Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Determine the volume contraction of a solid copper cube, 10 cm on an edge, when subjected to a hydraulic pressure of 7.0 ×106 Pa.
उत्तर १
Length of an edge of the solid copper cube, l = 10 cm = 0.1 m
Hydraulic pressure, p = 7.0 ×106 Pa
Bulk modulus of copper, B = 140 × 109 Pa
Bulk Modulus, `B = p/((triangle V)/V)`
Where
`(triangle V)/V` = Volumetric strain
ΔV = Change in volume
V = Original volume.
`triangleV = (pV)/B`
Original volume of the cube, `V = beta`
`:.triangle V = (pl^3)/B`
`= (7xx10^6xx (0.1)^3)/(140xx10^9)`
= 5 x 10-8 m3
= 5 x 10-2 cm-3
Therefore, the volume contraction of the solid copper cube is 5 × 10–2 cm–3.
उत्तर २
Here a side of copper cube a = 10 cm, hence volume V = a3 = 10-3 m3 , hydraulic pressure applied p = 7.0 x 106 Pa and from table we find that bulk modulus of copper B = 140 G Pa = 140 x 109 Pa.
Using the relation `B = p/((triangle V)/V)` we have decreased in
volume `triangle V = (PV)/B`
`:. triangleV = (7.0xx10^6xx10^(-3))/(140xx10^9) = 5xx 10^(-8) m^3 = 5 xx 10^(-2) cm^3`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A rope 1 cm in diameter breaks if the tension in it exceeds 500 N. The maximum tension that may be given to a similar rope of diameter 2 cm is
A load of 10 kg is suspended by a metal wire 3 m long and having a cross-sectional area 4 mm2. Find (a) the stress (b) the strain and (c) the elongation. Young modulus of the metal is 2.0 × 1011 N m−2.
A mild steel wire of length 2L and cross-sectional area A is stretched, well within elastic limit, horizontally between two pillars (Figure). A mass m is suspended from the mid point of the wire. Strain in the wire is ______.
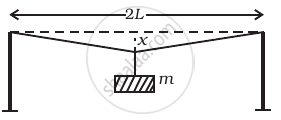
A wire is suspended from the ceiling and stretched under the action of a weight F suspended from its other end. The force exerted by the ceiling on it is equal and opposite to the weight.
- Tensile stress at any cross section A of the wire is F/A.
- Tensile stress at any cross section is zero.
- Tensile stress at any cross section A of the wire is 2F/A.
- Tension at any cross section A of the wire is F.
A rod of length l and negligible mass is suspended at its two ends by two wires of steel (wire A) and aluminium (wire B) of equal lengths (Figure). The cross-sectional areas of wires A and B are 1.0 mm2 and 2.0 mm2, respectively.
(YAl = 70 × 109 Nm−2 and Ysteel = 200 × 109 Nm–2)
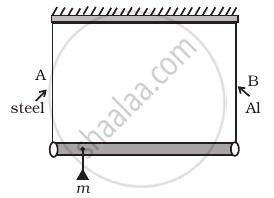
- Mass m should be suspended close to wire A to have equal stresses in both the wires.
- Mass m should be suspended close to B to have equal stresses in both the wires.
- Mass m should be suspended at the middle of the wires to have equal stresses in both the wires.
- Mass m should be suspended close to wire A to have equal strain in both wires.
Is stress a vector quantity?
Consider a long steel bar under a tensile stress due to forces F acting at the edges along the length of the bar (Figure). Consider a plane making an angle θ with the length. What are the tensile and shearing stresses on this plane
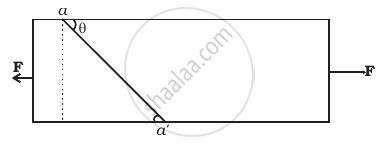
- For what angle is the tensile stress a maximum?
- For what angle is the shearing stress a maximum?
If 'S' is stress and 'Y' is young's modulus of the material of a wire, the energy stored in the wire per unit volume is ______.
A body of mass m = 10 kg is attached to one end of a wire of length 0.3 m. The maximum angular speed (in rad s-1) with which it can be rotated about its other end in the space station is (Breaking stress of wire = 4.8 × 107 Nm-2 and the area of cross-section of the wire = 10-2 cm2) is ______.
Answer in one sentence:
What is an elastomer?
