Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A man stands before a large wall at a distance of 50.0 m and claps his hands at regular intervals. Initially, the interval is large. He gradually reduces the interval and fixes it at a value when the echo of a clap merges every 3 seconds, find the velocity of sound in air.
उत्तर
Given:
Distance of the large wall from the man S = 50 m
He has to clap 10 times in 3 seconds.
So, time interval between two claps will be \[= \frac{3}{10}\text { second }\]
Therefore, the time taken \[\left( t \right)\] by sound to go the wall is \[t = \frac{3}{20}\text { second }\]
\[\text { We know that: } \]
\[\text { Velocity } v = \frac{S}{t}\]
\[\Rightarrow v = \frac{50}{\left( \frac{3}{20} \right)} = 333 m/s\]
Hence, the velocity of sound in air is 333 m/s.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The wavelengths of two sound waves in air are `81/173`m and `81/170`m. They produce 10 beats per second. Calculate the velocity of sound in air
What is the smallest positive phase constant which is equivalent to 7⋅5 π?
The equation \[y = A \sin^2 \left( kx - \omega t \right)\]
represents a wave motion with
The voice of a person, who has inhaled helium, has a remarkably high pitch. Explain on the basis of resonant vibration of vocal cord filled with air and with helium.
When two waves with same frequency and constant phase difference interfere,
The fundamental frequency of a vibrating organ pipe is 200 Hz.
(a) The first overtone is 400 Hz.
(b) The first overtone may be 400 Hz.
(c) The first overtone may be 600 Hz.
(d) 600 Hz is an overtone.
A listener is at rest with respect to the source of sound. A wind starts blowing along the line joining the source and the observer. Which of the following quantities do not change?
(a) Frequency
(b) Velocity of sound
(c) Wavelength
(d) Time period
Ultrasonic waves of frequency 4.5 MHz are used to detect tumour in soft tissue. The speed of sound in tissue is 1.5 km s−1 and that in air is 340 m s−1. Find the wavelength of this ultrasonic wave in air and in tissue.
A sources of sound operates at 2.0 kHz, 20 W emitting sound uniformly in all directions. The speed of sound in air is 340 m s−1 and the density of air is 1.2 kg m −3. (a) What is the intensity at a distance of 6.0 m from the source? (b) What will be the pressure amplitude at this point? (c) What will be the displacement amplitude at this point?
The length of the wire shown in figure between the pulley is 1⋅5 m and its mass is 12⋅0 g. Find the frequency of vibration with which the wire vibrates in two loops leaving the middle point of the wire between the pulleys at rest.
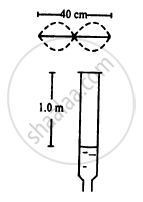
Sound with intensity larger than 120 dB appears pain full to a person. A small speaker delivers 2.0 W of audio output. How close can the person get to the speaker without hurting his ears?
A string, fixed at both ends, vibrates in a resonant mode with a separation of 2⋅0 cm between the consecutive nodes. For the next higher resonant frequency, this separation is reduced to 1⋅6 cm. Find the length of the string.
A string of length L fixed at both ends vibrates in its fundamental mode at a frequency ν and a maximum amplitude A. (a)
- Find the wavelength and the wave number k.
- Take the origin at one end of the string and the X-axis along the string. Take the Y-axis along the direction of the displacement. Take t = 0 at the instant when the middle point of the string passes through its mean position and is going towards the positive y-direction. Write the equation describing the standing wave.
Consider the situation shown in the figure.The wire which has a mass of 4.00 g oscillates in its second harmonic and sets the air column in the tube into vibrations in its fundamental mode. Assuming that the speed of sound in air is 340 m s−1, find the tension in the wire.
The fundamental frequency of a closed pipe is 293 Hz when the air in it is a temperature of 20°C. What will be its fundamental frequency when the temperature changes to 22°C?
A tuning fork of frequency 256 Hz produces 4 beats per second with a wire of length 25 cm vibrating in its fundamental mode. The beat frequency decreases when the length is slightly shortened. What could be the minimum length by which the wire we shortened so that it produces no beats with the tuning fork?
A sound source, fixed at the origin, is continuously emitting sound at a frequency of 660 Hz. The sound travels in air at a speed of 330 m s−1. A listener is moving along the lien x= 336 m at a constant speed of 26 m s−1. Find the frequency of the sound as observed by the listener when he is (a) at y = − 140 m, (b) at y = 0 and (c) at y = 140 m.
A source of sound emitting a 1200 Hz note travels along a straight line at a speed of 170 m s−1. A detector is placed at a distance 200 m from the line of motion of the source. (a) Find the frequency of sound receive by the detector at the instant when the source gets closest to it. (b) Find the distance between the source and the detector at the instant in detects the frequency 1200 Hz. Velocity of sound in air = 340 m s−1.
