Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A company manufactures two types of products A and B. Each unit of A requires 3 grams of nickel and 1 gram of chromium, while each unit of B requires 1 gram of nickel and 2 grams of chromium. The firm can produce 9 grams of nickel and 8 grams of chromium. The profit is ₹ 40 on each unit of the product of type A and ₹ 50 on each unit of type B. How many units of each type should the company manufacture so as to earn a maximum profit? Use linear programming to find the solution.
उत्तर
Let x units of type A and y units of type B be produced.
Now, max Z = 40x + 50y
sub to 3x + y ≤ 9
x + 2y ≤ 8
x, y ≥ 0
Point of intersection is given by :
6x + 2y = 18
x + 2y = 8
`((-) (-) (-))/(5x = 10)`
x = 2
y = `(8 - 2)/(2) = 3`
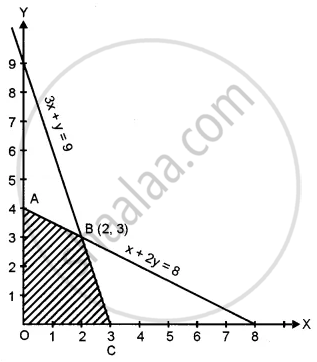
Coordinates of O is (0, 0)
Coordinates of A is (0, 4)
Coordinates of C is (3, 0)
Coordinates of B is (2, 3)
At O, Z = 0
At A, Z = 40 × 0 + 50 × 4 = ₹ 200
At B, Z = 40 × 2 + 50 × 3 = 80 + 150 = ₹ 230
At C, Z = 40 × 3 + 50 × 0 = ₹ 120
The feasible region is the shaded portion.
Maximum profit is ₹ 230 at B (2, 3) i.e., the company produces 2 units of type A product and 3 units of type B product.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Solve the following LPP by using graphical method.
Maximize : Z = 6x + 4y
Subject to x ≤ 2, x + y ≤ 3, -2x + y ≤ 1, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0.
Also find maximum value of Z.
A manufacturer produces two products A and B. Both the products are processed on two different machines. The available capacity of first machine is 12 hours and that of second machine is 9 hours per day. Each unit of product A requires 3 hours on both machines and each unit of product B requires 2 hours on first machine and 1 hour on second machine. Each unit of product A is sold at Rs 7 profit and B at a profit of Rs 4. Find the production level per day for maximum profit graphically.
Solve the following LPP by graphical method:
Maximize: z = 3x + 5y
Subject to: x + 4y ≤ 24
3x + y ≤ 21
x + y ≤ 9
x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0
Solve the following L. P. P. graphically:Linear Programming
Minimize Z = 6x + 2y
Subject to
5x + 9y ≤ 90
x + y ≥ 4
y ≤ 8
x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0
Solve the following LPP graphically :
Maximise Z = 105x + 90y
subject to the constraints
x + y ≤ 50
2x + y ≤ 80
x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0.
Maximize Z = 9x + 3y
Subject to
\[2x + 3y \leq 13\]
\[ 3x + y \leq 5\]
\[ x, y \geq 0\]
Minimize Z = 18x + 10y
Subject to
\[4x + y \geq 20\]
\[2x + 3y \geq 30\]
\[ x, y \geq 0\]
Maximize Z = 3x + 4y
Subject to
\[2x + 2y \leq 80\]
\[2x + 4y \leq 120\]
Minimize Z = 2x + 4y
Subject to
\[x + y \geq 8\]
\[x + 4y \geq 12\]
\[x \geq 3, y \geq 2\]
Minimize Z = 30x + 20y
Subject to
\[x + y \leq 8\]
\[ x + 4y \geq 12\]
\[5x + 8y = 20\]
\[ x, y \geq 0\]
Maximize Z = 3x1 + 4x2, if possible,
Subject to the constraints
\[x_1 - x_2 \leq - 1\]
\[ - x_1 + x_2 \leq 0\]
\[ x_1 , x_2 \geq 0\]
Show the solution zone of the following inequalities on a graph paper:
\[5x + y \geq 10\]
\[ x + y \geq 6\]
\[x + 4y \geq 12\]
\[x \geq 0, y \geq 0\]
Find x and y for which 3x + 2y is minimum subject to these inequalities. Use a graphical method.
A diet is to contain at least 80 units of vitamin A and 100 units of minerals. Two foods F1and F2 are available. Food F1 costs Rs 4 per unit and F2 costs Rs 6 per unit one unit of food F1 contains 3 units of vitamin A and 4 units of minerals. One unit of food F2contains 6 units of vitamin A and 3 units of minerals. Formulate this as a linear programming problem and find graphically the minimum cost for diet that consists of mixture of these foods and also meets the mineral nutritional requirements
A man owns a field of area 1000 sq.m. He wants to plant fruit trees in it. He has a sum of Rs 1400 to purchase young trees. He has the choice of two types of trees. Type A requires 10 sq.m of ground per tree and costs Rs 20 per tree and type B requires 20 sq.m of ground per tree and costs Rs 25 per tree. When fully grown, type A produces an average of 20 kg of fruit which can be sold at a profit of Rs 2.00 per kg and type B produces an average of 40 kg of fruit which can be sold at a profit of Rs. 1.50 per kg. How many of each type should be planted to achieve maximum profit when the trees are fully grown? What is the maximum profit?
