Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A galvanometer shows full-scale deflection for current Ig. A resistance R1 is required to convert it into a voltmeter of range (0 - V) and a resistance R2 to convert it into a voltmeter of range (0 - 2V). Find the resistance of the galvanometer.
उत्तर
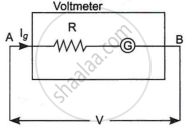
In the first case the potential difference between A and B,
`V = I_gR_1 + I_gG`
`I_g = V/(R_1 + G)`
Where G = Resistance of galvanometer
∴ `R_1 + G = V/I_g`
`R_1 = V/(Ig) - G`
⇒ G = `V/(Ig) - R_1`
In the second case,
`I_g = V/(R_2 + G)`
R2 is the Resistance required to change the range from 0 - 2V.
`I_g = (2V)/(R_2 + G)`
`R_2 + G = (2V)/I_g`
`R_2 = (2V)/I_g - G`
⇒ R = `(2V)/I_g - R_2`
Hence, the resistance of the galvanometer is respectively `V/(Ig) - R_1` and `(2V)/(Ig) - R_2`.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
An ideal voltmeter has _______.
(A) low resistance
(b) high resistance
(C) infinite resistance
(D) zero resistance
Two moving coil meters, M1 and M2 have the following particulars:
R1 = 10 Ω, N1 = 30,
A1 = 3.6 × 10–3 m2, B1 = 0.25 T
R2 = 14 Ω, N2 = 42,
A2 = 1.8 × 10–3 m2, B2 = 0.50 T
(The spring constants are identical for the two meters).
Determine the ratio of
- current sensitivity and
- voltage sensitivity of M2 and M1.
A moving coil galvanometer has a resistance of 25Ω and gives a full scale deflection for a current of 10mA. How will you convert it into a voltmeter having range 0 - 100 V?
Can a galvanometer as such be used for measuring the current? Explain.
How will you convert a moving coil galvanometer into a voltmeter?
A coil of radius 10 cm and resistance 40 Ω has 1000 turns. It is placed with its plane vertical and its axis parallel to the magnetic meridian. The coil is connected to a galvanometer and is rotated about the vertical diameter through an angle of 180°. Find the charge which flows through the galvanometer if the horizontal component of the earth's magnetic field is BH = 3.0 × 10−5 T.
The conversion of a moving coil galvanometer into a voltmeter is done by ______.
Assertion (A): On Increasing the current sensitivity of a galvanometer by increasing the number of turns may not necessarily increase its voltage sensitivity.
Reason (R): The resistance of the coil of the galvanometer increases on increasing the number of turns.
Select the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
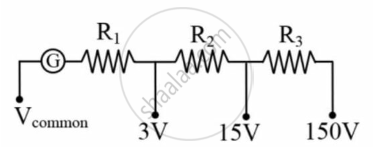
A voltmeter of variable ranges 3 V, 15 V, 150 V is to be designed by connecting resistances R1, R2, R3 in series with a galvanometer of resistance G = 20 Ω, as shown in Fig. The galvanometer gives full pass through its coil for 1 mA current i.e. "gives full pass through it's coil for 1 mA current". Then, the resistances R1, R2 and R3 (in kilo ohms) should be, respectively:
The figure below shows a circuit containing an ammeter A, a galvanometer G and a plug key K. When the key is closed: