Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A regular hexagon of side 10 cm has a charge 5 µC at each of its vertices. Calculate the potential at the centre of the hexagon.
उत्तर
The given figure shows six equal amounts of charges, q, at the vertices of a regular hexagon.
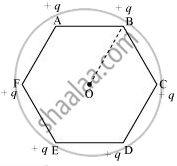
Where,
Charge, q = 5 µC = 5 × 10−6 C
Side of the hexagon, l = AB = BC = CD = DE = EF = FA = 10 cm
Distance of each vertex from centre O, d = 10 cm
Electric potential at point O,
`"V" = (6 xx "q")/(4piin_0"d")`
Where,
`in_0` = Permittivity of free space
`1/(4piin_0) = 9 xx 10^9 "NC"^-2 "m"^-2`
∴ `"V" = (6 xx 9 xx 10^9 xx 5 xx 10^-6)/0.1`
= 2.7 × 106 V
Therefore, the potential at the centre of the hexagon is 2.7 × 106 V.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Two charges 2 μC and −2 µC are placed at points A and B 6 cm apart.
- Identify an equipotential surface of the system.
- What is the direction of the electric field at every point on this surface?
Draw equipotential surfaces:
(1) in the case of a single point charge and
(2) in a constant electric field in Z-direction. Why are the equipotential surfaces about a single charge not equidistant?
(3) Can electric field exist tangential to an equipotential surface? Give reason
Why is there no work done in moving a charge from one point to another on an equipotential surface?
Depict the equipotential surfaces for a system of two identical positive point charges placed a distance(d) apart?
A particle of mass 'm' having charge 'q' is held at rest in uniform electric field of intensity 'E'. When it is released, the kinetic energy attained by it after covering a distance 'y' will be ______.
Assertion: Electric field is discontinuous across the surface of a spherical charged shell.
Reason: Electric potential is continuous across the surface of a spherical charged shell.
Equipotentials at a great distance from a collection of charges whose total sum is not zero are approximately.
The diagrams below show regions of equipotentials.
(i) |
(ii)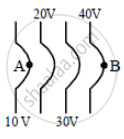 |
(iii) |
(iv) |
A positive charge is moved from A to B in each diagram.
- The potential at all the points on an equipotential surface is same.
- Equipotential surfaces never intersect each other.
- Work done in moving a charge from one point to other on an equipotential surface is zero.
Equipotential surfaces ______.
Which of the following is NOT the property of equipotential surface?
Can two equipotential surfaces intersect each other?
Consider a uniform electric field in the ẑ direction. The potential is a constant ______.
- in all space.
- for any x for a given z.
- for any y for a given z.
- on the x-y plane for a given z.
Prove that a closed equipotential surface with no charge within itself must enclose an equipotential volume.
Draw equipotential surfaces for (i) an electric dipole and (ii) two identical positive charges placed near each other.
Equipotential surfaces are shown in figure. Then the electric field strength will be ______.
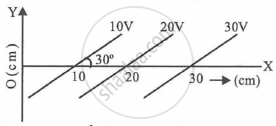
What is meant by an equipotential surface?
