Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A metallic bob A oscillates through the space between the poles of an electromagnet (See the figure). The oscillations are more quickly damped when the circuit is on, as compared to the case when the circuit is off. Explain.
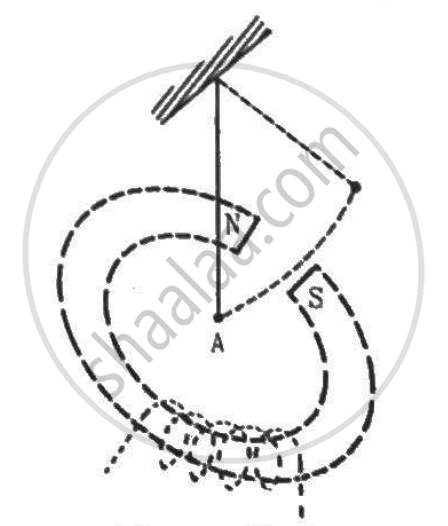
उत्तर
When the circuit is on, eddy currents are produced on the surface of the metallic bob. Due to these eddy currents, thermal energy is generated in it. This thermal energy comes at the cost of the kinetic energy of the bob; hence, oscillations are more quickly damped when the circuit is on compared to when the circuit is off.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State any two causes of energy loss in actual transformers.
Two spherical bobs, one metallic and the other of glass, of the same size are allowed to fall freely from the same height above the ground. Which of the two would reach earlier and why?
Give one example of use of eddy currents.
How are eddy currents produced ?
Metallic (nonferromagnetic) and nonmetallic particles in a solid waste may be separated as follows. The waste is allowed to slide down an incline over permanent magnets. The metallic particles slow down as compared to the nonmetallic ones and hence are separated. Discuss the role of eddy currents in the process.
A metal sheet is placed in front of a strong magnetic pole. A force is needed to ______________ .
(a) hold the sheet there if the metal is magnetic
(b) hold the sheet there if the metal is nonmagnetic
(c) move the sheet away from the pole with uniform velocity if the metal is magnetic
(d) move the sheet away from the pole with uniform velocity if the metal is nonmagnetic.
Neglect any effect of paramagnetism, diamagnetism and gravity.
Write two examples of their useful applications .
How can the disadvantages of eddy currents be minimized?
State applications of eddy currents.
The plane in which eddy currents are produced in a conductor is inclined to the plane of the magnetic field at an angle equal to ______.
Identify the wrong statement.
Two simple pendula of length L and 4L are pulled aside to the right and are at rest so that they make an angle 30° with the vertical. They are then released simultaneously at time t = 0. The time after which they will be in phase is ______.
If the length of a simple pendulum increases by 5%, then its period shall increase by ______.
Which one is not an application of eddy current?
A metal plate is getting heated. It can be because ______.
- a direct current is passing through the plate.
- it is placed in a time varying magnetic field.
- it is placed in a space varying magnetic field, but does not vary with time.
- a current (either direct or alternating) is passing through the plate.
Consider a metallic pipe with an inner radius of 1 cm. If a cylindrical bar magnet of radius 0.8 cm is dropped through the pipe, it takes more time to come down than it takes for a similar unmagnetised cylindrical iron bar dropped through the metallic pipe. Explain.
