Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A current carrying loop consists of 3 identical quarter circles of radius R, lying in the positive quadrants of the x-y, y-z and z-x planes with their centres at the origin, joined together. Find the direction and magnitude of B at the origin.
उत्तर
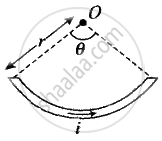
From Biot-Savart law we find the relation of magnetic field at centre of the current carrying coil which subtends an angle θ, B = `mu_0/(4pi) (Iθ)/R`.
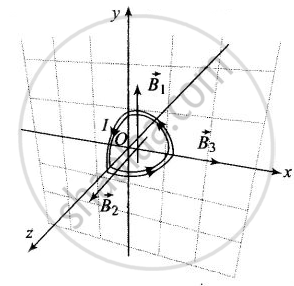
Magnetic field at origin due to the quarter circle lying in x-y plane:
`vecB_1 = (mu_0)/(4pi) (I(pi/2))/R hatk = (mu_0)/4 I/(2R) hatk`
Similarly, magnetic field at origin due to the quarter circle lying in the y-z plane:
`vecB_2 = (mu_0/4) I/(2R) hati`
Similarly, magnetic field at origin due to the quarter circle lying in the z-x plane:
`vecB_3 = (mu_0/4) I/(2R) hatj`
Now, vector sum of magnetic field at origin due to each quarter is given by
`vecB_("net") = 1/4 ((mu_0I)/(2R)) (hati + hatj + hatk)`.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What does a toroid consist of? Find out the expression for the magnetic field inside a toroid for N turns of the coil having the average radius r and carrying a current I. Show that the magnetic field in the open space inside and exterior to the toroid is zero.
A proton goes undeflected in a crossed electric and magnetic field (the fields are perpendicular to each other) at a speed of 2.0 × 105 m s−1. The velocity is perpendicular to both the fields. When the electric field is switched off, the proton moves along a circle of radius 4.0 cm. Find the magnitudes of the electric and magnetic fields. Take the mass of the proton = 1.6 × 10−27 kg
A wire of length l is bent in the form of an equilateral triangle and carries an electric current i. (a) Find the magnetic field B at the centre. (b) If the wire is bent in the form of a square, what would be the value of B at the centre?
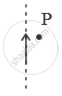
An electric current I flows through an infinitely long conductor as shown in Figure 2 (a) below. Write an expression and direction for the magnetic field at point P.
Derive the expression for the magnetic field due to a current carrying coil of radius r at a distance x from the centre along the X-axis.
State and explain the law used to determine the magnetic field at a point due to a current element. Derive the expression for the magnetic field due to a circular current-carrying loop of radius r at its center.
Derive the expression for the magnetic field due to a current-carrying coil of radius r at a distance x from the center along the X-axis.
- both are long range and inversely proportional to the square of distance from the source to the point of interest.
-
both are linear in source.
-
both are produced by scalar sources.
-
both follow principle of superposition.
Biot-Sawart law indicates that the moving electrons (velocity `overset(->)("v")`) produce a magnetic field B such that
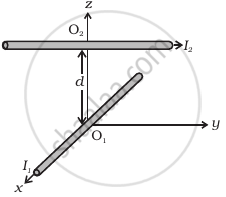
Two long wires carrying current I1 and I2 are arranged as shown in figure. The one carrying current I1 is along is the x-axis. The other carrying current I2 is along a line parallel to the y-axis given by x = 0 and z = d. Find the force exerted at O2 because of the wire along the x-axis.