Topics
Historiography : Development in the West
History : Applied History
Working of the Constitution
Historiography : Indian Tradition
The Electoral Process
Political Science : Working of the Indian Constitution
Applied History
Political Parties
History of Indian Arts
- What is ‘Art’?
- Indian Traditions of Visual Arts (Drik Kala): Painting
- Prehistoric Paintings
- Mural Paintings and Cave Painting
- Folk Styles of Paintings
- Classical Styles of Painting
- Miniature Paintings in Manuscripts
- Modern Indian Paintings
- Indian Traditions of Visual Arts (Drik Kala): Sculpture Art
- Indus Civilization Sculpture
- Folk Styles of Sculptural Art
- Classical Styles of Sculptural Art
- Indian Iconography
- Indian Traditions of Visual Arts (Drik Kala): Architecture and Sculpture
- Rock-cut Architecture
- Temple Architecture
- Indo-Islamic Architecture
- Indo-Gothic architecture
- Indian Traditions of Performing Arts
- Indian Theatre
- Indian Music
- Indian Dance
- Present Scenario of the Performing Arts
- Art, Applied Art, and Professional Opportunities
Social and Political Movements
- Movement
- Important Movements in India
- Tribal Movement
- Farmers Movement
- Worker's Movements
- Women’s Movement
- Environment Movements
- Consumer Movement
Mass Media and History
Challenges Faced by Indian Democracy
Entertainment and History
Sports and History
Tourism and History
Heritage Management
History - Imperialism
History - 20th Century Age of conflict
History - Emancipation of Asia and Africa
History - World after World War 2
Political Science
Geographical discoveries and colonization
- Concept for Geographical Discoveries and Colonization
Africa
- Imperialism - Africa
Asia: India, China, Japan
- Concept for Asia: India, China, Japan
Dictatorships in Europe, Second World War and world
- Concept on Dictatorships in Europe
- Concept for Second World War and World
First world war
- Concept on First World War
The League of Nations
- Concept for the League of Nations
Russian Revolution
- Concept for Russian Revolution
United Nations Organization
- Concept for United Nations Organization
Africa
- Emancipation of Africa
Asia
- Emancipation of Asia
Globalization
- Globalization After World War II
Scientific and Technological Progress
- Scientific and Technological Progress After World War II
Cold war
- Formation of the Cold War
Social Diversity and Democracy
- Social Diversity
- Coccept for Caste/Race and Democracy
- Concept for Language and Democracy
- Cocnept for Religion and Democracy
- Concept for Gender and Democracy
- Concept for Democracy and Diversity
Challenges to Democracy Remedial Measures to the Challenges
- Concept for Challenges to Democracy Remedial Measures to the Challenges
Internal work
Democracy
- Democracy - Meaning, Types and Characteristics
Political Parties and Types
- Political Parties
- Importance of Political Parties
- Major National and Regional Parties in India/ Types of Political Parties
Notes
Indian Music:
- The earliest tradition of Indian music may be traced to Sama Veda which contained the slokas that were put to music.
- The earliest treatise on music, drama, and dance is Bharata’s Natyashastra
- The seven swars of music – Sa, Re, Ga, Ma, Pa, Dha, Ni represent different scriptural deities: SA – Agni, RE – Brahma, GA – Saraswati, MA – Shiva, PA – Vishnu, DHA – Ganesha, NI – Surya
A. Indian Classical Music:
The origins of Indian classical music can be traced back to the recital of Vedic hymns in Hindu temples. Indian classical music during the Middle Ages was mostly centered on two traditions: the popular Hindustani classical music of North India and the Carnatic music of South India.
| Hindustani Music | Carnatic Music | |
| 1. | Its origins can be traced back to North India. Foreign traditions influenced it. | Its origins can be traced back to South India. There is no such foreign influence. |
|
2. |
There is no strict adherence to raga, tala, and Sruti unity as in Carnatic music. | Every piece contains unity of raga, tala, and Sruti. |
| 3. | There is no strong emphasis on Kriti. | There is a strong emphasis on Kriti. |
| 4. | More importance was given to vocal than instruments. | Equal importance was given to vocal as well as instruments. |
| 5. | Prevalence of a significant number of gharanas | No such prevalence of gharanas |
| 6. | Note by note raga development | Phrase by phrase raga development |
| 7. | Different styles of Hindustani music: Dhrupad, Dhamar, Thumri, Khayal and Tappa. | Different composition of Hindustani music: Gitam, Suladi, Svarajati, Jatisvaram, Varnam, Kritanam, Kriti, Pada, Javali, Tillana, Pallavi, Tanam. |
| 8. |
Hindustani musical instruments: Sitar, sarod, santoor and sarangi, Pakhawaj, tabla, and Mridangam
|
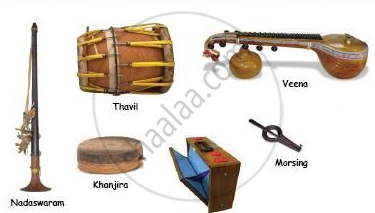
Carnatic musical instruments: Flute, veena, nadaswaram, mridangam, ghatam.
|
Folk Music
- Folk music, as opposed to established classical music, is the music of the common people.
- It gets its name from the German word volk, which means 'people.'
- Folk songs can include unique messages or meanings. They frequently talk about significant ceremonies and historical occurrences.
- They may be festivals, the advent of a new season, marriage, or the birth of a child.
- The forms of folk song in different provinces like:
State Folk songs Rajasthani Maand Bengal Bauls, Bhatiali Haryana Ragini Kashmir Gulraj Madhya Pradesh Pandavani Maharashtra Powada, Keertan, Jagar, Gondhal
Text
Do you know?
|
Kitab-e-Navras |
- A book titled "Kitab-e-Navras" was written in Dakhani Urdu by Ibrahim Adilshah II, the ruler of Bijapur.
- This text discusses classical music from India. It enables the listener to delight in outstanding poetry and includes verses performed in the Dhrupad style.
- Dr. Sayyad Yahya Nashit initially translated this work into Marathi. The editor of it is Dr. Arun Prabhune. The translation of the verse printed on the cover of this text reads as follows:
‘‘Oh, Mother Saraswati, you are the divine light in the world and you are complete with all qualities. If Ibrahim receives your grace (blessings), the poetry of the navras will become eternal.’’
If you would like to contribute notes or other learning material, please submit them using the button below.