Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A carpenter has 90, 80 and 50 running feet respectively of teak wood, plywood and rosewood which is used to product A and product B. Each unit of product A requires 2, 1 and 1 running feet and each unit of product B requires 1, 2 and 1 running feet of teak wood, plywood and rosewood respectively. If product A is sold for Rs. 48 per unit and product B is sold for Rs. 40 per unit, how many units of product A and product B should be produced and sold by the carpenter, in order to obtain the maximum gross income? Formulate the above as a Linear Programming Problem and solve it, indicating clearly the feasible region in the graph.
उत्तर
| Product | A | B | |
| Teak wood | 2 | 1 | ≤90 |
| plywood | 1 | 2 | ≤80 |
| Rosewood | 1 | 1 | ≤50 |
Selling price per unit Rs. 48/- for product A and for product B Rs. 40/Mathematical formation :
`Z_max = 48x_1 + 40x_2` (objective function)
s.t. 2x1 + x2 ≤ 90
x1 + 2x2 ≤ 80:
x1 + x2 ≤ 50;
x1,x2 ≥ 0
2x1 + x2 = 90 ...........(1)
x1 + 2x2 = 80 ..........(2)
X1 + x2 =50 ........(3)
from eq (3) and (2)
x2 = 30
x1 = 20
from eq. (1) & (3)
`x1 = 40`
`x2 = 10`
0(0,0)
| A(0,40) | Zmax = 48 × x1 + 40 × x2 | ZA = 1600 |
| B(20,30) | = 48 × 20 + 40 × 30 | ZB = 2160 |
| C(40,10) | = 48 × 40 + 40 +10 | Zc = 2320 |
| D(45,0) | = 48 × 45 + 40(0) | ZD = 2160 |
40, 10), ZC = 2320.
Hence the optimal solution is x1 = 40, x2 = 10 (Product A = 40 units, Product B = 10 units)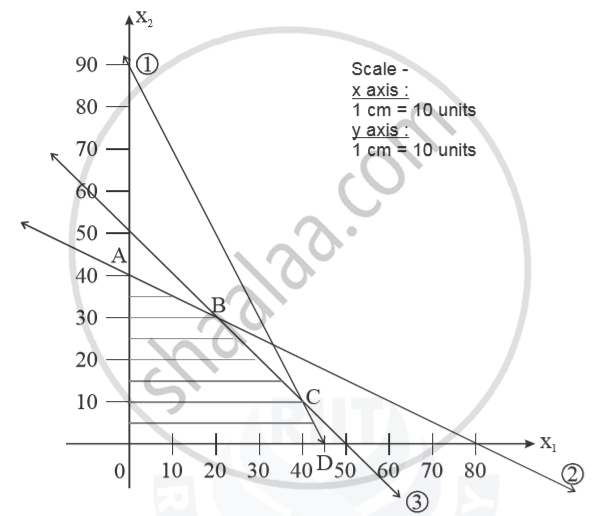
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Minimum and maximum z = 5x + 2y subject to the following constraints:
x-2y ≤ 2
3x+2y ≤ 12
-3x+2y ≤ 3
x ≥ 0,y ≥ 0
Maximise Z = x + 2y subject to the constraints
`x + 2y >= 100`
`2x - y <= 0`
`2x + y <= 200`
Solve the above LPP graphically
Solve the following L.P.P. graphically:
Minimise Z = 5x + 10y
Subject to x + 2y ≤ 120
Constraints x + y ≥ 60
x – 2y ≥ 0 and x, y ≥ 0
Solve the following LPP by graphical method:
Minimize Z = 7x + y subject to 5x + y ≥ 5, x + y ≥ 3, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0
Maximize Z = 5x + 3y
Subject to
\[3x + 5y \leq 15\]
\[5x + 2y \leq 10\]
\[ x, y \geq 0\]
Minimize Z = 30x + 20y
Subject to
\[x + y \leq 8\]
\[ x + 4y \geq 12\]
\[5x + 8y = 20\]
\[ x, y \geq 0\]
Minimize Z = x − 5y + 20
Subject to
\[x - y \geq 0\]
\[ - x + 2y \geq 2\]
\[ x \geq 3\]
\[ y \leq 4\]
\[ x, y \geq 0\]
Minimize Z = 3x1 + 5x2
Subject to
\[x_1 + 3 x_2 \geq 3\]
\[ x_1 + x_2 \geq 2\]
\[ x_1 , x_2 \geq 0\]
Find graphically, the maximum value of Z = 2x + 5y, subject to constraints given below:
2x + 4y ≤ 8
3x + y ≤ 6
x + y ≤ 4
x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0
Solve the following LPP graphically:
Maximize Z = 20 x + 10 y
Subject to the following constraints
\[x +\]2\[y \leq\]28
3x+ \[y \leq\]24
\[x \geq\] 2x.
\[y \geq\] 0
A dietician has to develop a special diet using two foods P and Q. Each packet (containing 30 g) of food P contains 12 units of calcium, 4 units of iron, 6 units of cholesterol and 6 units of vitamin A. Each packet of the same quantity of food Q contains 3 units of calcium, 20 units of iron, 4 units of cholesterol and 3 units of vitamin A. The diet requires atleast 240 units of calcium, atleast 460 units of iron and at most 300 units of cholesterol. How many packets of each food should be used to minimise the amount of vitamin A in the diet? What is the minimum of vitamin A.
