Topics
Historiography : Development in the West
History : Applied History
Working of the Constitution
Historiography : Indian Tradition
The Electoral Process
Political Science : Working of the Indian Constitution
Applied History
Political Parties
History of Indian Arts
- What is ‘Art’?
- Indian Traditions of Visual Arts (Drik Kala): Painting
- Prehistoric Paintings
- Mural Paintings and Cave Painting
- Folk Styles of Paintings
- Classical Styles of Painting
- Miniature Paintings in Manuscripts
- Modern Indian Paintings
- Indian Traditions of Visual Arts (Drik Kala): Sculpture Art
- Indus Civilization Sculpture
- Folk Styles of Sculptural Art
- Classical Styles of Sculptural Art
- Indian Iconography
- Indian Traditions of Visual Arts (Drik Kala): Architecture and Sculpture
- Rock-cut Architecture
- Temple Architecture
- Indo-Islamic Architecture
- Indo-Gothic architecture
- Indian Traditions of Performing Arts
- Indian Theatre
- Indian Music
- Indian Dance
- Present Scenario of the Performing Arts
- Art, Applied Art, and Professional Opportunities
Social and Political Movements
- Movement
- Important Movements in India
- Tribal Movement
- Farmers Movement
- Worker's Movements
- Women’s Movement
- Environment Movements
- Consumer Movement
Mass Media and History
Challenges Faced by Indian Democracy
Entertainment and History
Sports and History
Tourism and History
Heritage Management
History - Imperialism
History - 20th Century Age of conflict
History - Emancipation of Asia and Africa
History - World after World War 2
Political Science
Geographical discoveries and colonization
- Concept for Geographical Discoveries and Colonization
Africa
- Imperialism - Africa
Asia: India, China, Japan
- Concept for Asia: India, China, Japan
Dictatorships in Europe, Second World War and world
- Concept on Dictatorships in Europe
- Concept for Second World War and World
First world war
- Concept on First World War
The League of Nations
- Concept for the League of Nations
Russian Revolution
- Concept for Russian Revolution
United Nations Organization
- Concept for United Nations Organization
Africa
- Emancipation of Africa
Asia
- Emancipation of Asia
Globalization
- Globalization After World War II
Scientific and Technological Progress
- Scientific and Technological Progress After World War II
Cold war
- Formation of the Cold War
Social Diversity and Democracy
- Social Diversity
- Coccept for Caste/Race and Democracy
- Concept for Language and Democracy
- Cocnept for Religion and Democracy
- Concept for Gender and Democracy
- Concept for Democracy and Diversity
Challenges to Democracy Remedial Measures to the Challenges
- Concept for Challenges to Democracy Remedial Measures to the Challenges
Internal work
Democracy
- Democracy - Meaning, Types and Characteristics
Political Parties and Types
- Political Parties
- Importance of Political Parties
- Major National and Regional Parties in India/ Types of Political Parties
Notes
Modern Indian Paintings:
- Around 1857, Indian art entered its modern era.
- The British considered fine art to be exclusively European. They believed that Indians lacked the training and the sensibility needed to create and admire fine art.
- An accurate portrayal of the painting's subject distinguishes the European style.
Evolution of Modern Indian Painting:
- Indian painting, as an extension of Indian miniature painting, began to decline toward the end of the nineteenth century. Only a few minor forms of artistic expression - the "Bazar" and "Company" styles of painting, as well as some folk arts throughout the nation - were still in existence during this time.
- By the mid and late nineteenth century, art schools were established in major cities like
Lahore, Calcutta (now, Kolkata), Bombay (now, Mumbai), and Madras (now, Chennai), to propagate Western values in art education and the colonial agenda.
- After 1857, John Griffiths and John Lockwood Kipling travelled to India; John Griffith served as the head of the Sir J. J. School of Art and was regarded as one of the best Victorian painters to visit the country, while Kipling later served as the head of the J. J. School of Art as well as the Mayo School of Arts, which was founded in Lahore in 1878.
- Traditional Indian crafts as well as academic and naturalist artwork that suited Victorian sensibilities were frequently promoted by these art schools. Even the Indian crafts that were supported were those that catered to European tastes and market demands.
