Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A hot body is placed in a closed room maintained at a lower temperature. Is the number of photons in the room increasing?
उत्तर
As the hot body is placed in a closed room maintained at a lower temperature, there will be transfer of heat in the room through convection and radiation. Heat radiation also consists of photons; therefore, photons will be emitted by the hot body. Hence, the number of photons in the room will increase.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Light of intensity 10−5 W m−2 falls on a sodium photo-cell of surface area 2 cm2. Assuming that the top 5 layers of sodium absorb the incident energy, estimate time required for photoelectric emission in the wave-picture of radiation. The work function for the metal is given to be about 2 eV. What is the implication of your answer?
Is it always true that for two sources of equal intensity, the number of photons emitted in a given time are equal?
Can a photon be deflected by an electric field? Or by a magnetic field?
It is found that photosynthesis starts in certain plants when exposed to sunlight, but it does not start if the plants are exposed only to infrared light. Explain.
Light of wavelength λ falls on a metal with work-function hc/λ0. Photoelectric effect will take place only if
If the frequency of light in a photoelectric experiment is doubled, the stopping potential will ______.
When the intensity of a light source in increased,
(a) the number of photons emitted by the source in unit time increases
(b) the total energy of the photons emitted per unit time increases
(c) more energetic photons are emitted
(d) faster photons are emitted
If the wavelength of light in an experiment on photoelectric effect is doubled,
(a) photoelectric emission will not take place
(b) photoelectric emission may or may not take place
(c) the stopping potential will increase
(d) the stopping potential will decrease
A beam of white light is incident normally on a plane surface absorbing 70% of the light and reflecting the rest. If the incident beam carries 10 W of power, find the force exerted by it on the surface.
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
A 100 W light bulb is placed at the centre of a spherical chamber of radius 20 cm. Assume that 60% of the energy supplied to the bulb is converted into light and that the surface of the chamber is perfectly absorbing. Find the pressure exerted by the light on the surface of the chamber.
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
Find the maximum magnitude of the linear momentum of a photoelectron emitted when a wavelength of 400 nm falls on a metal with work function 2.5 eV.
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
In an experiment on photoelectric effect, the stopping potential is measured for monochromatic light beams corresponding to different wavelengths. The data collected are as follows:-
Wavelength (nm): 350 400 450 500 550
Stopping potential (V): 1.45 1.00 0.66 0.38 0.16
Plot the stopping potential against inverse of wavelength (1/λ) on a graph paper and find (a) Planck's constant (b) the work function of the emitter and (c) the threshold wavelength.
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
Answer the following question.
Plot a graph of photocurrent versus anode potential for radiation of frequency ν and intensities I1 and I2 (I1 < I2).
In the case of photoelectric effect experiment, explain the following facts, giving reasons.
The photoelectric current increases with increase of intensity of incident light.
In photoelectric effect, the photoelectric current started to flow. This means that the frequency of incident radiations is ______.
Why it is the frequency and not the intensity of the light source that determines whether the emission of photoelectrons will occur or not? Explain.
Read the following paragraph and answer the questions.
| The figure shows the variation of photoelectric current measured in a photocell circuit as a function of the potential difference between the plates of the photocell when light beams A, B, C and D of different wavelengths are incident on the photocell. Examine the given figure and answer the following questions: |
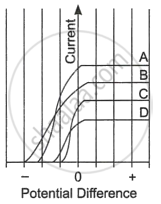
- Which light beam has the highest frequency and why?
- Which light beam has the longest wavelength and why?
- Which light beam ejects photoelectrons with maximum momentum and why?
How would the stopping potential for a given photosensitive surface change if the intensity of incident radiation was decreased? Justify your answer.
A metallic plate exposed to white light emits electrons. For which of the following colours of light, the stopping potential will be maximum?