Two tailors, A and B earn Rs 15 and Rs 20 per day respectively. A can stitch 6 shirts and 4 pants while B can stitch 10 shirts and 4 pants per day. How many days shall each work if it is desired to produce (at least) 60 shirts and 32 pants at a minimum labour cost?
A firm manufactures headache pills in two sizes A and B. Size A contains 2 grains of aspirin, 5 grains of bicarbonate and 1 grain of codeine; size B contains 1 grain of aspirin, 8 grains of bicarbonate and 66 grains of codeine. It has been found by users that it requires at least 12 grains of aspirin, 7.4 grains of bicarbonate and 24 grains of codeine for providing immediate effects. Determine graphically the least number of pills a patient should have to get immediate relief. Determine also the quantity of codeine consumed by patient.
A company manufactures two types of novelty Souvenirs made of plywood. Souvenirs of type A require 5 minutes each for cutting and 10 minutes each for assembling. Souvenirs of type B require 8 minutes each for cutting and 8 minutes each for assembling. There are 3 hours 20 minutes available for cutting and 4 hours available for assembling. The profit is 50 paise each for type A and 60 paise each for type B souvenirs. How many souvenirs of each type should the company manufacture in order to maximize the profit?
A merchant plans to sell two types of personal computers a desktop model and a portable model that will cost Rs 25,000 and Rs 40,000 respectively. He estimates that the total monthly demand of computers will not exceed 250 units. Determine the number of units of each type of computers which the merchant should stock to get maximum profit if he does not want to invest more than Rs 70 lakhs and his profit on the desktop model is Rs 4500 and on the portable model is Rs 5000. Make an LPP and solve it graphically.
A farmer has a supply of chemical fertilizer of type A which contains 10% nitrogen and 6% phosphoric acid and of type B which contains 5% nitrogen and 10% phosphoric acid. After the soil test, it is found that at least 7 kg of nitrogen and the same quantity of phosphoric acid is required for a good crop. The fertilizer of type A costs ₹ 5.00 per kg and the type B costs ₹ 8.00 per kg. Using Linear programming, find how many kilograms of each type of fertilizer should be bought to meet the requirement and for the cost to be minimum. Find the feasible region in the graph.
Maximum value of 4x + 13y subject to constraints x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0, x + y ≤ 5 and 3x + y ≤ 9 is ______.
The maximum value of Z = 5x + 4y, Subject to y ≤ 2x, x ≤ 2y, x + y ≤ 3, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0 is ______.
The region XOY - plane which is represented by the inequalities -5 ≤ x ≤ 5, -5 ≤ y ≤ 5 is ______
For the LPP, maximize z = x + 4y subject to the constraints x + 2y ≤ 2, x + 2y ≥ 8, x, y ≥ 0 ______.
In linear programming feasible region (or solution region) for the problem is ____________.
A manufacturer wishes to produce two commodities A and B. The number of units of material, labour and equipment needed to produce one unit of each commodity is shown in the table given below. Also shown is the available number of units of each item, material, labour, and equipment.
| Items | Commodity A | Commodity B | Available no. of Units |
| Material | 1 | 2 | 8 |
| Labour | 3 | 2 | 12 |
| Equipment | 1 | 1 | 10 |
Find the maximum profit if each unit of commodity A earns a profit of ₹ 2 and each unit of B earns a profit of ₹ 3.
The comer point of the feasible region determined by the following system of linear inequalities:
2x + y ≤ 10, x + 3y ≤ 15, x, y ≥ 0 are (0, 0), (5, 0), (3, 4) and (0, 5). Let x = Px + qx where P, q > 0 condition on P and Q so that the maximum of z occurs at both (3, 4) and (0, 5) is
The solution set of the inequality 3x + 5y < 4 is ______.
Solve the following Linear Programming Problem graphically:
Maximize: P = 70x + 40y
Subject to: 3x + 2y ≤ 9,
3x + y ≤ 9,
x ≥ 0,y ≥ 0.
If x – y ≥ 8, x ≥ 3, y ≥ 3, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0 then find the coordinates of the corner points of the feasible region.
Aman has ₹ 1500 to purchase rice and wheat for his grocery shop. Each sack of rice and wheat costs ₹ 180 and Rupee ₹ 120 respectively. He can store a maximum number of 10 bags in his shop. He will earn a profit of ₹ 11 per bag of rice and ₹ 9 per bag of wheat.
- Formulate a Linear Programming Problem to maximise Aman’s profit.
- Calculate the maximum profit.
