Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
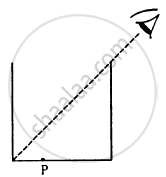
A cylindrical vessel, whose diameter and height both are equal to 30 cm, is placed on a horizontal surface and a small particle P is placed in it at a distance of 5.0 cm from the centre. An eye is placed at a position such that the edge of the bottom is just visible (see figure). The particle P is in the plane of drawing. Up to what minimum height should water be poured in the vessel to make the particle P visible?
उत्तर
Given,
Diameter and height (h) of the cylindrical vessel = 30 cm
Therefore, its radius (r) = 15 cm
We know the refractive index of water (μw) = 1.33
\[= \frac{4}{3}\] 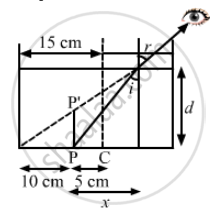
Using Snell's law,
\[\frac{\sin i}{\sin r} = \frac{1}{\mu_w}\]
\[\frac{\sin i}{\sin r} = \frac{3}{4}\]
\[As r = 45^\circ \]
\[ \Rightarrow \sin i = \frac{3}{4\sqrt{2}}\]
Point P will be visible when the refracted ray makes an angle of 45˚ at the point of refraction.
Let x be the distance of point P from X.
\[\tan 45^\circ= \frac{x + 10}{d}\]
\[ \Rightarrow d = x + 10 . . . (i)\]
\[and \]
\[\tan i = \frac{x}{d}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \frac{3}{\sqrt{23}} = \frac{d - 10}{d} \left( \because \sin i = \frac{3}{4\sqrt{2}} \Rightarrow \tan i = \frac{3}{\sqrt{23}} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow \frac{3}{\sqrt{23}} - 1 = \frac{- 10}{d}\]
\[ \Rightarrow d = \frac{\sqrt{23} \times 10}{\sqrt{23} - 3}\]
\[d = 26 . 7 cm\]
Hence, the required minimum height of water = 26.7 cm
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Give a scientific reason:
Danger signals are red in colour.
Show with the help of a diagram, how unpolarised light from Sun gets linearly polarised by scattering.
Draw the intensity distribution for the fringes produced in interference ?
Write two points of difference between the phenomena of interference and diffraction.
In the meterbridge experimental set up, shown in the figure, the null point ‘D’ is obtained at a distance of 40 cm from end A of the meterbridge wire. If a resistance of 10Ω is connected in series with R1, null point is obtained at AD = 60 cm. Calculate the values of R1 and R2.
What is linearly polarized light?
Describe briefly using a diagram how sunlight is polarised ?
A thin lens is made with a material having refractive index
\[\mu = 1 \cdot 5\]. Both the side are convex. It is dipped in water \[\mu = 1 \cdot 33\]. It will behave like
A point object O is placed on the principal axis of a convex lens of focal length f = 20 cm at a distance of 40 cm to the left of it. The diameter of the lens is 10 cm. An eye is placed 60 cm to right of the lens and a distance h below the principal axis. The maximum value of h to see the image is
Answer the following question in detail.
State the conditions under which a rainbow can be seen.
Answer the following question in detail.
Explain the formation of a primary rainbow. For which angular range with the horizontal is it visible?
Answer the following question in detail.
Explain the formation of a secondary rainbow. For which angular range with the horizontal is it visible?
Rainbow is the phenomenon due to ______.
Explain the formation of primary and secondary rainbow.
A short pulse of white light is incident from air to a glass slab at normal incidence. After travelling through the slab, the first colour to emerge is ______.
