Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Two charges 2 μC and −2 µC are placed at points A and B 6 cm apart.
- Identify an equipotential surface of the system.
- What is the direction of the electric field at every point on this surface?
उत्तर
- The situation is represented in the given figure.
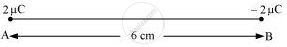
An equipotential surface is a plane on which total potential is zero everywhere. This plane is normal to line AB. The plane is located at the mid-point of line AB because the magnitude of charges is the same. - The direction of the electric field at every point on this surface is normal to the plane in the direction of AB.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Draw a sketch of equipotential surfaces due to a single charge (-q), depicting the electric field lines due to the charge
Describe schematically the equipotential surfaces corresponding to
(a) a constant electric field in the z-direction,
(b) a field that uniformly increases in magnitude but remains in a constant (say, z) direction,
(c) a single positive charge at the origin, and
(d) a uniform grid consisting of long equally spaced parallel charged wires in a plane.
Draw equipotential surfaces:
(1) in the case of a single point charge and
(2) in a constant electric field in Z-direction. Why are the equipotential surfaces about a single charge not equidistant?
(3) Can electric field exist tangential to an equipotential surface? Give reason
What is the geometrical shape of equipotential surfaces due to a single isolated charge?
Draw the equipotential surfaces due to an electric dipole. Locate the points where the potential due to the dipole is zero.
Why is there no work done in moving a charge from one point to another on an equipotential surface?
Depict the equipotential surfaces for a system of two identical positive point charges placed a distance(d) apart?
Draw the equipotential surfaces due to an electric dipole.
Answer the following question.
Write two important characteristics of equipotential surfaces.
Find the amount of work done in rotating an electric dipole of dipole moment 3.2 x 10- 8Cm from its position of stable equilibrium to the position of unstable equilibrium in a uniform electric field if intensity 104 N/C.
Consider the following statements and select the correct statement(s).
- Electric field lines are always perpendicular to equipotential surface.
- No two equipotential surfaces can intersect each other.
- Electric field lines are in the direction of tangent to an equipotential surface.
The diagrams below show regions of equipotentials.
(i) |
(ii)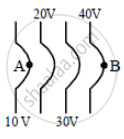 |
(iii) |
(iv) |
A positive charge is moved from A to B in each diagram.
- The potential at all the points on an equipotential surface is same.
- Equipotential surfaces never intersect each other.
- Work done in moving a charge from one point to other on an equipotential surface is zero.
Which of the following is NOT the property of equipotential surface?
Consider a uniform electric field in the ẑ direction. The potential is a constant ______.
- in all space.
- for any x for a given z.
- for any y for a given z.
- on the x-y plane for a given z.
Find the equation of the equipotentials for an infinite cylinder of radius r0, carrying charge of linear density λ.
