Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Find the equation of the equipotentials for an infinite cylinder of radius r0, carrying charge of linear density λ.
उत्तर
To find the potential at distance r from the line consider the electric field. We note that from symmetry the field lines must be radially outward. Draw a cylindrical Gaussian surface of radius r and length l. Then
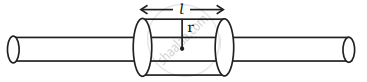
Or
⇒
Hence, if r0 is the radius,
For a given V,
ln
⇒ r = r0e –2πε0Vr0/λe + 2πε0V(r)/λ
The equipotential surfaces are cylinders of radius r = r0e –2πε0[V(r) – V(r0)]/λ
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Draw a sketch of equipotential surfaces due to a single charge (-q), depicting the electric field lines due to the charge
Two charges 2 μC and −2 µC are placed at points A and B 6 cm apart.
- Identify an equipotential surface of the system.
- What is the direction of the electric field at every point on this surface?
Describe schematically the equipotential surfaces corresponding to
(a) a constant electric field in the z-direction,
(b) a field that uniformly increases in magnitude but remains in a constant (say, z) direction,
(c) a single positive charge at the origin, and
(d) a uniform grid consisting of long equally spaced parallel charged wires in a plane.
A man fixes outside his house one evening a two metre high insulating slab carrying on its top a large aluminium sheet of area 1 m2. Will he get an electric shock if he touches the metal sheet next morning?
The discharging current in the atmosphere due to the small conductivity of air is known to be 1800 A on an average over the globe. Why then does the atmosphere not discharge itself completely in due course and become electrically neutral? In other words, what keeps the atmosphere charged?
Find the amount of work done in rotating an electric dipole of dipole moment 3.2 x 10- 8Cm from its position of stable equilibrium to the position of unstable equilibrium in a uniform electric field if intensity 104 N/C.
Assertion: Electric field is discontinuous across the surface of a spherical charged shell.
Reason: Electric potential is continuous across the surface of a spherical charged shell.
Prove that a closed equipotential surface with no charge within itself must enclose an equipotential volume.
