
- Concept on Dictatorships in Europe
- Concept for Second World War and World
First world war
- Concept on First World War
The League of Nations
- Concept for the League of Nations
Russian Revolution
- Concept for Russian Revolution
United Nations Organization
- Concept for United Nations Organization
Africa
- Emancipation of Africa
Asia
- Emancipation of Asia
Globalization
- Globalization After World War II
Scientific and Technological Progress
- Scientific and Technological Progress After World War II
Cold war
- Formation of the Cold War
Social Diversity and Democracy
- Social Diversity
- Coccept for Caste/Race and Democracy
- Concept for Language and Democracy
- Cocnept for Religion and Democracy
- Concept for Gender and Democracy
- Concept for Democracy and Diversity
Challenges to Democracy Remedial Measures to the Challenges
- Concept for Challenges to Democracy Remedial Measures to the Challenges
Internal work
Democracy
- Democracy - Meaning, Types and Characteristics
Political Parties and Types
- Political Parties
- Importance of Political Parties
- Major National and Regional Parties in India/ Types of Political Parties
Notes
Temple architecture:
- India's temple architecture started to take shape in the Gupta era, about the fourth century C.E. The only components of the early Gupta period temples were the Garbhagriha and a veranda with four columns.
- By the eighth century C.E., temple architecture in India had reached its pinnacle.
- The magnificent composition of Verul's Kailas temple testifies to this. By the medieval period, India had created a number of different temple architectural styles.
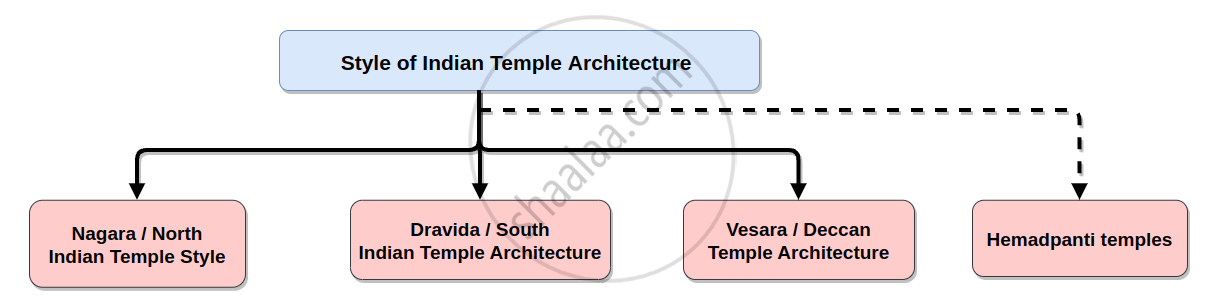
1. Nagara Style or North India Temple style:
 |
 |
| Nagara Indian Style Architecture | |
- The Nagara style of temple architecture became popular in northern India
- The entire temple is built on a single stone platform with steps leading up to it.
- Another unique characteristic is that it does not usually have elaborate boundary walls or gateways.
- Garbhagriha: It is always located directly under the tallest tower.
- Assembly halls or mandaps: It is present in front of the main deity.
- Earlier temples had one shikhara whereas the later temples had many.
- Another distinguishing feature of this temple style is the installation of Amalaka or Kalash on Shikhara.
- Examples of Nagara Style of Temples are Kandariya Mahadev Temple in Madhya Pradesh, Sun temple in Konark, and Sun temple at Modhera.
|
Kandariya Mahadev Temple |
Sun temple in Konark |
2. Dravida style of temple architecture:
|
|
- The Pallavas, who ruled in parts of Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, and northern Tamil Nadu until the ninth century, pioneered the Dravidian style of temple architecture in South India.
- The Dravida temple is surrounded by a compound wall.
- A Gopuram, or entrance gateway, is located in the centre of the front wall.
- The main temple tower, known as vimana in Tamil Nadu, is shaped like a stepped pyramid that rises up geometrically, as opposed to the curving shikhara of North India.
- The term 'shikhara' is only used for the crowning element at the top of a South Indian temple, which is usually shaped like a small stupika or an octagonal cupola - this is equivalent to the amalak and kalasha of North Indian temples.
- The entrance to Garbhagriha is adorned with fierce Dvarapalas or temple doorkeepers.
- Within the complex, it is common to find a large water reservoir, also known as a temple tank.
- The Kailashnath temple in Ellora is a well-known example of a temple built entirely in the Dravidian style. Other well-known Dravidian temples in the south include Rajarajeswara or Brihadeshwara temple, Tiruvannamalai, Tamil Nadu's Annamalaiyar Temple, Meenakshi, and Airavatesvara temples.
|
Brihadeshwara Temple |
Annamalaiyar Temple |
3. Vesara style of temple architecture:
- Vesara is a hybridised architecture style that combines Nagara and Dravidian elements.
- Vesara is thought to be derived from the Sanskrit word vishra, which means a place to take a long walk.
- Vesara style originated in Karnataka.
- The Chalukyas of Badami started the trend by building temples in a Vesara style, which was refined by the Rashtrakutas of Manyakheta in Ellora, Chalukyas of Kalyani in Lakkundi, Dambal, Gadag, etc., and was epitomized by the Hoysalas.
- Ornamentation: The ornamentation of the temple walls and pillars on the Chalukyan temple shows indigenous quality.
- Transformation of Dravida tower: The Chalukyan builders altered the Dravida towers by reducing the height of each storey and arranging them in descending order of height from base to top, with much ornamentation in each storey.
- Transformation of Nagara tower: Instead of inclined storeys, the vertical shape of the tower has been modified.
- Mantapa: The roof of the mantapa is divided into two types: dome ceilings (the dome-like ceilings standing on four pillars are very attractive) and square ceilings (these are vigorously ornamented with mythological pictures).
- Pillars: The miniature decorative pillars of Chalukya temples have their own artistic value.
- Examples - Kallesvara temple, Kukkanur; Ramalingesvara temple, Gudur; Mahadeva temple, Ittagi; Kasivisvesvara temple, Lakkundi (and several other temples at Lakkundi); Brahmadeva temple, Savadi – notable for being fully stellate; Mallikarjuna temple, Sudi (and Joda-kalasha temple)
|
Kallesvara temple |
 Mahadeva temple |
4. Hemadpanti style of Temple:
- Temples in Maharashtra built in the 12th-13th centuries are known as Hemadpanti temples.
- Temples at Hemadpanti are constructed with star-shaped exterior walls. The outer walls of the temple have a zigzag pattern in the star-shaped plan. This produces an intriguing impression of shifting between light and shadow.
- The stonework of the Hemadpanti temple is a key feature. The walls are built without using any mortar, by locking the stones by using the technique of tenon and mortise joints.
- Among the best examples of the Hemadpanti style is the Ambreshwar temple at Ambarnath near Mumbai, the Gondeshwar temple at Sinnar near Nashik, and the Aundha Nagnath temple in the Hingoli district. Their strategy resembles a star. There are various locations in Maharashtra where you can find Hemadpanti temples.
|
Ambreshwar temple |
Gondeshwar temple |
If you would like to contribute notes or other learning material, please submit them using the button below.








