Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In the figure, AE = BE. Prove that the area of triangle ACE is equal in area to the parallelogram ABCD.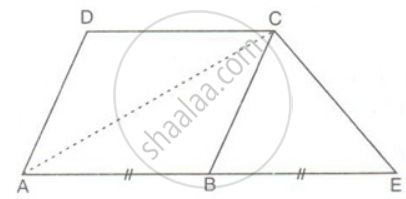
उत्तर
In parallelogram ABCD,
ar(ΔABC) = `(1)/(2)` x ar(parallelogram ABCD)
(The area of a triangle is half that of a parallelogram on the same base and between the same parallels)
ar(parallelogram ABCD) = 2ar(ΔABC) ........(i)
In ΔACE,
ar(ΔACE) = ar(ΔABC) + ar(ΔBCE)
but ar(ΔABC) = ar(ΔBCE) ...(since BC is median)
ar(ΔACE) = 2ar(ΔABC) .........(ii)
From (i) and (ii)
ar(parallelogram ABCD) = ar(ΔACE).
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
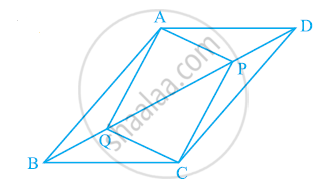
In parallelogram ABCD, two points P and Q are taken on diagonal BD such that DP = BQ (see the given figure). Show that:
- ΔAPD ≅ ΔCQB
- AP = CQ
- ΔAQB ≅ ΔCPD
- AQ = CP
- APCQ is a parallelogram
State, 'true' or 'false'
Every rhombus is a parallelogram.
State, 'true' or 'false'
If the diagonals of a quadrilateral bisect each other at right angle, the quadrilateral is a square.
In the given figure ABCD is a rhombus with angle A = 67°

If DEC is an equilateral triangle, calculate:
- ∠CBE
- ∠DBE
In a square ABCD, diagonals meet at O. P is a point on BC such that OB = BP.
Show that:
- ∠POC = `[ 22 ( 1°)/( 2 ) ]`
- ∠BDC = 2 ∠POC
- ∠BOP = 3 ∠CPO
In the figure, PT is parallel to SR. QTSR is a parallelogram and PQSR is a rectangle. If the area of ΔQTS is 60cm2, find:
(i) the area o || gm QTSR
(ii) the area of the rectangle PQRS
(iii) the area of the triangle PQS.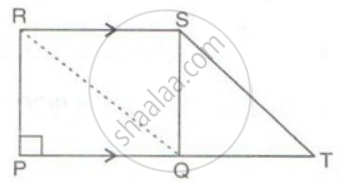
In the given figure, if AB ∥ DC ∥ FG and AE is a straight line. Also, AD ∥ FC. Prove that: area of ∥ gm ABCD = area of ∥ gm BFGE.
In the given figure, BC ∥ DE.
(a) If area of ΔADC is 20 sq. units, find the area of ΔAEB.
(b) If the area of ΔBFD is 8 square units, find the area of ΔCEF
In the given figure, ABC is a triangle and AD is the median.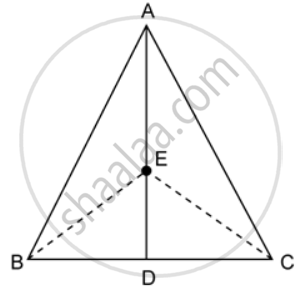
If E is the midpoint of the median AD, prove that: Area of ΔABC = 4 × Area of ΔABE
Find the area of each of the following figure: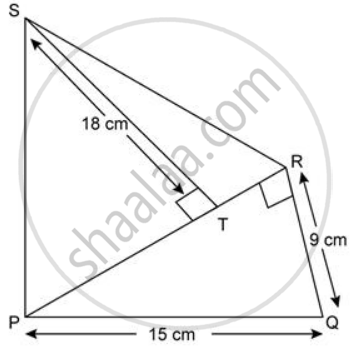
Find the area of quadrilateral, whose diagonals of lengths 18 cm and 13 cm intersect each other at right angle.
One side of a parallelogram is 12cm and the altitude corresponding to i is 8cm. If the length of the altitude corresponding to its adjacent side is 16cm, find the length of the adjacent side.
In a trapezium the parallel sides are 12cm and 8cm. If the distance between them is 6cm, find the area of the trapezium.
The perimeter of a square is 128cm and that of another is 96cm. Find the perimeter and the diagonal of a square whose area is equal to the sum of the areas of these two squares.
ABCD is a trapezium in which AB || DC and ∠A = ∠B = 45º. Find angles C and D of the trapezium.
A figure is said to be regular if its sides are equal in length and angles are equal in measure. Can you identify the regular quadrilateral?
Name polygon.
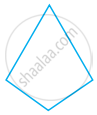
Make two more examples of this.
Name polygon.

Make two more examples of this.
