Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Light of wavelength λ falls on a metal with work-function hc/λ0. Photoelectric effect will take place only if
विकल्प
λ ≥ λ0
λ ≥ 2λ0
λ ≤ λ0
λ < λ0/2
उत्तर
λ ≤ λ0
As the work-function of the metal is hc/λ0, its threshold wavelength is λ0.
For photoelectric effect, the wavelength of the incident light should be less than or equal to the threshold wavelength of the metal on which light is incident.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Define the term 'intensity of radiation' in terms of photon picture of light.
Monochromatic radiation of wavelength 640.2 nm (1 nm = 10−9 m) from a neon lamp irradiates photosensitive material made of caesium on tungsten. The stopping voltage is measured to be 0.54 V. The source is replaced by an iron source and its 427.2 nm line irradiates the same photo-cell. Predict the new stopping voltage.
The following graph shows the variation of photocurrent for a photosensitive metal :
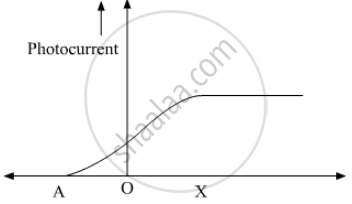
(a) Identify the variable X on the horizontal axis.
(b) What does the point A on the horizontal axis represent?
(c) Draw this graph for three different values of frequencies of incident radiation v1, v2 and v3 (v1 > v2 > v3) for same intensity.
(d) Draw this graph for three different values of intensities of incident radiation I1, I2 and I3 (I1 > I2 > I3) having same frequency.
Planck's constant has the same dimensions as
If the wavelength of light in an experiment on photoelectric effect is doubled,
(a) photoelectric emission will not take place
(b) photoelectric emission may or may not take place
(c) the stopping potential will increase
(d) the stopping potential will decrease
The collector plate in an experiment on photoelectric effect is kept vertically above the emitter plate. A light source is put on and a saturation photocurrent is recorded. An electric field is switched on that has a vertically downward direction.
In which of the following situations, the heavier of the two particles has smaller de Broglie wavelength? The two particles
(a) move with the same speed
(b) move with the same linear momentum
(c) move with the same kinetic energy
(d) have fallen through the same height
Calculate the momentum of a photon of light of wavelength 500 nm.
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
When the sun is directly overhead, the surface of the earth receives 1.4 × 103 W m−2 of sunlight. Assume that the light is monochromatic with average wavelength 500 nm and that no light is absorbed in between the sun and the earth's surface. The distance between the sun and the earth is 1.5 × 1011 m. (a) Calculate the number of photons falling per second on each square metre of earth's surface directly below the sun. (b) How many photons are there in each cubic metre near the earth's surface at any instant? (c) How many photons does the sun emit per second?
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
A parallel beam of monochromatic light of wavelength 663 nm is incident on a totally reflecting plane mirror. The angle of incidence is 60° and the number of photons striking the mirror per second is 1.0 × 1019. Calculate the force exerted by the light beam on the mirror.
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
A sphere of radius 1.00 cm is placed in the path of a parallel beam of light of large aperture. The intensity of the light is 0.5 W cm−2. If the sphere completely absorbs the radiation falling on it, find the force exerted by the light beam on the sphere.
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
The work function of a metal is 2.5 × 10−19 J. (a) Find the threshold frequency for photoelectric emission. (b) If the metal is exposed to a light beam of frequency 6.0 × 1014 Hz, what will be the stopping potential?
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
A small piece of cesium metal (φ = 1.9 eV) is kept at a distance of 20 cm from a large metal plate with a charge density of 1.0 × 10−9 C m−2 on the surface facing the cesium piece. A monochromatic light of wavelength 400 nm is incident on the cesium piece. Find the minimum and maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons reaching the large metal plate. Neglect any change in electric field due to the small piece of cesium present.
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
Define the terms "stopping potential' and 'threshold frequency' in relation to the photoelectric effect. How does one determine these physical quantities using Einstein's equation?
Two monochromatic beams A and B of equal intensity I, hit a screen. The number of photons hitting the screen by beam A is twice that by beam B. Then what inference can you make about their frequencies?
Consider a thin target (10–2 cm square, 10–3 m thickness) of sodium, which produces a photocurrent of 100 µA when a light of intensity 100W/m2 (λ = 660 nm) falls on it. Find the probability that a photoelectron is produced when a photons strikes a sodium atom. [Take density of Na = 0.97 kg/m3].
Why it is the frequency and not the intensity of the light source that determines whether the emission of photoelectrons will occur or not? Explain.
A metallic plate exposed to white light emits electrons. For which of the following colours of light, the stopping potential will be maximum?
- Assertion (A): For the radiation of a frequency greater than the threshold frequency, the photoelectric current is proportional to the intensity of the radiation.
- Reason (R): Greater the number of energy quanta available, the greater the number of electrons absorbing the energy quanta and the greater the number of electrons coming out of the metal.
