Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A rigid bar of mass 15 kg is supported symmetrically by three wires each 2.0 m long. Those at each end are of copper and the middle one is of iron. Determine the ratio of their diameters if each is to have the same tension.
उत्तर १
The tension force acting on each wire is the same. Thus, the extension in each case is the same. Since the wires are of the same length, the strain will also be the same.
The relation for Young’s modulus is given as:
`Y = "Stress"/"Strain" = (F/A)/"Strain" = ((4F)/(pid^2))/"Strain"` .....(i)
Where,
F = Tension force
A = Area of cross-section
d = Diameter of the wire
It can be inferred from equation (i) that `Y prop 1/d^2`
Young’s modulus for iron, Y1 = 190 × 109 Pa
Diameter of the iron wire = d1
Young’s modulus for copper, Y2 = 120 × 109 Pa
Diameter of the copper wire = d2
Therefore, the ratio of their diameters is given as:
`d_2/d_1 = sqrt(Y_1/Y_2) = sqrt((190xx10^9)/(120xx10^9)) = sqrt(19/12) = 1:25:1`
उत्तर २
Since each wire is to have same tension, therefore, each wire has the same extension. Moreover, each wire has the same initial length.So, the strain is same for each wire.
Now, `Y = "Stress"/"Strain" = (F/((piD^2)/4))/"Strain"`
or `Y prop 1/D^2 => D prop 1/sqrtY`
`D_"copper"/(D_"iron") = sqrt((Y_""iron)/(Y_"copper")) = sqrt((190 xx 10^9)/(110 xx 10^9)) = sqrt(19/11) =1.314`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Determine the volume contraction of a solid copper cube, 10 cm on an edge, when subjected to a hydraulic pressure of 7.0 ×106 Pa.
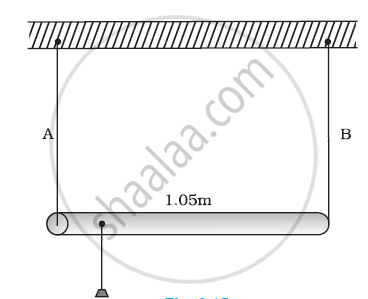
A rod of length 1.05 m having negligible mass is supported at its ends by two wires of steel (wire A) and aluminium (wire B) of equal lengths as shown in Figure. The cross-sectional areas of wires A and B are 1.0 mm2 and 2.0 mm2, respectively. At what point along the rod should a mass m be suspended in order to produce (a) equal stresses and (b) equal strains in both steel and aluminium wires.
The ratio stress/strain remain constant for small deformation of a metal wire. When the deformation is made larger, will this ratio increase or decrease?
When the skeleton of an elephant and the skeleton of a mouse are prepared in the same size, the bones of the elephant are shown thicker than those of the mouse. Explain why the bones of an elephant are thicker than proportionate. The bones are expected to withstand the stress due to the weight of the animal.
A heave uniform rod is hanging vertically form a fixed support. It is stretched by its won weight. The diameter of the rod is
Answer in one sentence.
Define strain.
A charged particle is moving in a uniform magnetic field in a circular path of radius R. When the energy of the particle becomes three times the original, the new radius will be ______.
Modulus of rigidity of ideal liquids is ______.
Is stress a vector quantity?
A steel wire having a radius of 2.0 mm, carrying a load of 4 kg, is hanging from a ceiling. Given that g = 3.1πms-2, what will be the tensile stress that would be developed in the wire?
