Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Show the solution zone of the following inequalities on a graph paper:
\[5x + y \geq 10\]
\[ x + y \geq 6\]
\[x + 4y \geq 12\]
\[x \geq 0, y \geq 0\]
Find x and y for which 3x + 2y is minimum subject to these inequalities. Use a graphical method.
उत्तर
First, we will convert the given inequations into equations, we obtain the following equations:
5x + y = 10, x +y = 6, x + 4y = 12, x = 0 and y = 0
Region represented by 5x + y ≥ 10:
The line 5x + y = 10 meets the coordinate axes at A(2, 0) and B(0, 10) respectively. By joining these points we obtain the line 5x + y = 10.
Clearly (0,0) does not satisfies the inequation 5x + y ≥ 10. So,the region in xy plane which does not contain the origin represents the solution set of the inequation 5x + y ≥ 10.
Region represented by x +y ≥ 6:
The line x +y = 6 meets the coordinate axes at C(6,0) and D(0, 6) respectively. By joining these points we obtain the line
2x +3y = 30.Clearly (0,0) does not satisfies the inequation x +y ≥ 6. So,the region which does not contain the origin represents the solution set of the inequation 2x+3y ≥ 30.
Region represented by x + 4y ≥ 12
The line x + 4y = 12 meets the coordinate axes at E(12, 0) and F(0, 3) respectively. By joining these points we obtain the line
x + 4y = 12.Clearly (0,0) does not satisfies the inequation x + 4y ≥ 12. So,the region which does not contain the origin represents the solution set of the inequation x + 4y≥ 12.
Region represented by x ≥ 0 and y ≥ 0:
Since, every point in the first quadrant satisfies these inequations. So, the first quadrant is the region represented by the inequations x ≥ 0, and y ≥ 0.
The feasible region determined by the system of constraints 5x + y ≥ 10, x +y ≥ 6,x + 4y ≥ 12, x ≥ 0, and y ≥ 0, are as follows .
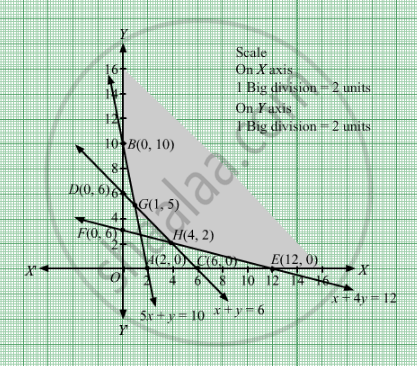 .
.
The corner points of the feasible region are B(0, 10), G(1,5), H(4,2) and E(12,0).
The values of Z at these corner points are as follows.
| Corner point | Z = 3x + 2y |
| B(0, 10) | 3 × 0 + 3 × 10 = 30 |
| G(1,5) | 3 × 1 + 2 × 5 = 13 |
| H(4,2) | 3 × 4 + 2 × 2 = 16 |
| E(12,0) | 3 × 12 + 2 × 0 = 36 |
Therefore, the minimum value of Z is 13 at the point G(1,5). Hence, x = 1 and y = 5 is the optimal solution of the given LPP.
Thus, the optimal value of Z is 13.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Minimize `z=4x+5y ` subject to `2x+y>=7, 2x+3y<=15, x<=3,x>=0, y>=0` solve using graphical method.
Solve the following LPP by using graphical method.
Maximize : Z = 6x + 4y
Subject to x ≤ 2, x + y ≤ 3, -2x + y ≤ 1, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0.
Also find maximum value of Z.
Solve the following LPP by graphical method:
Minimize Z = 7x + y subject to 5x + y ≥ 5, x + y ≥ 3, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0
Maximize Z = 5x + 3y
Subject to
\[3x + 5y \leq 15\]
\[5x + 2y \leq 10\]
\[ x, y \geq 0\]
Maximize Z = 9x + 3y
Subject to
\[2x + 3y \leq 13\]
\[ 3x + y \leq 5\]
\[ x, y \geq 0\]
Maximize Z = 15x + 10y
Subject to
\[3x + 2y \leq 80\]
\[2x + 3y \leq 70\]
\[ x, y \geq 0\]
Minimize Z = 30x + 20y
Subject to
\[x + y \leq 8\]
\[ x + 4y \geq 12\]
\[5x + 8y = 20\]
\[ x, y \geq 0\]
Maximize Z = 4x + 3y
Subject to
\[3x + 4y \leq 24\]
\[8x + 6y \leq 48\]
\[ x \leq 5\]
\[ y \leq 6\]
\[ x, y \geq 0\]
Find the maximum and minimum value of 2x + y subject to the constraints:
x + 3y ≥ 6, x − 3y ≤ 3, 3x + 4y ≤ 24, − 3x + 2y ≤ 6, 5x + y ≥ 5, x, y ≥ 0.