A company manufactures two types of toys A and B. Type A requires 5 minutes each for cutting and 10 minutes each for assembling. Type B requires 8 minutes each for cutting and 8 minutes each for assembling. There are 3 hours available for cutting and 4 hours available for assembling in a day. The profit is Rs 50 each on type A and Rs 60 each on type B. How many toys of each type should the company manufacture in a day to maximize the profit?
A medical company has factories at two places, A and B. From these places, supply is made to each of its three agencies situated at P, Q and R. The monthly requirements of the agencies are respectively 40, 40 and 50 packets of the medicines, while the production capacity of the factories, A and B, are 60 and 70 packets respectively. The transportation cost per packet from the factories to the agencies are given below:
| Transportation Cost per packet(in Rs.) | ||
| From-> | A | B |
| To | ||
| P | 5 | 4 |
| Q | 4 | 2 |
| R | 3 | 5 |
The region represented by the inequation system x, y ≥ 0, y ≤ 6, x + y ≤ 3 is
A carpenter has 90, 80 and 50 running feet respectively of teak wood, plywood and rosewood which is used to product A and product B. Each unit of product A requires 2, 1 and 1 running feet and each unit of product B requires 1, 2 and 1 running feet of teak wood, plywood and rosewood respectively. If product A is sold for Rs. 48 per unit and product B is sold for Rs. 40 per unit, how many units of product A and product B should be produced and sold by the carpenter, in order to obtain the maximum gross income? Formulate the above as a Linear Programming Problem and solve it, indicating clearly the feasible region in the graph.
The graph of the inequality 3X − 4Y ≤ 12, X ≤ 1, X ≥ 0, Y ≥ 0 lies in fully in
Find the graphical solution for the system of linear inequation 2x + y ≤ 2, x − y ≤ 1
Find the solution set of inequalities 0 ≤ x ≤ 5, 0 ≤ 2y ≤ 7
The maximum value of z = 3x + 10y subjected to the conditions 5x + 2y ≤ 10, 3x + 5y ≤ 15, x, y ≥ 0 is ______.
The minimum value of z = 7x + 9y subject to 3x + y ≤ 6, 5x + 8y ≤ 40, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 2 is ______.
Of all the points of the feasible region for maximum or minimum of objective function the points.
Let R be the feasible region (convex polygon) for a linear programming problem and let Z = ax + by be the objective function. When Z has an optimal value (maximum or minimum), where the variables x and y are subject to constraints described by linear inequalities,
Let R be the feasible region for a linear programming problem, and let Z = ax + by be the objective function. If R is bounded, then the objective function Z has both a maximum and a minimum value on R and ____________.
The corner points of the shaded unbounded feasible region of an LPP are (0, 4), (0.6, 1.6) and (3, 0) as shown in the figure. The minimum value of the objective function Z = 4x + 6y occurs at ______.
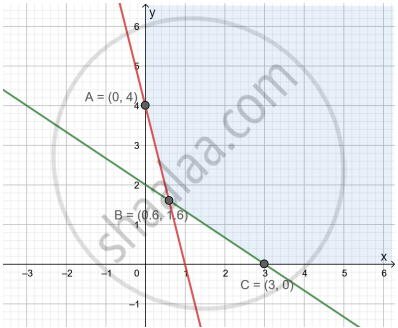
The feasible region corresponding to the linear constraints of a Linear Programming Problem is given below.
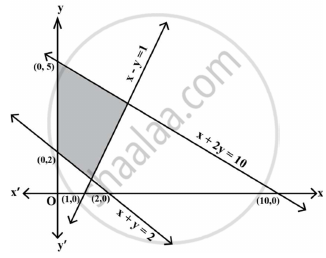
Which of the following is not a constraint to the given Linear Programming Problem?
Find feasible solution for the following system of linear inequation graphically.
3x + 4y ≥ 12, 4x + 7y ≤ 28, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0
Aman has ₹ 1500 to purchase rice and wheat for his grocery shop. Each sack of rice and wheat costs ₹ 180 and Rupee ₹ 120 respectively. He can store a maximum number of 10 bags in his shop. He will earn a profit of ₹ 11 per bag of rice and ₹ 9 per bag of wheat.
- Formulate a Linear Programming Problem to maximise Aman’s profit.
- Calculate the maximum profit.
