Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A monochromatic light of wavelength 500 nm is incident normally on a single slit of width 0.2 mm to produce a diffraction pattern. Find the angular width of the central maximum obtained on the screen.
Estimate the number of fringes obtained in Young's double slit experiment with fringe width 0.5 mm, which can be accommodated within the region of total angular spread of the central maximum due to single slit.
उत्तर
The angular width of the central maximum obtained on the screen.
`=(2λ)/d`
`=(2×500×10^-9)/(0.2×10^-3)`
`=5×10^-3 m`
The number of fringes obtained in Young's double slit experiment
`"Angular width"/"Fringe width"=(5×10^-3)/(0.5×10^-3)=10`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
(i) In Young's double-slit experiment, deduce the condition for (a) constructive and (b) destructive interferences at a point on the screen. Draw a graph showing variation of intensity in the interference pattern against position 'x' on the screen.
(b) Compare the interference pattern observed in Young's double-slit experiment with single-slit diffraction pattern, pointing out three distinguishing features.
Show that the angular width of the first diffraction fringe is half that of the central fringe.
In Young's double slit experiment, using monochromatic light of wavelength λ, the intensity of light at a point on the screen where path difference is λ, is K units. Find out the intensity of light at a point where path difference is `λ/3`.
A beam of light consisting of two wavelengths, 650 nm and 520 nm, is used to obtain interference fringes in a Young’s double-slit experiment.
What is the least distance from the central maximum where the bright fringes due to both the wavelengths coincide?
In a double-slit experiment the angular width of a fringe is found to be 0.2° on a screen placed 1 m away. The wavelength of light used is 600 nm. What will be the angular width of the fringe if the entire experimental apparatus is immersed in water? Take refractive index of water to be 4/3.
A beam of light consisting of two wavelengths, 800 nm and 600 nm is used to obtain the interference fringes in a Young's double slit experiment on a screen placed 1 · 4 m away. If the two slits are separated by 0·28 mm, calculate the least distance from the central bright maximum where the bright fringes of the two wavelengths coincide.
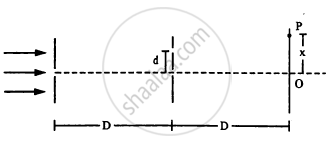
Consider the arrangement shown in the figure. The distance D is large compared to the separation d between the slits.
- Find the minimum value of d so that there is a dark fringe at O.
- Suppose d has this value. Find the distance x at which the next bright fringe is formed.
- Find the fringe-width.
In Young’s double slit experiment, what is the effect on fringe pattern if the slits are brought closer to each other?
Two slits, 4mm apart, are illuminated by light of wavelength 6000 A° what will be the fringe width on a screen placed 2 m from the slits?
In Young's double-slit experiment, the separation between the two slits is d and the distance of the screen from the slits is 1000 d. If the first minima fall at a distance d from the central maximum, obtain the relation between d and λ.