Find graphically, the maximum value of Z = 2x + 5y, subject to constraints given below:
2x + 4y ≤ 8
3x + y ≤ 6
x + y ≤ 4
x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0
A dietician mixes together two kinds of food in such a way that the mixture contains at least 6 units of vitamin A, 7 units of vitamin B, 11 units of vitamin C and 9 units of vitamin D. The vitamin contents of 1 kg of food X and 1 kg of food Y are given below:
| Vitamin A |
Vitamin B |
Vitamin |
Vitamin D |
|
| Food X Food Y |
1 2 |
1 1 |
1 3 |
2 1 |
One kg food X costs Rs 5, whereas one kg of food Y costs Rs 8. Find the least cost of the mixture which will produce the desired diet.
A dietician has to develop a special diet using two foods P and Q. Each packet (containing 30 g) of food P contains 12 units of calcium, 4 units of iron, 6 units of cholesterol and 6 units of vitamin A. Each packet of the same quantity of food Q contains 3 units of calcium, 20 units of iron, 4 units of cholesterol and 3 units of vitamin A. The diet requires atleast 240 units of calcium, atleast 460 units of iron and at most 300 units of cholesterol. How many packets of each food should be used to minimise the amount of vitamin A in the diet? What is the minimum of vitamin A.
A farmer mixes two brands P and Q of cattle feed. Brand P, costing ₹250 per bag, contains 2 units of nutritional element A, 2.5 units of element B and 2 units of element C. Brand Q costing ₹200 per bag contains 1.5 units of nutritional element A, 11.25 units of element B and 3 units of element C. The minimum requirements of nutrients A, B and C are 18 units, 45 units and 24 units respectively. Determine the number of bags of each brand which should be mixed in order to produce a mixture having a minimum cost per bag? What is the minimum cost of the mixture per bag?
A factory owner purchases two types of machines, A and B, for his factory. The requirements and limitations for the machines are as follows:
| Area occupied by the machine |
Labour force for each machine |
Daily output in units |
|
| Machine A Machine B |
1000 sq. m 1200 sq. m |
12 men 8 men |
60 40 |
He has an area of 7600 sq. m available and 72 skilled men who can operate the machines.
How many machines of each type should he buy to maximize the daily output?
A company produces two types of goods, A and B, that require gold and silver. Each unit of type A requires 3 gm of silver and 1 gm of gold while that of type B requires 1 gm of silver and 2 gm of gold. The company can produce 9 gm of silver and 8 gm of gold. If each unit of type A brings a profit of Rs 40 and that of type B Rs 50, find the number of units of each type that the company should produce to maximize the profit. What is the maximum profit?
A factory uses three different resources for the manufacture of two different products, 20 units of the resources A, 12 units of B and 16 units of C being available. 1 unit of the first product requires 2, 2 and 4 units of the respective resources and 1 unit of the second product requires 4, 2 and 0 units of respective resources. It is known that the first product gives a profit of 2 monetary units per unit and the second 3. Formulate the linear programming problem. How many units of each product should be manufactured for maximizing the profit? Solve it graphically.
A publisher sells a hard cover edition of a text book for Rs 72.00 and paperback edition of the same ext for Rs 40.00. Costs to the publisher are Rs 56.00 and Rs 28.00 per book respectively in addition to weekly costs of Rs 9600.00. Both types require 5 minutes of printing time, although hardcover requires 10 minutes binding time and the paperback requires only 2 minutes. Both the printing and binding operations have 4,800 minutes available each week. How many of each type of book should be produced in order to maximize profit?
A chemical company produces two compounds, A and B. The following table gives the units of ingredients, C and D per kg of compounds A and B as well as minimum requirements of C and D and costs per kg of A and B. Find the quantities of A and B which would give a supply of C and D at a minimum cost.
| Compound | Minimum requirement | ||
| A | B | ||
| Ingredient C Ingredient D |
1 3 |
2 1 |
80 75 |
| Cost (in Rs) per kg | 4 | 6 | - |
A man owns a field of area 1000 sq.m. He wants to plant fruit trees in it. He has a sum of Rs 1400 to purchase young trees. He has the choice of two types of trees. Type A requires 10 sq.m of ground per tree and costs Rs 20 per tree and type B requires 20 sq.m of ground per tree and costs Rs 25 per tree. When fully grown, type A produces an average of 20 kg of fruit which can be sold at a profit of Rs 2.00 per kg and type B produces an average of 40 kg of fruit which can be sold at a profit of Rs. 1.50 per kg. How many of each type should be planted to achieve maximum profit when the trees are fully grown? What is the maximum profit?