- Nationalist art developed in opposition to this colonial prejudice, with the Bengal School of Art, as fostered by Abanindranath Tagore and E. B. Havell, serving as a shining example. Rabindranath Tagore, a poet, created the Visva-Bharati University in Shantiniketan, which included the first nationalist art school in India, Kala Bhavana.
Examples of Modern Indian Painting:
- When Savai Madhavrao Peshwe was in power, James Wales, a Scottish artist, founded an art school in Shaniwar Wada, a neighborhood in Pune. He had painted portraits of Nana Phadnavis and Savai Madhavrao.
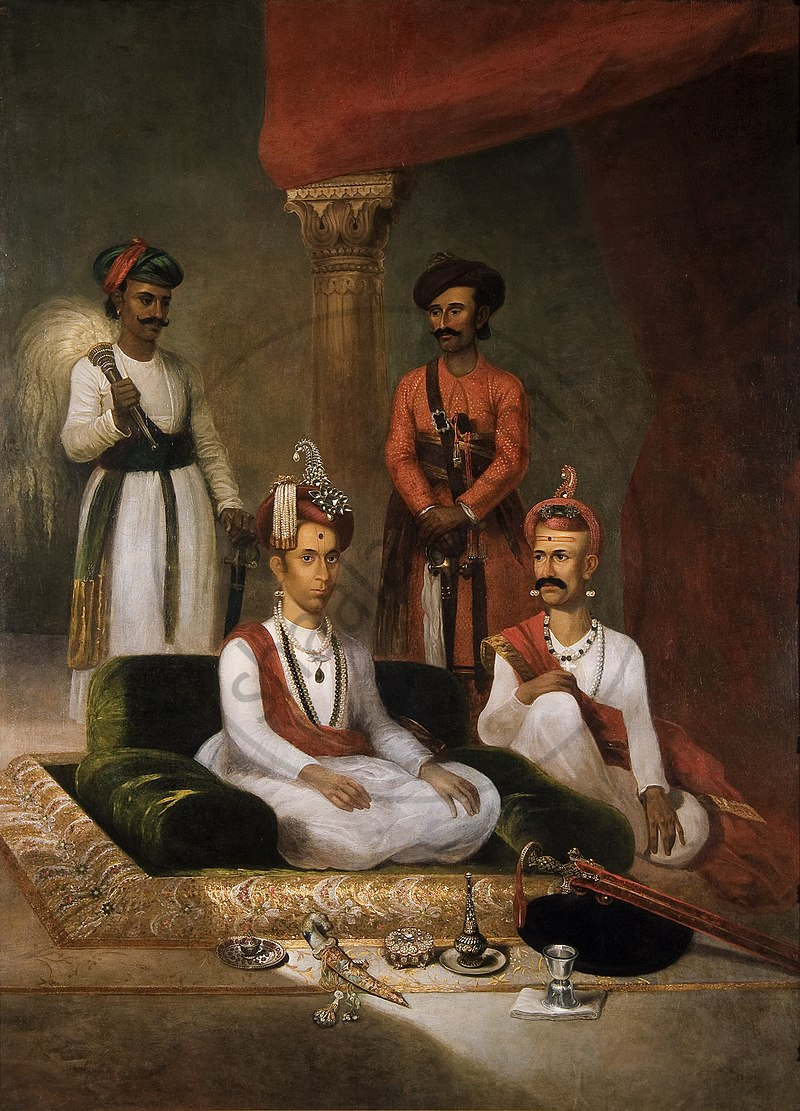

Savai Madhavrao and Nana Phadnavis
- The Marathi artist Gagaram Tambat, who collaborated with Wales, receives a special note in this context. The rock-cut caves at Karle and Verul have been captured in paintings by him. His sketches are archived in Yale University's Yale Centre of British Art.

Gangaram Tambat with his Guru
- Replicas of Ajanta paintings were created by Pestonji Bomanji.
Lahore, Calcutta (now, Kolkata), Bombay (now, Mumbai), and Madras (now, Chennai), to propagate Western values in art education and the colonial agenda.
|
Savai Madhavrao and Nana Phadnavis |
 Gangaram Tambat with his Guru |
If you would like to contribute notes or other learning material, please submit them using the button below.