Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A piano wire A vibrates at a fundamental frequency of 600 Hz. A second identical wire Bproduces 6 beats per second with it when the tension in A is slightly increased. Find the the ratio of the tension in A to the tension in B.
उत्तर
Mass per unit length of both the wires = m
Fundamental frequency of wire of length \[\left( l \right)\] and tension \[\left( T \right)\] is given by :
\[n = \frac{1}{2I}\sqrt{\frac{T}{m}}\]
It is clear from the above relation that as the tension increases, the frequency increases.
Fundamental frequency of wire A is given by : \[n_A = \frac{1}{2I}\sqrt{\frac{T_A}{m}}\]
Fundamental frequency of wire B is given by:
\[n_B = \frac{1}{2I}\sqrt{\frac{T_B}{m}}\]
It is given that 6 beats are produced when the tension in A is increased.
⇒ \[n_A = 606 = \frac{1}{2l}\sqrt{\frac{T_A}{m}}\]
Therefore, the ratio can be obtained as:
\[ \frac{n_A}{n_B} = \frac{606}{600} = \frac{\left( 1/2I \right)\sqrt{\left( T_A /m \right)}}{\left( 1/2I \right)\sqrt{T_B /m}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \frac{606}{600} = \frac{\sqrt{T_A}}{\sqrt{T_B}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \frac{\sqrt{T_A}}{\sqrt{T_B}} = \frac{606}{600} = 1 . 01\]
\[ \Rightarrow \frac{T_A}{T_B} = 1 . 02\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Explain what is Doppler effect in sound
The wavelengths of two sound waves in air are `81/173`m and `81/170`m. They produce 10 beats per second. Calculate the velocity of sound in air
Can you hear your own words if you are standing in a perfect vacuum? Can you hear your friend in the same conditions?
The voice of a person, who has inhaled helium, has a remarkably high pitch. Explain on the basis of resonant vibration of vocal cord filled with air and with helium.
When we clap our hands, the sound produced is best described by Here p denotes the change in pressure from the equilibrium value.
When two waves with same frequency and constant phase difference interfere,
Two point sources of sound are kept at a separation of 10 cm. They vibrate in phase to produce waves of wavelength 5.0 cm. What would be the phase difference between the two waves arriving at a point 20 cm from one source (a) on the line joining the sources and (b) on the perpendicular bisector of the line joining the sources?
A sources of sound operates at 2.0 kHz, 20 W emitting sound uniformly in all directions. The speed of sound in air is 340 m s−1 and the density of air is 1.2 kg m −3. (a) What is the intensity at a distance of 6.0 m from the source? (b) What will be the pressure amplitude at this point? (c) What will be the displacement amplitude at this point?
Sound with intensity larger than 120 dB appears pain full to a person. A small speaker delivers 2.0 W of audio output. How close can the person get to the speaker without hurting his ears?
A particular guitar wire is 30⋅0 cm long and vibrates at a frequency of 196 Hz when no finger is placed on it. The next higher notes on the scale are 220 Hz, 247 Hz, 262 Hz and 294 Hz. How far from the end of the string must the finger be placed to play these notes?
The noise level in a classroom in absence of the teacher is 50 dB when 50 students are present. Assuming that on the average each student output same sound energy per second, what will be the noise level if the number of students is increased to 100?
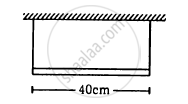
A uniform horizontal rod of length 40 cm and mass 1⋅2 kg is supported by two identical wires as shown in figure. Where should a mass of 4⋅8 kg be placed on the rod so that the same tuning fork may excite the wire on left into its fundamental vibrations and that on right into its first overtone? Take g = 10 m s−2.
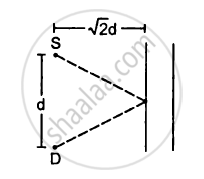
A source S and a detector D are placed at a distance d apart. A big cardboard is placed at a distance \[\sqrt{2}d\] from the source and the detector as shown in figure. The source emits a wave of wavelength = d/2 which is received by the detector after reflection from the cardboard. It is found to be in phase with the direct wave received from the source. By what minimum distance should the cardboard be shifted away so that the reflected wave becomes out of phase with the direct wave?
The two sources of sound, S1 and S2, emitting waves of equal wavelength 20.0 cm, are placed with a separation of 20.0 cm between them. A detector can be moved on a line parallel to S1 S2 and at a distance of 20.0 cm from it. Initially, the detector is equidistant from the two sources. Assuming that the waves emitted by the sources are in detector should be shifted to detect a minimum of sound.
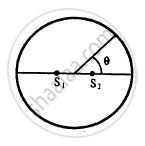
Figure shown two coherent sources S1 and S2 which emit sound of wavelength λ in phase. The separation between the sources is 3λ. A circular wire of large radius is placed in such way that S1,S2 is at the centre of the wire. Find the angular positions θ on the wire for which constructive interference takes place.
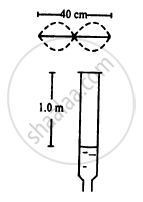
Consider the situation shown in the figure.The wire which has a mass of 4.00 g oscillates in its second harmonic and sets the air column in the tube into vibrations in its fundamental mode. Assuming that the speed of sound in air is 340 m s−1, find the tension in the wire.
The fundamental frequency of a closed pipe is 293 Hz when the air in it is a temperature of 20°C. What will be its fundamental frequency when the temperature changes to 22°C?
A source of sound with adjustable frequency produces 2 beats per second with a tuning fork when its frequency is either 476 Hz of 480 Hz. What is the frequency of the tuning fork?
A tuning fork of frequency 256 Hz produces 4 beats per second with a wire of length 25 cm vibrating in its fundamental mode. The beat frequency decreases when the length is slightly shortened. What could be the minimum length by which the wire we shortened so that it produces no beats with the tuning fork?
Which of the following statements are true for wave motion?
