Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A piano wire A vibrates at a fundamental frequency of 600 Hz. A second identical wire Bproduces 6 beats per second with it when the tension in A is slightly increased. Find the the ratio of the tension in A to the tension in B.
Solution
Mass per unit length of both the wires = m
Fundamental frequency of wire of length \[\left( l \right)\] and tension \[\left( T \right)\] is given by :
\[n = \frac{1}{2I}\sqrt{\frac{T}{m}}\]
It is clear from the above relation that as the tension increases, the frequency increases.
Fundamental frequency of wire A is given by : \[n_A = \frac{1}{2I}\sqrt{\frac{T_A}{m}}\]
Fundamental frequency of wire B is given by:
\[n_B = \frac{1}{2I}\sqrt{\frac{T_B}{m}}\]
It is given that 6 beats are produced when the tension in A is increased.
⇒ \[n_A = 606 = \frac{1}{2l}\sqrt{\frac{T_A}{m}}\]
Therefore, the ratio can be obtained as:
\[ \frac{n_A}{n_B} = \frac{606}{600} = \frac{\left( 1/2I \right)\sqrt{\left( T_A /m \right)}}{\left( 1/2I \right)\sqrt{T_B /m}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \frac{606}{600} = \frac{\sqrt{T_A}}{\sqrt{T_B}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \frac{\sqrt{T_A}}{\sqrt{T_B}} = \frac{606}{600} = 1 . 01\]
\[ \Rightarrow \frac{T_A}{T_B} = 1 . 02\]
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
What is the smallest positive phase constant which is equivalent to 7⋅5 π?
The equation \[y = A \sin^2 \left( kx - \omega t \right)\]
represents a wave motion with
If you are walking on the moon, can you hear the sound of stones cracking behind you? Can you hear the sound of your own footsteps?
The bulk modulus and the density of water are greater than those of air. With this much of information, we can say that velocity of sound in air
When sound wave is refracted from air to water, which of the following will remain unchanged?
A person can hear sound waves in the frequency range 20 Hz to 20 kHz. Find the minimum and the maximum wavelengths of sound that is audible to the person. The speed of sound is 360 m s−1.
Find the minimum and maximum wavelengths of sound in water that is in the audible range (20−20000 Hz) for an average human ear. Speed of sound in water = 1450 m s−1.
Two point sources of sound are kept at a separation of 10 cm. They vibrate in phase to produce waves of wavelength 5.0 cm. What would be the phase difference between the two waves arriving at a point 20 cm from one source (a) on the line joining the sources and (b) on the perpendicular bisector of the line joining the sources?
At what temperature will the speed of sound be double of its value at 0°C?
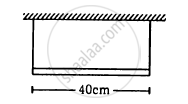
A uniform horizontal rod of length 40 cm and mass 1⋅2 kg is supported by two identical wires as shown in figure. Where should a mass of 4⋅8 kg be placed on the rod so that the same tuning fork may excite the wire on left into its fundamental vibrations and that on right into its first overtone? Take g = 10 m s−2.
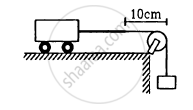
A heavy string is tied at one end to a movable support and to a light thread at the other end as shown in following figure. The thread goes over a fixed pulley and supports a weight to produce a tension. The lowest frequency with which the heavy string resonates is 120 Hz. If the movable support is pushed to the right by 10 cm so that the joint is placed on the pulley, what will be the minimum frequency at which the heavy string can resonate?
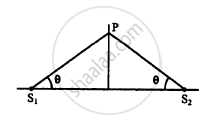
Two sources of sound S1 and S2 vibrate at same frequency and are in phase. The intensity of sound detected at a point P as shown in the figure is I0. (a) If θ equals 45°, what will be the intensity of sound detected at this point if one of the sources is switched off? (b) What will be the answer of the previous part if θ = 60°?
Show that if the room temperature changes by a small amount from T to T + ∆T, the fundamental frequency of an organ pipe changes from v to v + ∆v, where \[\frac{∆ v}{v} = \frac{1}{2}\frac{∆ T}{T} .\]
A boy riding on his bike is going towards east at a speed of 4√2 m s−1. At a certain point he produces a sound pulse of frequency 1650 Hz that travels in air at a speed of 334 m s−1. A second boy stands on the ground 45° south of east from his. Find the frequency of the pulse as received by the second boy.
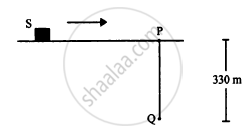
Figure shows a source of sound moving along X-axis at a speed of 22 m s−1continuously emitting a sound of frequency 2.0 kHz which travels in air at a speed of 330 m s−1. A listener Q stands on the Y-axis at a distance of 330 m from the origin. At t = 0, the sources crosses the origin P. (a) When does the sound emitted from the source at P reach the listener Q? (b) What will be the frequency heard by the listener at this instant? (c) Where will the source be at this instant?
A source of sound emitting a 1200 Hz note travels along a straight line at a speed of 170 m s−1. A detector is placed at a distance 200 m from the line of motion of the source. (a) Find the frequency of sound receive by the detector at the instant when the source gets closest to it. (b) Find the distance between the source and the detector at the instant in detects the frequency 1200 Hz. Velocity of sound in air = 340 m s−1.
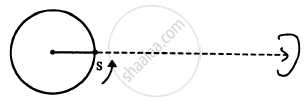
A small source of sound S of frequency 500 Hz is attached to the end of a light string and is whirled in a vertical circle of radius 1.6 m. The string just remains tight when the source is at the highest point. (a) An observer is located in the same vertical plane at a large distance and at the same height as the centre of the circle. The speed of sound in air = 330 m s−1 and g = 10 m s−2. Find the maximum frequency heard by the observer. (b) An observer is situated at a large distance vertically above the centre of the circle. Find the frequency heard by the observer corresponding to the sound emitted by the source when it is at the same height as the centre.
In an experiment to determine the velocity of sound in air at room temperature using a resonance tube, the first resonance is observed when the air column has a length of 20.0 cm for a tuning fork of frequency 400 Hz is used. The velocity of the sound at room temperature is 336 ms-1. The third resonance is observed when the air column has a length of ______ cm.
In the wave equation
`y = 0.5sin (2pi)/lambda(400t - x)m`
the velocity of the wave will be ______.
