Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A figure is said to be regular if its sides are equal in length and angles are equal in measure. Can you identify the regular quadrilateral?
उत्तर
In a square, all the interior angles are of 90° and all the sides are of the same length. Therefore, a square is a regular quadrilateral.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State, 'true' or 'false'
Every rhombus is a parallelogram.
In the figure, if the area of ||gm PQRS is 84cm2; find the area of
(i) || gm PQMN
(ii) ΔPQS
(iii) ΔPQN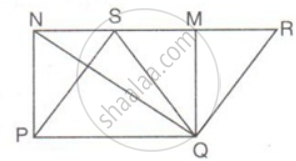
If the medians of a ΔABBC intersect at G, show that ar(ΔAGB) = ar(ΔAGC) = ar(ΔBGC) = `(1)/(3)"ar(ΔABC)"`.
In the given figure, ABC is a triangle and AD is the median.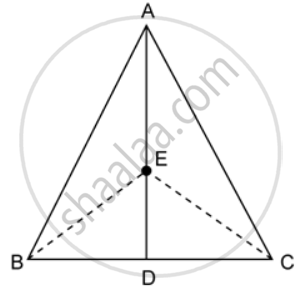
If E is the midpoint of the median AD, prove that: Area of ΔABC = 4 × Area of ΔABE
Find the area of each of the following figure: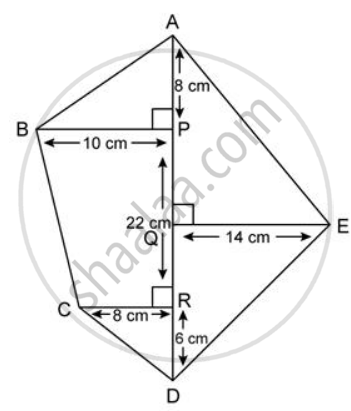
A rectangular floor 45 in long and 12 m broad is to be paved exactly with square tiles, of side 60 cm. Find the total number of tiles required to pave it.
If a carpet is laid on the floor such as a space of 50 cm exists between its edges and the edges of the floor, find what fraction of the floor is uncovered.
The area of a rhombus is 234 cm2. If its one diagonal is 18 cm, find the lengths of its side and the other diagonal. Also, find perimeter of the rhombus.
PQRS is a square with each side 6cm. T is a point on QR such that the `"area of ΔPQT"/"area of trapezium PTRS" = (1)/(3)` Find the length of TR.
ABCD is a trapezium in which AB || DC and ∠A = ∠B = 45º. Find angles C and D of the trapezium.
The opposite sides of a trapezium are parallel.
