Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A rectangular floor 45 in long and 12 m broad is to be paved exactly with square tiles, of side 60 cm. Find the total number of tiles required to pave it.
If a carpet is laid on the floor such as a space of 50 cm exists between its edges and the edges of the floor, find what fraction of the floor is uncovered.
उत्तर
Length of a rectangular floor = 45m
Breadth of a rectangular floor = 12m
∴ Area of a rectangular floor
= 45m x 12m
= 540m2
Side of a square title
= 60cm
= 0.6m
∴ Area of one square title
= (0.6m)2
= 0.36m2
Thus, total number of titles required
= `"Area of a rectangular floor"/"Area of one square title"`
= `(540)/(0.36)`
= 1500
Space
= 50cm
= 0.5m
⇒ On both sides, space
= 0.5 x 2
= 1m
∴ Area of carpet
= (45 - 1) x (12 - 1)
= 44 x 11
= 484m2
⇒ Uncovered area
= Area of a rectangular floor - Area of carpet
= (540 - 484)m2
= 56m2
∴ Fraction of floor uncovered
= `"Uncovered area"/"Area of a rectangular floor"`
= `(56)/(540)`
= `(14)/(135)`.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Show that the diagonals of a square are equal and bisect each other at right angles.
Diagonal AC of a parallelogram ABCD bisects ∠A (see the given figure). Show that
- It bisects ∠C also,
- ABCD is a rhombus

ABCD is a rectangle in which diagonal AC bisects ∠A as well as ∠C. Show that:
- ABCD is a square
- diagonal BD bisects ∠B as well as ∠D.
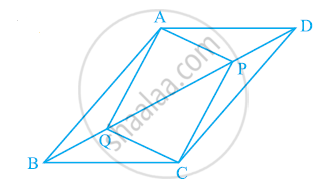
In parallelogram ABCD, two points P and Q are taken on diagonal BD such that DP = BQ (see the given figure). Show that:
- ΔAPD ≅ ΔCQB
- AP = CQ
- ΔAQB ≅ ΔCPD
- AQ = CP
- APCQ is a parallelogram
ABCD is a rectangle with ∠ABD = 40°. Determine ∠DBC .
The angles of a quadrilateral are in the ratio 3: 4: 5: 6. Show that the quadrilateral is a trapezium.
In the following figures, ABCD is a parallelogram.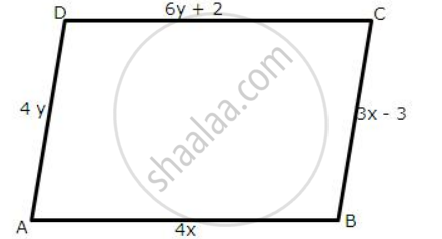
find the values of x and y.
The given figure shows a square ABCD and an equilateral triangle ABP. 
Calculate: (i) ∠AOB
(ii) ∠BPC
(iii) ∠PCD
(iv) Reflex ∠APC
The diagonals of a parallelogram ABCD intersect at O. A line through O meets AB in P and CD in Q. Show that
(a) Area of APQD = `(1)/(2)` area of || gm ABCD
(b) Area of APQD = Area of BPQC
Find the area of each of the following figure: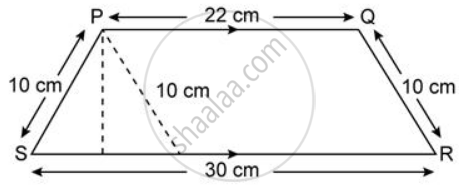
Find the area of each of the following figure: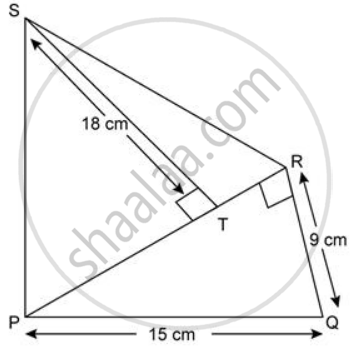
Find the area of a parallelogram whose base is 12cm and the height is 5cm.
Two adjacent sides of a parallelogram are 34 cm and 20 cm. If one of its diagonal is 42 cm, find: distance between its shorter sides
Find the perimeter and area of a square whose diagonal is `5sqrt(2)"cm"`. Give your answer correct to two decimal places if `sqrt(2)` = 1.414.
The perimeter of a square is 128cm and that of another is 96cm. Find the perimeter and the diagonal of a square whose area is equal to the sum of the areas of these two squares.
The area of a square plot of side 80m is equal to the area of a rectangular plot of length 160m. Calculate the width of the rectangular plot and the cost of fencing it Rs.7.50per m.
How many tiles, each of area 625 cm2, will be needed to pave a footpath which is 1 m wide and surrounds a grass plot of size 38 m x 14 m?
Each angle of a rectangle is a right angle.
The diagonals of a square are perpendicular to one another.
