Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Find the area of each of the following figure: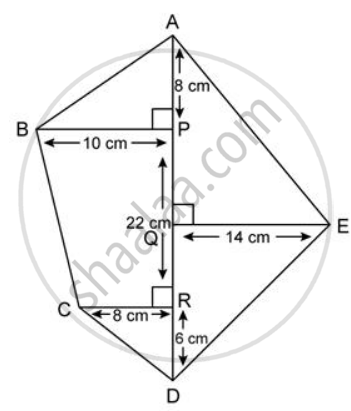
उत्तर
Area of given figure
= Area of ΔAED + Area of ΔABP + Area of trapezium BPRC + Area of ΔCRD
= `(1)/(2) xx "AD" xx "EQ" + (1)/(2) xx "AP" xx "BP" + (1)/(2) xx ("BP" + "CR") xx "PR" + (1)/(2) xx "RD" xx "CR"`
= `(1)/(2)[("AD" xx "EQ") + ("AP" xx "BP") + ("BP" + "CR") xx "PR" + ("RD" xx "CR")]`
= `(1)/(2)[("AP" + "PR" + "RD") xx "EQ" + ("AP" xx "BP") + ("BP" + "CR") xx "PR" + ("RD" xx "CR")]`
= `(1)/(2)[(8 + 22 + 6) xx 14 + (8 xx 10) + (10 + 8) xx 22 + (6 xx 8)]`
= `(1)/(2)[504 + 80 + 396 + 48]`
= `(1)/(2) xx 1028`
= 514cm2.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
If the diagonals of a parallelogram are equal, then show that it is a rectangle.
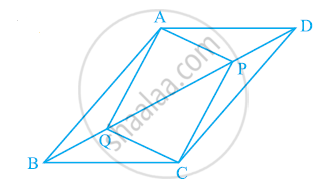
In parallelogram ABCD, two points P and Q are taken on diagonal BD such that DP = BQ (see the given figure). Show that:
- ΔAPD ≅ ΔCQB
- AP = CQ
- ΔAQB ≅ ΔCPD
- AQ = CP
- APCQ is a parallelogram
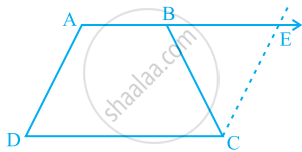
ABCD is a trapezium in which AB || CD and AD = BC (see the given figure). Show that
- ∠A = ∠B
- ∠C = ∠D
- ΔABC ≅ ΔBAD
- diagonal AC = diagonal BD
[Hint: Extend AB and draw a line through C parallel to DA intersecting AB produced at E.]
In parallelogram ABCD, AP and AQ are perpendiculars from the vertex of obtuse angle A as shown.
If ∠x: ∠y = 2: 1.
find angles of the parallelogram.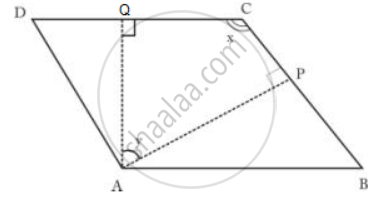
In the following figure, AE and BC are equal and parallel and the three sides AB, CD, and DE are equal to one another. If angle A is 102o. Find angles AEC and BCD.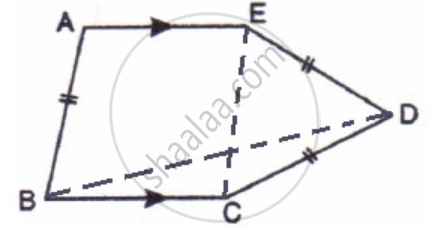
In the given figure ABCD is a rhombus with angle A = 67°

If DEC is an equilateral triangle, calculate:
- ∠CBE
- ∠DBE
In the given figure area of ∥ gm PQRS is 30 cm2. Find the height of ∥ gm PQFE if PQ = 6 cm.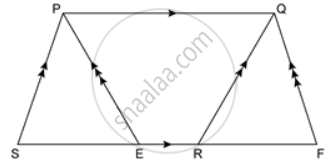
In the given figure, PQRS is a ∥ gm. A straight line through P cuts SR at point T and QR produced at N. Prove that area of triangle QTR is equal to the area of triangle STN.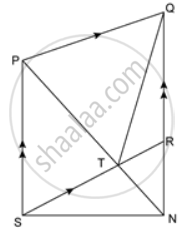
In the given figure, ST ∥ PR. Prove that: area of quadrilateral PQRS = area of ΔPQT.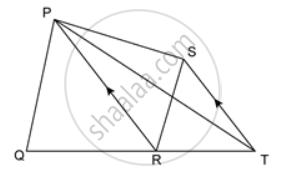
In the given figure, if AB ∥ DC ∥ FG and AE is a straight line. Also, AD ∥ FC. Prove that: area of ∥ gm ABCD = area of ∥ gm BFGE.
The diagonals of a parallelogram ABCD intersect at O. A line through O meets AB in P and CD in Q. Show that
(a) Area of APQD = `(1)/(2)` area of || gm ABCD
(b) Area of APQD = Area of BPQC
Find the area of a parallelogram whose base is 12cm and the height is 5cm.
Find the area of quadrilateral, whose diagonals of lengths 18 cm and 13 cm intersect each other at right angle.
A rectangular field 240m long has an area 36000m2. Find the cost of fencing the field at Rs.2.50per m.
A rectangular floor 45 in long and 12 m broad is to be paved exactly with square tiles, of side 60 cm. Find the total number of tiles required to pave it.
If a carpet is laid on the floor such as a space of 50 cm exists between its edges and the edges of the floor, find what fraction of the floor is uncovered.
Find the area of a square whose diagonal is `12sqrt(12)"cm"`
Find the perimeter of a rhombus whose diagonals are 24cm and 10cm.
The perimeter of a square plot of land is 64m. The area of a nearby rectangular plot is 24m2 more than the area of the given square. If the length of the rectangle is 14m, find its breadth.
In quadrilateral ABCD, ∠A + ∠D = 180º. What special name can be given to this quadrilateral?
All the sides of a rhombus are of equal length.