A small firm manufactures gold rings and chains. The total number of rings and chains manufactured per day is at most 24. It takes 1 hour to make a ring and 30 minutes to make a chain. The maximum number of hours available per day is 16. If the profit on a ring is Rs 300 and that on a chain is Rs 190, find the number of rings and chains that should be manufactured per day, so as to earn the maximum profit. Make it as an LPP and solve it graphically.
A manufacturer has three machine I, II, III installed in his factory. Machines I and II are capable of being operated for at most 12 hours whereas machine III must be operated for atleast 5 hours a day. She produces only two items M and N each requiring the use of all the three machines.
The number of hours required for producing 1 unit each of M and N on the three machines are given in the following table:
| Items | Number of hours required on machines | ||
| I | II | III | |
| M | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| N | 2 | 1 | 1.25 |
She makes a profit of ₹600 and ₹400 on items M and N respectively. How many of each item should she produce so as to maximise her profit assuming that she can sell all the items that she produced? What will be the maximum profit?
There are two factories located one at place P and the other at place Q. From these locations, a certain commodity is to be delivered to each of the three depots situated at A, B and C. The weekly requirements of the depots are respectively 5, 5 and 4 units of the commodity while the production capacity of the factories at P and Q are respectively 8 and 6 units. The cost of transportation per unit is given below:
| From \ To | Cost (in ₹) | ||
| A | B | C | |
| P | 160 | 100 | 150 |
| Q | 100 | 120 | 100 |
How many units should be transported from each factory to each depot in order that the transportation cost is minimum. What will be the minimum transportation cost?
An aeroplane can carry a maximum of 200 passengers. A profit of ₹1000 is made on each executive class ticket and a profit of ₹600 is made on each economy class ticket. The airline reserves atleast 20 seats for executive class. However, atleast 4 times as many passengers prefer to travel by economy class than by the executive class. Determine how many tickets of each type must be sold in order to maximise the profit of the airline. What is the maximum profit?
A small firm manufactures necklaces and bracelets. The total number of necklaces and bracelets that it can handle per day is at most 24. It takes one hour to make a bracelet and half an hour to make a necklace. The maximum number of hours available per day is 16. If the profit on a necklace is Rs 100 and that on a bracelet is Rs 300. Formulate on L.P.P. for finding how many of each should be produced daily to maximize the profit?
It is being given that at least one of each must be produced.
The value of objective function is maximum under linear constraints ______.
Sketch the graph of inequation x ≥ 5y in xoy co-ordinate system
Find the graphical solution for the system of linear inequation 2x + y ≤ 2, x − y ≤ 1
The minimum value of z = 2x + 9y subject to constraints x + y ≥ 1, 2x + 3y ≤ 6, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0 is ______.
The maximum value of z = 3x + 10y subjected to the conditions 5x + 2y ≤ 10, 3x + 5y ≤ 15, x, y ≥ 0 is ______.
The constraints of an LPP are 7 ≤ x ≤ 12, 8 ≤ y ≤ 13. Determine the vertices of the feasible region formed by them.
A feasible region in the set of points which satisfy ____________.
A set of values of decision variables which satisfies the linear constraints and nn-negativity conditions of an L.P.P. is called its ____________.
In linear programming feasible region (or solution region) for the problem is ____________.
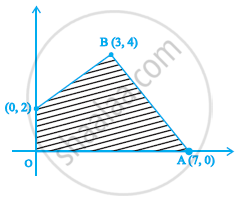
The feasible region (shaded) for a L.P.P is shown in the figure. The maximum Z = 5x + 7y is ____________.
Solve the following Linear Programming Problem graphically:
Maximize Z = 400x + 300y subject to x + y ≤ 200, x ≤ 40, x ≥ 20, y ≥ 0
The objective function Z = x1 + x2, subject to the constraints are x1 + x2 ≤ 10, – 2x1 + 3x2 ≤ 15, x1 ≤ 6, x1, x2 ≥ 0, has maximum value ______ of the feasible region.
Solve the following linear programming problem graphically:
Maximize: Z = x + 2y
Subject to constraints:
x + 2y ≥ 100,
2x – y ≤ 0
2x + y ≤ 200,
x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0.
Solve the following Linear Programming Problem graphically:
Maximize: z = – x + 2y,
Subject to the constraints: x ≥ 3, x + y ≥ 5, x + 2y ≥ 6, y ≥ 0.
Solve the following Linear Programming Problem graphically.
Maximise Z = 5x + 2y subject to:
x – 2y ≤ 2,
3x + 2y ≤ 12,
– 3x + 2y ≤ 3,
x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0
Find feasible solution for the following system of linear inequation graphically.
3x + 4y ≥ 12, 4x + 7y ≤ 28, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0
