Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In parallelogram ABCD, AP and AQ are perpendiculars from the vertex of obtuse angle A as shown.
If ∠x: ∠y = 2: 1.
find angles of the parallelogram.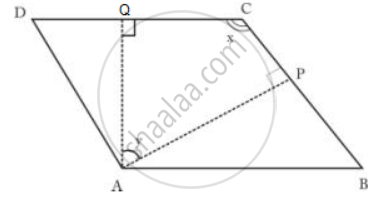
उत्तर
We know that AQCP is a quadrilateral. So sum of all angles must be 360.
∴ x + y + 90 + 90 = 360
x + y = 180
Given x : y = 2 : 1
So substitute x = 2y
3y = 180
y = 60
x = 120
We know that angle C = angle A = x = 120
Angle D = Angle B = 180 - x = 180 - 120 = 60
Hence, angles of a parallelogram are 120, 60, 120 and 60.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
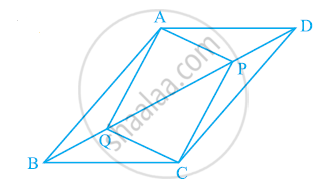
In parallelogram ABCD, two points P and Q are taken on diagonal BD such that DP = BQ (see the given figure). Show that:
- ΔAPD ≅ ΔCQB
- AP = CQ
- ΔAQB ≅ ΔCPD
- AQ = CP
- APCQ is a parallelogram
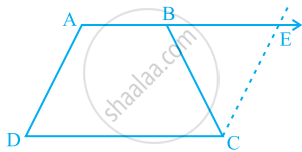
ABCD is a trapezium in which AB || CD and AD = BC (see the given figure). Show that
- ∠A = ∠B
- ∠C = ∠D
- ΔABC ≅ ΔBAD
- diagonal AC = diagonal BD
[Hint: Extend AB and draw a line through C parallel to DA intersecting AB produced at E.]
State, 'true' or 'false'
The diagonals of a rectangle bisect each other.
State, 'true' or 'false'
Diagonals of a rhombus are equal.
State, 'true' or 'false'
If the diagonals of a quadrilateral bisect each other at right angle, the quadrilateral is a square.
In the following figures, ABCD is a parallelogram.

Find the values of x and y.
ABCD is a parallelogram having an area of 60cm2. P is a point on CD. Calculate the area of ΔAPB.
In the figure, PT is parallel to SR. QTSR is a parallelogram and PQSR is a rectangle. If the area of ΔQTS is 60cm2, find:
(i) the area o || gm QTSR
(ii) the area of the rectangle PQRS
(iii) the area of the triangle PQS.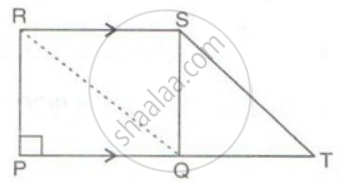
In the given figure, PQRS is a ∥ gm. A straight line through P cuts SR at point T and QR produced at N. Prove that area of triangle QTR is equal to the area of triangle STN.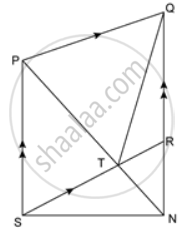
Find the area of each of the following figure:
The area of a floor of a rectangular room is 360m2. If its length is 24cm, find its perimeter.
The area of a square garden is equal to the area of a rectangular plot of length 160m and width 40m. Calculate the cost of fencing the square garden at Rs.12per m.
Find the area of a square whose diagonal is `12sqrt(12)"cm"`
Find the area of a rhombus whose perimeter is 260cm and the length of one of its diagonal is 66cm.
A footpath of uniform width runs all around the inside of a rectangular garden of 40 m x 30 m. If the path occupies 136 m2, find the width of the path.
The perimeter of a rectangular plot is 300m. It has an area of 5600m2. Taking the length of the plot as x m, calculate the breadth of the plot in terms of x, form an equation and solve it to find the dimensions of the plot.
ABCD is a trapezium in which AB || DC and ∠A = ∠B = 45º. Find angles C and D of the trapezium.
Examine whether the following is a polygon. If it is not, say why?

Name polygon.

Make two more examples of this.
