Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The angles of a quadrilateral are in the ratio 3: 4: 5: 6. Show that the quadrilateral is a trapezium.
उत्तर
Given that the angles of a quadrilateral are in the ratio 3:4:5:6
Let the angles be 3x, 4x, 5x, 6x.
3x + 4x + 5x + 6x = 360°
⇒ x = `(360°)/18`
⇒ x = 20°
Therefore the angles are
3 x 20 = 60°
4 x 20 = 80°
5 x 20 = 100°
6 x 20 = 120°
Since all the angles are of different degrees thus forms a trapezium.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Diagonal AC of a parallelogram ABCD bisects ∠A (see the given figure). Show that
- It bisects ∠C also,
- ABCD is a rhombus

State, 'true' or 'false'
The quadrilateral, whose four sides are equal, is a square.
State, 'true' or 'false'
Every parallelogram is a rhombus.
In the following figures, ABCD is a parallelogram.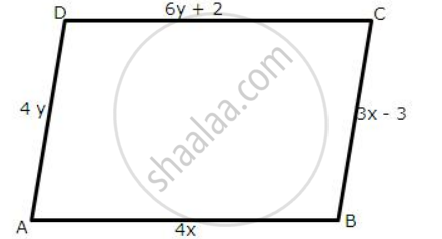
find the values of x and y.
State, 'true' or 'false'
If two adjacent sides of a parallelogram are equal, it is a rhombus.
State, 'true' or 'false'
If the diagonals of a quadrilateral bisect each other at right angle, the quadrilateral is a square.
In a square ABCD, diagonals meet at O. P is a point on BC such that OB = BP.
Show that:
- ∠POC = `[ 22 ( 1°)/( 2 ) ]`
- ∠BDC = 2 ∠POC
- ∠BOP = 3 ∠CPO
In the figure, PT is parallel to SR. QTSR is a parallelogram and PQSR is a rectangle. If the area of ΔQTS is 60cm2, find:
(i) the area o || gm QTSR
(ii) the area of the rectangle PQRS
(iii) the area of the triangle PQS.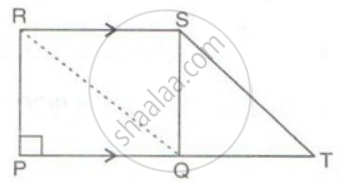
In the figure, AE = BE. Prove that the area of triangle ACE is equal in area to the parallelogram ABCD.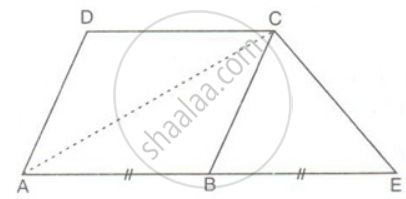
Find the area of a parallelogram whose base is 12cm and the height is 5cm.
The length of a rectangular field is thrice of its width. If the perimeter of this field is 1.6km, find its area in sq.m.
Find the perimeter of a rhombus whose diagonals are 24cm and 10cm.
The side of a square exceeds the side of another square by 4cm and the sum of the areas of the squares is 400cm2. Find the dimensions of the squares.
The length and breadth of a rectangular field are in the ratio 8 : 5. A 2m wide path runs all around outside the field. The area of the path is 848m2. Find the length and breadth of the field.
PQRS is a square with each side 6cm. T is a point on QR such that the `"area of ΔPQT"/"area of trapezium PTRS" = (1)/(3)` Find the length of TR.
ABCD is a trapezium in which AB || DC and ∠A = ∠B = 45º. Find angles C and D of the trapezium.
All the sides of a rhombus are of equal length.
Name polygon.

Make two more examples of this.
