Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A circular loop of area 1 cm2, carrying a current of 10 A, is placed in a magnetic field of 0.1 T perpendicular to the plane of the loop. The torque on the loop due to the magnetic field is
विकल्प
zero
10−4 N m
10−2 N m
1 N m
उत्तर
zero
When a circular loop is placed in a uniform magnetic field, it always experiences zero toque. We all know that a current-carrying wire experiences a force when placed in an external magnetic field. But in the case of a circular loop, forces are present in pairs, i.e. they are equal and opposite in magnitude. So, for every point on the loop, there exists another point on the diametrically opposite edge for which the force is equal and opposite to the force acting on first point. So, these two forces cancel in pair. In this way, the net torque on the loop is always zero when placed in a uniform magnetic field.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Draw a neat and labelled diagram of suspended coil type moving coil galvanometer.
Two identical circular loops, P and Q, each of radius r and carrying equal currents are
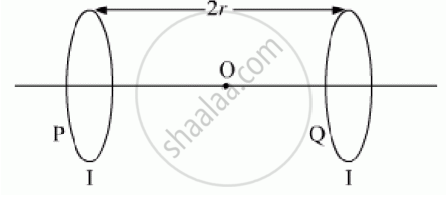
kept in the parallel planes having a common axis passing through O. The direction of current in P is clockwise and in Q is anti-clockwise as seen from O which is equidistant from the loops P and Q. Find the magnitude of the net magnetic field at O.
Write the expression for the magnetic moment `vecm`due to a planar square loop of side ‘l’ carrying a steady current I in a vector form.
In the given figure this loop is placed in a horizontal plane near a long straight conductor carrying a steady current I1 at a distance l as shown. Give reason to explain that the loop will experience a net force but no torque. Write the expression for this force acting on the loop.

Is it possible for a current loop to stay without rotating in a uniform magnetic field? If yes, what should be the orientation of the loop?
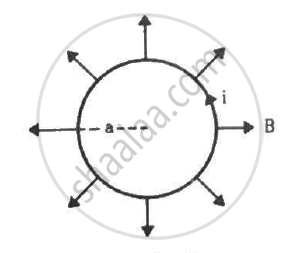
A circular loop of radius a, carrying a current i, is placed in a two-dimensional magnetic field. The centre of the loop coincides with the centre of the field (figure). The strength of the magnetic field at the periphery of the loop is B. Find the magnetic force on the wire.
A 50-turn circular coil of radius 2.0 cm carrying a current of 5.0 A is rotated in a magnetic field of strength 0.20 T. (a) What is the maximum torque that acts on the coil? (b) In a particular position of the coil, the torque acting on it is half of this maximum. What is the angle between the magnetic field and the plane of the coil?
Derive the expression for the torque on a current-carrying coil in a magnetic field.
A triangular loop of side `l` carries a current I. It is placed in a magnetic field B such that the plane of the loop is in the direction of B. The torque on the loop is ____________.
If in a moving coil galvanometer, a current I produces a deflection `theta,` then ____________.
A rectangular coil has 200 turns each of area 50 cm2 . It is capable of rotation about an axis joining the mid points of two opposite sides. When a current of 10 A is passed through it while its plane is at right angles to a uniform magnetic field, it experiences a torque of 5 Nm. The magnetic field will be ____________.
The sensitivity of moving coil galvanometer is inversely proportional to ____________.
The magnetic field developed due to current carrying coil at its centre is 'B'. If the new coil of two turns is prepared from the above coil and same current is passed, then the magnetic field at the centre of the new coil will be ____________.
An ammeter is obtained by shunting 'n' `Omega` galvanometer with 'n' `Omega` resistance. The additional shunt required to be connected across it to double the range is ____________.
What is the magnetic moment of a current-carrying circular coil if the radius of the circular coil is 'R' and magnetic induction at the center is 'B'?
When the plane of the coil is parallel to the field, torque will be ______
A uniform conducting wire of length 12a and resistance R is wound up as a current-carrying coil in the shape of (i) an equilateral triangle of side a; (ii) a square of sides a and, (iii) a regular hexagon of sides a. The coil is connected to a voltage source V0. Find the magnetic moment of the coils in each case.
Equal current i flows in two segments of a circular loop in the direction shown in figure. Radius of the loop is r. The magnitude of magnetic field induction at the centre of the loop is ______.
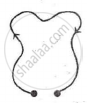
A thin flexible wire of length L is connected to two adjacent fixed points and carries a current I in the clockwise direction, as shown in the figure. When the system is put in a uniform magnetic field of strength B going into the plane of the paper, the wire takes the shape of a circle. The tension in the wire is ______.